|
|
# RocketMQ Example
|
|
|
|
|
|
## Project Instruction
|
|
|
|
|
|
This example illustrates how to use RocketMQ Binder implement pub/sub messages for Spring Cloud applications.
|
|
|
|
|
|
[RocketMQ](https://rocketmq.apache.org/) is a distributed messaging and streaming platform with low latency, high performance and reliability, trillion-level capacity and flexible scalability.
|
|
|
|
|
|
Before we start the demo, let's look at Spring Cloud Stream.
|
|
|
|
|
|
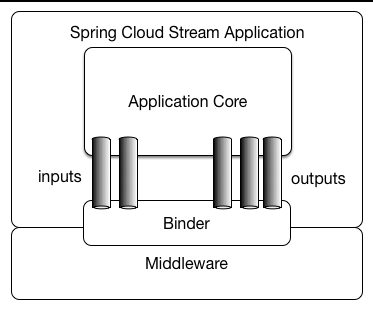
Spring Cloud Stream is a framework for building message-driven microservice applications. Spring Cloud Stream builds upon Spring Boot to create standalone, production-grade Spring applications and uses Spring Integration to provide connectivity to message brokers. It provides opinionated configuration of middleware from several vendors, introducing the concepts of persistent publish-subscribe semantics, consumer groups, and partitions.
|
|
|
|
|
|
There are two concepts in Spring Cloud Stream: Binder 和 Binding.
|
|
|
|
|
|
* Binder: A strategy interface used to bind an app interface to a logical name.
|
|
|
|
|
|
Binder Implementations includes `KafkaMessageChannelBinder` of kafka, `RabbitMessageChannelBinder` of RabbitMQ and `RocketMQMessageChannelBinder` of `RocketMQ`.
|
|
|
|
|
|
* Binding: Including Input Binding and Output Binding.
|
|
|
|
|
|
Binding is Bridge between the external messaging systems and application provided Producers and Consumers of messages.
|
|
|
|
|
|
This is a overview of Spring Cloud Stream.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
## Preparation
|
|
|
|
|
|
### Download and Startup RocketMQ
|
|
|
|
|
|
You should startup Name Server and Broker before using RocketMQ Binder.
|
|
|
|
|
|
1. Download [RocketMQ](https://archive.apache.org/dist/rocketmq/4.3.2/rocketmq-all-4.3.2-bin-release.zip) and unzip it.
|
|
|
|
|
|
2. Startup Name Server
|
|
|
|
|
|
```bash
|
|
|
sh bin/mqnamesrv
|
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
|
|
3. Startup Broker
|
|
|
|
|
|
```bash
|
|
|
sh bin/mqbroker -n localhost:9876
|
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
|
|
### Declare dependency
|
|
|
|
|
|
Add dependency spring-cloud-starter-stream-rocketmq to the `pom.xml` file in your Spring Cloud project.
|
|
|
|
|
|
```xml
|
|
|
<dependency>
|
|
|
<groupId>com.alibaba.cloud</groupId>
|
|
|
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-stream-rocketmq</artifactId>
|
|
|
</dependency>
|
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
|
|
## Simple example
|
|
|
|
|
|
### Create topic
|
|
|
|
|
|
```sh
|
|
|
sh bin/mqadmin updateTopic -n localhost:9876 -c DefaultCluster -t test-topic
|
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
|
|
### Integration with RocketMQ Binder
|
|
|
|
|
|
Configure Input and Output Binding and cooperate with `@EnableBinding` annotation
|
|
|
|
|
|
```java
|
|
|
@SpringBootApplication
|
|
|
@EnableBinding({ Source.class, Sink.class })
|
|
|
public class RocketMQApplication {
|
|
|
public static void main(String[] args) {
|
|
|
SpringApplication.run(RocketMQApplication.class, args);
|
|
|
}
|
|
|
}
|
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
|
|
Configure Binding:
|
|
|
```properties
|
|
|
# configure the nameserver of rocketmq
|
|
|
spring.cloud.stream.rocketmq.binder.name-server=127.0.0.1:9876
|
|
|
# configure the output binding named output
|
|
|
spring.cloud.stream.bindings.output.destination=test-topic
|
|
|
spring.cloud.stream.bindings.output.content-type=application/json
|
|
|
# configure the input binding named input
|
|
|
spring.cloud.stream.bindings.input.destination=test-topic
|
|
|
spring.cloud.stream.bindings.input.content-type=application/json
|
|
|
spring.cloud.stream.bindings.input.group=test-group
|
|
|
|
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
|
|
### Start Application
|
|
|
|
|
|
1. Add necessary configurations to file `/src/main/resources/application.properties`.
|
|
|
|
|
|
```properties
|
|
|
spring.application.name=rocketmq-example
|
|
|
server.port=28081
|
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
|
|
2. Start the application in IDE or by building a fatjar.
|
|
|
|
|
|
1. Start in IDE: Find main class `RocketMQApplication`, and execute the main method.
|
|
|
2. Build a fatjar: Execute command `mvn clean package` to build a fatjar, and run command `java -jar rocketmq-example.jar` to start the application.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
### Message Handle
|
|
|
|
|
|
Using the binding named output and sent messages to `test-topic` topic.
|
|
|
|
|
|
And using two input bindings to subscribe messages.
|
|
|
|
|
|
* input1: subscribe the message of `test-topic` topic and consume ordered messages(all messages should in the same MessageQueue if you want to consuming ordered messages).
|
|
|
|
|
|
* input2: subscribe the message of `test-topic` topic and consume concurrent messages which tags is `tagStr`, the thread number in pool is 20 in Consumer side.
|
|
|
|
|
|
see the configuration below:
|
|
|
|
|
|
```properties
|
|
|
spring.cloud.stream.rocketmq.binder.name-server=127.0.0.1:9876
|
|
|
|
|
|
spring.cloud.stream.bindings.output.destination=test-topic
|
|
|
spring.cloud.stream.bindings.output.content-type=application/json
|
|
|
|
|
|
spring.cloud.stream.bindings.input1.destination=test-topic
|
|
|
spring.cloud.stream.bindings.input1.content-type=text/plain
|
|
|
spring.cloud.stream.bindings.input1.group=test-group1
|
|
|
spring.cloud.stream.rocketmq.bindings.input1.consumer.orderly=true
|
|
|
|
|
|
spring.cloud.stream.bindings.input2.destination=test-topic
|
|
|
spring.cloud.stream.bindings.input2.content-type=text/plain
|
|
|
spring.cloud.stream.bindings.input2.group=test-group2
|
|
|
spring.cloud.stream.rocketmq.bindings.input2.consumer.orderly=false
|
|
|
spring.cloud.stream.rocketmq.bindings.input2.consumer.tags=tagStr
|
|
|
spring.cloud.stream.bindings.input2.consumer.concurrency=20
|
|
|
|
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
|
|
#### Pub Messages
|
|
|
|
|
|
Using MessageChannel to send messages:
|
|
|
|
|
|
```java
|
|
|
public class ProducerRunner implements CommandLineRunner {
|
|
|
@Autowired
|
|
|
private MessageChannel output;
|
|
|
@Override
|
|
|
public void run(String... args) throws Exception {
|
|
|
Map<String, Object> headers = new HashMap<>();
|
|
|
headers.put(MessageConst.PROPERTY_TAGS, "tagStr");
|
|
|
Message message = MessageBuilder.createMessage(msg, new MessageHeaders(headers));
|
|
|
output.send(message);
|
|
|
}
|
|
|
}
|
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
|
|
Or you can using the native API of RocketMQ to send messages:
|
|
|
|
|
|
```java
|
|
|
public class RocketMQProducer {
|
|
|
DefaultMQProducer producer = new DefaultMQProducer("producer_group");
|
|
|
producer.setNamesrvAddr("127.0.0.1:9876");
|
|
|
producer.start();
|
|
|
|
|
|
Message msg = new Message("test-topic", "tagStr", "message from rocketmq producer".getBytes());
|
|
|
producer.send(msg);
|
|
|
}
|
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
|
|
#### Sub Messages
|
|
|
|
|
|
Using `@StreamListener` to receive messages:
|
|
|
|
|
|
```java
|
|
|
@Service
|
|
|
public class ReceiveService {
|
|
|
|
|
|
@StreamListener("input1")
|
|
|
public void receiveInput1(String receiveMsg) {
|
|
|
System.out.println("input1 receive: " + receiveMsg);
|
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
|
|
@StreamListener("input2")
|
|
|
public void receiveInput2(String receiveMsg) {
|
|
|
System.out.println("input2 receive: " + receiveMsg);
|
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
|
|
}
|
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
|
|
## Broadcasting exmaple
|
|
|
|
|
|
### Create topic
|
|
|
|
|
|
```sh
|
|
|
sh bin/mqadmin updateTopic -n localhost:9876 -c DefaultCluster -t broadcast
|
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
|
|
### Producer
|
|
|
|
|
|
**application.yml**
|
|
|
|
|
|
```yaml
|
|
|
server:
|
|
|
port: 28085
|
|
|
spring:
|
|
|
application:
|
|
|
name: rocketmq-broadcast-producer-example
|
|
|
cloud:
|
|
|
stream:
|
|
|
rocketmq:
|
|
|
binder:
|
|
|
name-server: localhost:9876
|
|
|
bindings:
|
|
|
producer-out-0:
|
|
|
producer:
|
|
|
group: output_1
|
|
|
bindings:
|
|
|
producer-out-0:
|
|
|
destination: broadcast
|
|
|
logging:
|
|
|
level:
|
|
|
org.springframework.context.support: debug
|
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
|
|
**code**
|
|
|
|
|
|
Use `ApplicationRunner` and `StreamBridge` to send messages.
|
|
|
|
|
|
```java
|
|
|
@SpringBootApplication
|
|
|
public class RocketMQBroadcastProducerApplication {
|
|
|
private static final Logger log = LoggerFactory
|
|
|
.getLogger(RocketMQBroadcastProducerApplication.class);
|
|
|
@Autowired
|
|
|
private StreamBridge streamBridge;
|
|
|
public static void main(String[] args) {
|
|
|
SpringApplication.run(RocketMQBroadcastProducerApplication.class, args);
|
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
|
|
@Bean
|
|
|
public ApplicationRunner producer() {
|
|
|
return args -> {
|
|
|
for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) {
|
|
|
String key = "KEY" + i;
|
|
|
Map<String, Object> headers = new HashMap<>();
|
|
|
headers.put(MessageConst.PROPERTY_KEYS, key);
|
|
|
headers.put(MessageConst.PROPERTY_ORIGIN_MESSAGE_ID, i);
|
|
|
Message<SimpleMsg> msg = new GenericMessage<SimpleMsg>(new SimpleMsg("Hello RocketMQ " + i), headers);
|
|
|
streamBridge.send("producer-out-0", msg);
|
|
|
}
|
|
|
};
|
|
|
}
|
|
|
}
|
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
|
|
### Consumer
|
|
|
|
|
|
Startup two consumers.
|
|
|
|
|
|
#### Consumer1
|
|
|
|
|
|
**application.yml**
|
|
|
|
|
|
```yaml
|
|
|
server:
|
|
|
port: 28084
|
|
|
spring:
|
|
|
application:
|
|
|
name: rocketmq-broadcast-consumer1-example
|
|
|
cloud:
|
|
|
stream:
|
|
|
function:
|
|
|
definition: consumer;
|
|
|
rocketmq:
|
|
|
binder:
|
|
|
name-server: localhost:9876
|
|
|
bindings:
|
|
|
consumer-in-0:
|
|
|
consumer:
|
|
|
messageModel: BROADCASTING
|
|
|
bindings:
|
|
|
consumer-in-0:
|
|
|
destination: broadcast
|
|
|
group: broadcast-consumer
|
|
|
logging:
|
|
|
level:
|
|
|
org.springframework.context.support: debug
|
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
|
|
**code**
|
|
|
|
|
|
```java
|
|
|
@SpringBootApplication
|
|
|
public class RocketMQBroadcastConsumer1Application {
|
|
|
private static final Logger log = LoggerFactory
|
|
|
.getLogger(RocketMQBroadcastConsumer1Application.class);
|
|
|
|
|
|
public static void main(String[] args) {
|
|
|
SpringApplication.run(RocketMQBroadcastConsumer1Application.class, args);
|
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
|
|
@Bean
|
|
|
public Consumer<Message<SimpleMsg>> consumer() {
|
|
|
return msg -> {
|
|
|
log.info(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " Consumer1 Receive New Messages: " + msg.getPayload().getMsg());
|
|
|
};
|
|
|
}
|
|
|
}
|
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
|
|
#### Consumer2
|
|
|
|
|
|
**application.yml**
|
|
|
|
|
|
```yaml
|
|
|
server:
|
|
|
port: 28083
|
|
|
spring:
|
|
|
application:
|
|
|
name: rocketmq-broadcast-consumer2-example
|
|
|
cloud:
|
|
|
stream:
|
|
|
function:
|
|
|
definition: consumer;
|
|
|
rocketmq:
|
|
|
binder:
|
|
|
name-server: localhost:9876
|
|
|
bindings:
|
|
|
consumer-in-0:
|
|
|
consumer:
|
|
|
messageModel: BROADCASTING
|
|
|
bindings:
|
|
|
consumer-in-0:
|
|
|
destination: broadcast
|
|
|
group: broadcast-consumer
|
|
|
logging:
|
|
|
level:
|
|
|
org.springframework.context.support: debug
|
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
|
|
**code**
|
|
|
|
|
|
```java
|
|
|
@SpringBootApplication
|
|
|
public class RocketMQBroadcastConsumer2Application {
|
|
|
private static final Logger log = LoggerFactory
|
|
|
.getLogger(RocketMQBroadcastConsumer2Application.class);
|
|
|
|
|
|
public static void main(String[] args) {
|
|
|
SpringApplication.run(RocketMQBroadcastConsumer2Application.class, args);
|
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
|
|
@Bean
|
|
|
public Consumer<Message<SimpleMsg>> consumer() {
|
|
|
return msg -> {
|
|
|
log.info(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " Consumer2 Receive New Messages: " + msg.getPayload().getMsg());
|
|
|
};
|
|
|
}
|
|
|
}
|
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
|
|
## Order example
|
|
|
|
|
|
RocketMQ provides ordered messages using FIFO order.
|
|
|
|
|
|
There are two types of ordered messages.
|
|
|
|
|
|
* Global: For a specified topic, all messages are published and consumed in strict FIFO (First In First Out) order.
|
|
|
* Partition: For a specified topic, all messages are partitioned according to the `Sharding Key`. Messages within the same partition are published and consumed in strict FIFO order. `Sharding Key` is a key field used to distinguish different partitions in sequential messages, and it is a completely different concept from the Key of ordinary messages.
|
|
|
|
|
|
### Create Topic
|
|
|
|
|
|
```sh
|
|
|
sh bin/mqadmin updateTopic -n localhost:9876 -c DefaultCluster -t orderly
|
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
|
|
### Example code
|
|
|
|
|
|
**application.yml**
|
|
|
|
|
|
```yaml
|
|
|
server:
|
|
|
port: 28082
|
|
|
spring:
|
|
|
application:
|
|
|
name: rocketmq-orderly-consume-example
|
|
|
cloud:
|
|
|
stream:
|
|
|
function:
|
|
|
definition: consumer;
|
|
|
rocketmq:
|
|
|
binder:
|
|
|
name-server: localhost:9876
|
|
|
bindings:
|
|
|
producer-out-0:
|
|
|
producer:
|
|
|
group: output_1
|
|
|
# 定义messageSelector
|
|
|
messageQueueSelector: orderlyMessageQueueSelector
|
|
|
consumer-in-0:
|
|
|
consumer:
|
|
|
# tag: {@code tag1||tag2||tag3 }; sql: {@code 'color'='blue' AND 'price'>100 } .
|
|
|
subscription: 'TagA || TagC || TagD'
|
|
|
push:
|
|
|
orderly: true
|
|
|
bindings:
|
|
|
producer-out-0:
|
|
|
destination: orderly
|
|
|
consumer-in-0:
|
|
|
destination: orderly
|
|
|
group: orderly-consumer
|
|
|
|
|
|
logging:
|
|
|
level:
|
|
|
org.springframework.context.support: debug
|
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
|
|
**MessageQueueSelector**
|
|
|
|
|
|
Choose a partition selection algorithm for you, and ensure that the same parameters get the same results.
|
|
|
|
|
|
```java
|
|
|
@Component
|
|
|
public class OrderlyMessageQueueSelector implements MessageQueueSelector {
|
|
|
private static final Logger log = LoggerFactory
|
|
|
.getLogger(OrderlyMessageQueueSelector.class);
|
|
|
@Override
|
|
|
public MessageQueue select(List<MessageQueue> mqs, Message msg, Object arg) {
|
|
|
Integer id = (Integer) ((MessageHeaders) arg).get(MessageConst.PROPERTY_ORIGIN_MESSAGE_ID);
|
|
|
String tag = (String) ((MessageHeaders) arg).get(MessageConst.PROPERTY_TAGS);
|
|
|
int index = id % RocketMQOrderlyConsumeApplication.tags.length % mqs.size();
|
|
|
return mqs.get(index);
|
|
|
}
|
|
|
}
|
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
|
|
**Producer&Consumer**
|
|
|
|
|
|
```java
|
|
|
@SpringBootApplication
|
|
|
public class RocketMQOrderlyConsumeApplication {
|
|
|
private static final Logger log = LoggerFactory
|
|
|
.getLogger(RocketMQOrderlyConsumeApplication.class);
|
|
|
|
|
|
@Autowired
|
|
|
private StreamBridge streamBridge;
|
|
|
|
|
|
/***
|
|
|
* tag array.
|
|
|
*/
|
|
|
public static final String[] tags = new String[] {"TagA", "TagB", "TagC", "TagD", "TagE"};
|
|
|
|
|
|
public static void main(String[] args) {
|
|
|
SpringApplication.run(RocketMQOrderlyConsumeApplication.class, args);
|
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
|
|
@Bean
|
|
|
public ApplicationRunner producer() {
|
|
|
return args -> {
|
|
|
for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) {
|
|
|
String key = "KEY" + i;
|
|
|
Map<String, Object> headers = new HashMap<>();
|
|
|
headers.put(MessageConst.PROPERTY_KEYS, key);
|
|
|
headers.put(MessageConst.PROPERTY_TAGS, tags[i % tags.length]);
|
|
|
headers.put(MessageConst.PROPERTY_ORIGIN_MESSAGE_ID, i);
|
|
|
Message<SimpleMsg> msg = new GenericMessage(new SimpleMsg("Hello RocketMQ " + i), headers);
|
|
|
streamBridge.send("producer-out-0", msg);
|
|
|
}
|
|
|
};
|
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
|
|
@Bean
|
|
|
public Consumer<Message<SimpleMsg>> consumer() {
|
|
|
return msg -> {
|
|
|
String tagHeaderKey = RocketMQMessageConverterSupport.toRocketHeaderKey(
|
|
|
MessageConst.PROPERTY_TAGS).toString();
|
|
|
log.info(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " Receive New Messages: " + msg.getPayload().getMsg() + " TAG:" +
|
|
|
msg.getHeaders().get(tagHeaderKey).toString());
|
|
|
try {
|
|
|
Thread.sleep(100);
|
|
|
}
|
|
|
catch (InterruptedException ignored) {
|
|
|
}
|
|
|
};
|
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
|
|
}
|
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
|
|
## Schedule example
|
|
|
|
|
|
Scheduled messages differ from normal messages in that they won’t be delivered until a provided time later.
|
|
|
|
|
|
### Create topic
|
|
|
|
|
|
```sh
|
|
|
sh bin/mqadmin updateTopic -n localhost:9876 -c DefaultCluster -t delay
|
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
|
|
### Example code
|
|
|
|
|
|
**application.yml**
|
|
|
|
|
|
```yaml
|
|
|
server:
|
|
|
port: 28086
|
|
|
spring:
|
|
|
application:
|
|
|
name: rocketmq-delay-consume-example
|
|
|
cloud:
|
|
|
stream:
|
|
|
function:
|
|
|
definition: consumer;
|
|
|
rocketmq:
|
|
|
binder:
|
|
|
name-server: localhost:9876
|
|
|
bindings:
|
|
|
producer-out-0:
|
|
|
producer:
|
|
|
group: output_1
|
|
|
bindings:
|
|
|
producer-out-0:
|
|
|
destination: delay
|
|
|
consumer-in-0:
|
|
|
destination: delay
|
|
|
group: delay-group
|
|
|
logging:
|
|
|
level:
|
|
|
org.springframework.context.support: debug
|
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
|
|
**code**
|
|
|
|
|
|
```java
|
|
|
@SpringBootApplication
|
|
|
public class RocketMQDelayConsumeApplication {
|
|
|
private static final Logger log = LoggerFactory
|
|
|
.getLogger(RocketMQDelayConsumeApplication.class);
|
|
|
@Autowired
|
|
|
private StreamBridge streamBridge;
|
|
|
|
|
|
public static void main(String[] args) {
|
|
|
SpringApplication.run(RocketMQDelayConsumeApplication.class, args);
|
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
|
|
@Bean
|
|
|
public ApplicationRunner producerDelay() {
|
|
|
return args -> {
|
|
|
for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) {
|
|
|
String key = "KEY" + i;
|
|
|
Map<String, Object> headers = new HashMap<>();
|
|
|
headers.put(MessageConst.PROPERTY_KEYS, key);
|
|
|
headers.put(MessageConst.PROPERTY_ORIGIN_MESSAGE_ID, i);
|
|
|
// Set the delay level 1~10
|
|
|
headers.put(MessageConst.PROPERTY_DELAY_TIME_LEVEL, 2);
|
|
|
Message<SimpleMsg> msg = new GenericMessage(new SimpleMsg("Delay RocketMQ " + i), headers);
|
|
|
streamBridge.send("producer-out-0", msg);
|
|
|
}
|
|
|
};
|
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
|
|
@Bean
|
|
|
public Consumer<Message<SimpleMsg>> consumer() {
|
|
|
return msg -> {
|
|
|
log.info(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " Consumer Receive New Messages: " + msg.getPayload().getMsg());
|
|
|
};
|
|
|
}
|
|
|
}
|
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
|
|
## Filter example
|
|
|
|
|
|
### Create topic
|
|
|
|
|
|
```sh
|
|
|
sh bin/mqadmin updateTopic -n localhost:9876 -c DefaultCluster -t sql
|
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
|
|
### Example code
|
|
|
|
|
|
**application.yml**
|
|
|
|
|
|
RocketMQ stream binder supports filter by tag or sql, just setting `spring.cloud.stream.rocketmq.bindings.<channelName>.consumer.subscription`.
|
|
|
|
|
|
Tag example: `tag:red || blue`
|
|
|
|
|
|
Sql example: `sql:(color in ('red1', 'red2', 'red4') and price>3)`
|
|
|
|
|
|
More: [Filter](https://rocketmq.apache.org/docs/filter-by-sql92-example/)
|
|
|
|
|
|
```yaml
|
|
|
server:
|
|
|
port: 28087
|
|
|
spring:
|
|
|
application:
|
|
|
name: rocketmq-sql-consume-example
|
|
|
cloud:
|
|
|
stream:
|
|
|
function:
|
|
|
definition: consumer;
|
|
|
rocketmq:
|
|
|
binder:
|
|
|
name-server: localhost:9876
|
|
|
bindings:
|
|
|
producer-out-0:
|
|
|
producer:
|
|
|
group: output_1
|
|
|
consumer-in-0:
|
|
|
consumer:
|
|
|
# tag: {@code tag1||tag2||tag3 }; sql: {@code 'color'='blue' AND 'price'>100 } .
|
|
|
subscription: sql:(color in ('red1', 'red2', 'red4') and price>3)
|
|
|
bindings:
|
|
|
producer-out-0:
|
|
|
destination: sql
|
|
|
consumer-in-0:
|
|
|
destination: sql
|
|
|
group: sql-group
|
|
|
logging:
|
|
|
level:
|
|
|
org.springframework.context.support: debug
|
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
|
|
**code**
|
|
|
|
|
|
```java
|
|
|
@SpringBootApplication
|
|
|
public class RocketMQSqlConsumeApplication {
|
|
|
private static final Logger log = LoggerFactory
|
|
|
.getLogger(RocketMQSqlConsumeApplication.class);
|
|
|
@Autowired
|
|
|
private StreamBridge streamBridge;
|
|
|
public static void main(String[] args) {
|
|
|
SpringApplication.run(RocketMQSqlConsumeApplication.class, args);
|
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
|
|
/**
|
|
|
* color array.
|
|
|
*/
|
|
|
public static final String[] color = new String[] {"red1", "red2", "red3", "red4", "red5"};
|
|
|
|
|
|
/**
|
|
|
* price array.
|
|
|
*/
|
|
|
public static final Integer[] price = new Integer[] {1, 2, 3, 4, 5};
|
|
|
|
|
|
@Bean
|
|
|
public ApplicationRunner producer() {
|
|
|
return args -> {
|
|
|
for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) {
|
|
|
String key = "KEY" + i;
|
|
|
Map<String, Object> headers = new HashMap<>();
|
|
|
headers.put(MessageConst.PROPERTY_KEYS, key);
|
|
|
headers.put("color", color[i % color.length]);
|
|
|
headers.put("price", price[i % price.length]);
|
|
|
headers.put(MessageConst.PROPERTY_ORIGIN_MESSAGE_ID, i);
|
|
|
Message<SimpleMsg> msg = new GenericMessage(new SimpleMsg("Hello RocketMQ " + i), headers);
|
|
|
streamBridge.send("producer-out-0", msg);
|
|
|
}
|
|
|
};
|
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
|
|
@Bean
|
|
|
public Consumer<Message<SimpleMsg>> consumer() {
|
|
|
return msg -> {
|
|
|
String colorHeaderKey = "color";
|
|
|
String priceHeaderKey = "price";
|
|
|
log.info(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " Receive New Messages: " + msg.getPayload().getMsg() + " COLOR:" +
|
|
|
msg.getHeaders().get(colorHeaderKey).toString() + " " +
|
|
|
"PRICE: " + msg.getHeaders().get(priceHeaderKey).toString());
|
|
|
};
|
|
|
}
|
|
|
}
|
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
|
|
## Transaction example
|
|
|
|
|
|
### What is transactional message?
|
|
|
|
|
|
Refer to [Transaction Example](https://rocketmq.apache.org/docs/transaction-example/).
|
|
|
|
|
|
> It can be thought of as a two-phase commit message implementation to ensure eventual consistency in distributed system. Transactional message ensures that the execution of local transaction and the sending of message can be performed atomically.
|
|
|
|
|
|
### Application
|
|
|
|
|
|
> 1、 Transactional status
|
|
|
>
|
|
|
> There are three states for transactional message:
|
|
|
> (1) TransactionStatus.CommitTransaction: commit transaction,it means that allow consumers to consume this message.
|
|
|
> (2) TransactionStatus.RollbackTransaction: rollback transaction,it means that the message will be deleted and not allowed to consume.
|
|
|
> (3) TransactionStatus.Unknown: intermediate state,it means that MQ is needed to check back to determine the status.
|
|
|
|
|
|
### Create topic
|
|
|
|
|
|
```sh
|
|
|
sh bin/mqadmin updateTopic -n localhost:9876 -c DefaultCluster -t tx
|
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
|
|
### Example code
|
|
|
|
|
|
**application.yml**
|
|
|
|
|
|
```yaml
|
|
|
server:
|
|
|
port: 28088
|
|
|
spring:
|
|
|
application:
|
|
|
name: rocketmq-tx-example
|
|
|
cloud:
|
|
|
stream:
|
|
|
function:
|
|
|
definition: consumer;
|
|
|
rocketmq:
|
|
|
binder:
|
|
|
name-server: localhost:9876
|
|
|
bindings:
|
|
|
producer-out-0:
|
|
|
producer:
|
|
|
group: output_1
|
|
|
transactionListener: myTransactionListener
|
|
|
producerType: Trans
|
|
|
bindings:
|
|
|
producer-out-0:
|
|
|
destination: tx
|
|
|
consumer-in-0:
|
|
|
destination: tx
|
|
|
group: tx-group
|
|
|
logging:
|
|
|
level:
|
|
|
org.springframework.context.support: debug
|
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
|
|
**TransactionListenerImpl**
|
|
|
|
|
|
To execute local transaction.
|
|
|
|
|
|
```java
|
|
|
@Component("myTransactionListener")
|
|
|
public class TransactionListenerImpl implements TransactionListener {
|
|
|
|
|
|
@Override
|
|
|
public LocalTransactionState executeLocalTransaction(Message msg, Object arg) {
|
|
|
Object num = msg.getProperty("test");
|
|
|
|
|
|
if ("1".equals(num)) {
|
|
|
System.out.println("executer: " + new String(msg.getBody()) + " unknown");
|
|
|
return LocalTransactionState.UNKNOW;
|
|
|
}
|
|
|
else if ("2".equals(num)) {
|
|
|
System.out.println("executer: " + new String(msg.getBody()) + " rollback");
|
|
|
return LocalTransactionState.ROLLBACK_MESSAGE;
|
|
|
}
|
|
|
System.out.println("executer: " + new String(msg.getBody()) + " commit");
|
|
|
return LocalTransactionState.COMMIT_MESSAGE;
|
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
|
|
@Override
|
|
|
public LocalTransactionState checkLocalTransaction(MessageExt msg) {
|
|
|
System.out.println("check: " + new String(msg.getBody()));
|
|
|
return LocalTransactionState.COMMIT_MESSAGE;
|
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
|
|
}
|
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
|
|
**producer and consumer**
|
|
|
|
|
|
```java
|
|
|
@SpringBootApplication
|
|
|
public class RocketMQTxApplication {
|
|
|
private static final Logger log = LoggerFactory
|
|
|
.getLogger(RocketMQTxApplication.class);
|
|
|
@Autowired
|
|
|
private StreamBridge streamBridge;
|
|
|
public static void main(String[] args) {
|
|
|
SpringApplication.run(RocketMQTxApplication.class, args);
|
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
@Bean
|
|
|
public ApplicationRunner producer() {
|
|
|
return args -> {
|
|
|
for (int i = 1; i <= 4; i++) {
|
|
|
MessageBuilder builder = MessageBuilder.withPayload(new SimpleMsg("Hello Tx msg " + i));
|
|
|
builder.setHeader("test", String.valueOf(i))
|
|
|
.setHeader(MessageHeaders.CONTENT_TYPE, MimeTypeUtils.APPLICATION_JSON);
|
|
|
builder.setHeader(RocketMQConst.USER_TRANSACTIONAL_ARGS, "binder");
|
|
|
Message<SimpleMsg> msg = builder.build();
|
|
|
streamBridge.send("producer-out-0", msg);
|
|
|
System.out.println("send Msg:" + msg.toString());
|
|
|
}
|
|
|
};
|
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
|
|
@Bean
|
|
|
public Consumer<Message<SimpleMsg>> consumer() {
|
|
|
return msg -> {
|
|
|
Object arg = msg.getHeaders();
|
|
|
log.info(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " Receive New Messages: " + msg.getPayload().getMsg() + " ARG:"
|
|
|
+ arg.toString());
|
|
|
};
|
|
|
}
|
|
|
}
|
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
|
|
## Endpoint
|
|
|
|
|
|
Add dependency `spring-cloud-starter-stream-rocketmq` to your pom.xml file, and configure your endpoint security strategy.
|
|
|
|
|
|
* Spring Boot1.x: Add configuration `management.security.enabled=false`
|
|
|
* Spring Boot2.x: Add configuration `management.endpoints.web.exposure.include=*`
|
|
|
|
|
|
To view the endpoint information, visit the following URLS:
|
|
|
* Spring Boot1.x: Sentinel Endpoint URL is http://127.0.0.1:18083/rocketmq_binder.
|
|
|
* Spring Boot2.x: Sentinel Endpoint URL is http://127.0.0.1:18083/actuator/rocketmq-binder.
|
|
|
|
|
|
Endpoint will metrics some data like last send timestamp, sending or receive message successfully times or unsuccessfully times.
|
|
|
|
|
|
```json
|
|
|
{
|
|
|
"runtime": {
|
|
|
"lastSend.timestamp": 1542786623915
|
|
|
},
|
|
|
"metrics": {
|
|
|
"scs-rocketmq.consumer.test-topic.totalConsumed": {
|
|
|
"count": 11
|
|
|
},
|
|
|
"scs-rocketmq.consumer.test-topic.totalConsumedFailures": {
|
|
|
"count": 0
|
|
|
},
|
|
|
"scs-rocketmq.producer.test-topic.totalSentFailures": {
|
|
|
"count": 0
|
|
|
},
|
|
|
"scs-rocketmq.consumer.test-topic.consumedPerSecond": {
|
|
|
"count": 11,
|
|
|
"fifteenMinuteRate": 0.012163847780107841,
|
|
|
"fiveMinuteRate": 0.03614605351360527,
|
|
|
"meanRate": 0.3493213353657594,
|
|
|
"oneMinuteRate": 0.17099243039490175
|
|
|
},
|
|
|
"scs-rocketmq.producer.test-topic.totalSent": {
|
|
|
"count": 5
|
|
|
},
|
|
|
"scs-rocketmq.producer.test-topic.sentPerSecond": {
|
|
|
"count": 5,
|
|
|
"fifteenMinuteRate": 0.005540151995103271,
|
|
|
"fiveMinuteRate": 0.01652854617838251,
|
|
|
"meanRate": 0.10697493212602836,
|
|
|
"oneMinuteRate": 0.07995558537067671
|
|
|
},
|
|
|
"scs-rocketmq.producer.test-topic.sentFailuresPerSecond": {
|
|
|
"count": 0,
|
|
|
"fifteenMinuteRate": 0.0,
|
|
|
"fiveMinuteRate": 0.0,
|
|
|
"meanRate": 0.0,
|
|
|
"oneMinuteRate": 0.0
|
|
|
},
|
|
|
"scs-rocketmq.consumer.test-topic.consumedFailuresPerSecond": {
|
|
|
"count": 0,
|
|
|
"fifteenMinuteRate": 0.0,
|
|
|
"fiveMinuteRate": 0.0,
|
|
|
"meanRate": 0.0,
|
|
|
"oneMinuteRate": 0.0
|
|
|
}
|
|
|
}
|
|
|
}
|
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
|
|
Note: You should add [metrics-core dependency](https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/io.dropwizard.metrics/metrics-core) if you want to see metrics data. endpoint will show warning information if you don't add that dependency:
|
|
|
|
|
|
```json
|
|
|
{
|
|
|
"warning": "please add metrics-core dependency, we use it for metrics"
|
|
|
}
|
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
|
|
## More
|
|
|
|
|
|
For more information about RocketMQ, see [RocketMQ Project](https://rocketmq.apache.org).
|
|
|
|
|
|
If you have any ideas or suggestions for Spring Cloud RocketMQ Binder, please don't hesitate to tell us by submitting github issues.
|
|
|
|