markdown docs added
parent
b70035df24
commit
2047a4f913
@ -0,0 +1,92 @@
|
|||||||
|
# Redisson - Easy Redis Java client<br/>and Real-Time Data Platform
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
High-performance async and lock-free Java client for Redis and Valkey based on [Netty](http://netty.io) framework.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
## Features
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
* Thread-safe implementation
|
||||||
|
* JDK 1.8+ up to the latest version compatible
|
||||||
|
* Android compatible
|
||||||
|
* [Redis](https://redis.io) compatible - from 3.0 up to the latest version
|
||||||
|
* [Valkey](https://valkey.io) compatible - from 7.2.5 up to the latest version
|
||||||
|
* Supported deployment types
|
||||||
|
* [Proxy](configuration.md/#proxy-mode)
|
||||||
|
* [Multi-Cluster](configuration.md/#multi-cluster-mode)
|
||||||
|
* [Multi-Sentinel](configuration.md/#multi-sentinel-mode)
|
||||||
|
* [Single](configuration.md/#single-mode)
|
||||||
|
* [Cluster](configuration.md/#cluster-mode)
|
||||||
|
* [Sentinel](configuration.md/#sentinel-mode)
|
||||||
|
* [Replicated](configuration.md/#replicated-mode)
|
||||||
|
* [Master and Slaves](configuration.md/#master-slave-mode)
|
||||||
|
* Amazon Web Services compatible
|
||||||
|
* [AWS Elasticache Serverless](https://aws.amazon.com/elasticache/features/#Serverless)
|
||||||
|
* [AWS Redis Global Datastore](https://docs.aws.amazon.com/AmazonElastiCache/latest/red-ug/Redis-Global-Datastore.html)
|
||||||
|
* [AWS ElastiCache](https://docs.aws.amazon.com/AmazonElastiCache/latest/red-ug/WhatIs.html)
|
||||||
|
* [Amazon MemoryDB](https://aws.amazon.com/memorydb)
|
||||||
|
* Microsoft Azure compatible
|
||||||
|
* [Azure Redis Cache](https://azure.microsoft.com/en-us/services/cache/)
|
||||||
|
* [Azure Redis Cache active-passive replication](https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/azure-cache-for-redis/cache-how-to-geo-replication)
|
||||||
|
* [Azure Redis Cache active-active replication](https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/azure-cache-for-redis/cache-how-to-active-geo-replication)
|
||||||
|
* Google Cloud Memorystore compatible
|
||||||
|
* [Google Cloud Redis](https://cloud.google.com/memorystore/docs/redis/)
|
||||||
|
* [Google Cloud Redis High availability](https://cloud.google.com/memorystore/docs/redis/high-availability)
|
||||||
|
* Redis Enterprise compatible
|
||||||
|
* [Redis Enterprise](https://redis.com/redis-enterprise/)
|
||||||
|
* [Redis Enterprise Active-Active databases](https://docs.redis.com/latest/rs/databases/active-active/get-started/)
|
||||||
|
* [Redis Enterprise Multiple Active Proxy](https://docs.redis.com/latest/rs/databases/configure/proxy-policy/#about-multiple-active-proxy-support)
|
||||||
|
* IBM Cloud compatible
|
||||||
|
* [IBM Cloud Databases for Redis](https://www.ibm.com/cloud/databases-for-redis)
|
||||||
|
* Aiven compatible
|
||||||
|
* [Aiven for Redis](https://aiven.io/redis)
|
||||||
|
* Supports auto-reconnection
|
||||||
|
* Supports failed to send command auto-retry
|
||||||
|
* Supports OSGi
|
||||||
|
* Supports SSL
|
||||||
|
* Asynchronous connection pool
|
||||||
|
* Lua scripting
|
||||||
|
* [RediSearch](data-and-services/services.md/#redisearch-service)
|
||||||
|
* [JSON datatype](data-and-services/objects.md/#json-object-holder)
|
||||||
|
* [JSON Store](data-and-services/collections.md/#json-store)
|
||||||
|
* [Reactive Streams](api-models.md/#reactive-api) API
|
||||||
|
* [RxJava3](api-models.md/#rxjava-api) API
|
||||||
|
* [Asynchronous](api-models.md/#synchronous-and-asynchronous-api) API
|
||||||
|
* Local cache support including [Caffeine](https://github.com/ben-manes/caffeine)-based implementation
|
||||||
|
* [Cache API implementations](cache-api-implementations.md)
|
||||||
|
Spring Cache, JCache API (JSR-107), Hibernate Cache, MyBatis Cache, Quarkus Cache, Micronaut Cache
|
||||||
|
* [Distributed Java objects](data-and-services/objects.md)
|
||||||
|
Object holder, JSON holder, Binary stream holder, Geospatial holder, BitSet, PublishSubscribe, Bloom filter, HyperLogLog
|
||||||
|
* [Distributed Java counters](data-and-services/counters.md)
|
||||||
|
AtomicLong, AtomicDouble, LongAdder, DoubleAdder
|
||||||
|
* [Distributed Java collections](data-and-services/collections.md)
|
||||||
|
JSON Store, Map, Multimap, Set, List, SortedSet, ScoredSortedSet, LexSortedSet, Queue, Deque, Blocking Queue, Bounded Blocking Queue, Blocking Deque, Delayed Queue, Priority Queue, Priority Deque
|
||||||
|
* [Distributed Java locks and synchronizers](data-and-services/locks-and-synchronizers.md)
|
||||||
|
Lock, FairLock, MultiLock, RedLock, ReadWriteLock, Semaphore, PermitExpirableSemaphore, CountDownLatch
|
||||||
|
* [Distributed services](data-and-services/services.md)
|
||||||
|
Remote service, Live Object service, Executor service, Scheduler service, MapReduce service
|
||||||
|
* [Microservices integration](microservices-integration.md)
|
||||||
|
Helidon, Micronaut, Quarkus
|
||||||
|
* [Integration with Spring framework](integration-with-spring.md)
|
||||||
|
Spring Boot Starter, Spring Cache, Spring Session, Spring Transaction Manager, Spring Cloud Stream, Spring Data Redis
|
||||||
|
* [Web Session Management](web-session-management.md)
|
||||||
|
Apache Tomcat Session, Spring Session, Micronaut Session
|
||||||
|
* [Transactions API](transactions.md)
|
||||||
|
* [Redis pipelining](pipelining.md) (command batches)
|
||||||
|
* Supports many popular codecs ([Kryo](https://github.com/EsotericSoftware/kryo), [Jackson JSON](https://github.com/FasterXML/jackson), [Avro](http://avro.apache.org/), [Smile](http://wiki.fasterxml.com/SmileFormatSpec), [CBOR](http://cbor.io/), [MsgPack](http://msgpack.org/), [Amazon Ion](https://amzn.github.io/ion-docs/), [LZ4](https://github.com/jpountz/lz4-java), [Snappy](https://github.com/xerial/snappy-java), [Protobuf](https://github.com/protocolbuffers/protobuf) and JDK Serialization)
|
||||||
|
* 2000+ unit tests
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
## Comparing solutions
|
||||||
|
- [Redisson vs Jedis](https://redisson.org/feature-comparison-redisson-vs-jedis.html)
|
||||||
|
- [Redisson vs Lettuce](https://redisson.org/feature-comparison-redisson-vs-lettuce.html)
|
||||||
|
- [Redis vs Apache Ignite](https://redisson.org/feature-comparison-redis-vs-ignite.html)
|
||||||
|
- [Redis vs Hazelcast](https://redisson.org/feature-comparison-redis-vs-hazelcast.html)
|
||||||
|
- [Redis vs Ehcache](https://redisson.org/feature-comparison-redis-vs-ehcache.html)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
## Success stories
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
- [Moving from Hazelcast to Redis / Datorama](https://engineering.datorama.com/moving-from-hazelcast-to-redis-b90a0769d1cb)
|
||||||
|
- [Migrating from Hazelcast to Redis / Halodoc](https://blogs.halodoc.io/why-and-how-we-move-from-hazelcast-to-redis-2/)
|
||||||
|
- [Distributed Locking with Redis (Migration from Hazelcast) / ContaAzul](https://carlosbecker.com/posts/distributed-locks-redis/)
|
||||||
|
- [Migrating from Coherence to Redis](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=JF5R2ucKTEg)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Upgrade to __[Redisson PRO](https://redisson.pro)__ with **advanced features**.
|
||||||
@ -0,0 +1,121 @@
|
|||||||
|
### Synchronous and Asynchronous API
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Redisson instances are fully thread-safe.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Synchronous and Asynchronous API could be reached via [RedissonClient](https://www.javadoc.io/doc/org.redisson/redisson/latest/org/redisson/api/RedissonClient.html) interface.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Most Redisson objects extend asynchronous interface with asynchronous methods which mirrors synchronous methods. Like below:
|
||||||
|
```java
|
||||||
|
// RAtomicLong extends RAtomicLongAsync
|
||||||
|
RAtomicLong obj = client.getAtomicLong("myLong");
|
||||||
|
obj.compareAndSet(1, 401);
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
RAtomicLongAsync objAsync = client.getAtomicLong("myLong");
|
||||||
|
RFuture<Boolean> future = objAsync.compareAndSetAsync(1, 401);
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
Asynchronous methods return [RFuture](https://www.javadoc.io/doc/org.redisson/redisson/latest/org/redisson/api/RFuture.html) object which extends [CompletionStage](https://docs.oracle.com/javase/8/docs/api/java/util/concurrent/CompletionStage.html) interface.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
```java
|
||||||
|
future.whenComplete((res, exception) -> {
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
// handle both result and exception
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
});
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
// or
|
||||||
|
future.thenAccept(res -> {
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
// handle result
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
}).exceptionally(exception -> {
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
// handle exception
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
});
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
Avoid to use blocking methods in future listeners. Listeners executed by netty-threads and delays in listeners may cause errors in Redis or Valkey request/response processing. Use follow methods to execute blocking methods in listeners:
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
```java
|
||||||
|
future.whenCompleteAsync((res, exception) -> {
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
// handle both result and exception
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
}, executor);
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
// or
|
||||||
|
future.thenAcceptAsync(res -> {
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
// handle result
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
}, executor).exceptionallyAsync(exception -> {
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
// handle exception
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
}, executor);
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
### Reactive API
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Reactive API could be reached via [RedissonReactiveClient](https://www.javadoc.io/doc/org.redisson/redisson/latest/org/redisson/api/RedissonReactiveClient.html) interface.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Redisson's implementation based on [Project Reactor](https://projectreactor.io).
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Usage example:
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
```java
|
||||||
|
RedissonReactiveClient client = redissonClient.reactive();
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
RAtomicLongReactive atomicLong = client.getAtomicLong("myLong");
|
||||||
|
Mono<Boolean> cs = longObject.compareAndSet(10, 91);
|
||||||
|
Mono<Long> get = longObject.get();
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
get.doOnSuccess(res -> {
|
||||||
|
// ...
|
||||||
|
}).subscribe();
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
### RxJava API
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
RxJava API could be reached via [RedissonRxClient](https://www.javadoc.io/doc/org.redisson/redisson/latest/org/redisson/api/RedissonRxClient.html) interface.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Redisson's implementation based on [RxJava3](https://github.com/ReactiveX/RxJava).
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Usage example:
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
```java
|
||||||
|
RedissonRxClient client = redissonClient.rxJava();
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
RAtomicLongRx atomicLong = client.getAtomicLong("myLong");
|
||||||
|
Single<Boolean> cs = longObject.compareAndSet(10, 91);
|
||||||
|
Single<Long> get = longObject.get();
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
get.doOnSuccess(res -> {
|
||||||
|
// ...
|
||||||
|
}).subscribe();
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
### Retry policy
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Redisson implements auto-retry policy per operation. Retry policy is controlled by [retryAttempts](configuration.md) and [retryInterval](configuration.md) settings. These settings are applied to each Redisson object. [timeout](configuration.md) setting is applied when the Redis or Valkey command was successfully sent.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Settings above can be overridden per Redisson object instance. These settings apply to each method of a given Redisson object instance.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Here is an example with `RBucket` object:
|
||||||
|
```java
|
||||||
|
RedissonClient client = Redisson.create(config);
|
||||||
|
RBucket<MyObject> bucket = client.getBucket('myObject');
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
// sync way
|
||||||
|
bucket.get();
|
||||||
|
// async way
|
||||||
|
RFuture<MyObject> result = bucket.getAsync();
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
// instance with overridden retryInterval and timeout parameters
|
||||||
|
RBucket<MyObject> bucket = client.getBucket(PlainOptions.name('myObject')
|
||||||
|
.timeout(Duration.ofSeconds(3))
|
||||||
|
.retryInterval(Duration.ofSeconds(5)));
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
File diff suppressed because it is too large
Load Diff
@ -0,0 +1,250 @@
|
|||||||
|
## Spring Cache
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Redisson provides various Spring Cache implementations. Each Cache instance has two important parameters: `ttl` and `maxIdleTime`. Data is stored infinitely if these settings are not defined or equal to `0`.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Config example:
|
||||||
|
```java
|
||||||
|
@Configuration
|
||||||
|
@ComponentScan
|
||||||
|
@EnableCaching
|
||||||
|
public static class Application {
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
@Bean(destroyMethod="shutdown")
|
||||||
|
RedissonClient redisson() throws IOException {
|
||||||
|
Config config = new Config();
|
||||||
|
config.useClusterServers()
|
||||||
|
.addNodeAddress("redis://127.0.0.1:7004", "redis://127.0.0.1:7001");
|
||||||
|
return Redisson.create(config);
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
@Bean
|
||||||
|
CacheManager cacheManager(RedissonClient redissonClient) {
|
||||||
|
Map<String, CacheConfig> config = new HashMap<String, CacheConfig>();
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
// create "testMap" cache with ttl = 24 minutes and maxIdleTime = 12 minutes
|
||||||
|
config.put("testMap", new CacheConfig(24*60*1000, 12*60*1000));
|
||||||
|
return new RedissonSpringCacheManager(redissonClient, config);
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Cache configuration can be read from YAML configuration files:
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
```java
|
||||||
|
@Configuration
|
||||||
|
@ComponentScan
|
||||||
|
@EnableCaching
|
||||||
|
public static class Application {
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
@Bean(destroyMethod="shutdown")
|
||||||
|
RedissonClient redisson(@Value("classpath:/redisson.yaml") Resource configFile) throws IOException {
|
||||||
|
Config config = Config.fromYAML(configFile.getInputStream());
|
||||||
|
return Redisson.create(config);
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
@Bean
|
||||||
|
CacheManager cacheManager(RedissonClient redissonClient) throws IOException {
|
||||||
|
return new RedissonSpringCacheManager(redissonClient, "classpath:/cache-config.yaml");
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
### Eviction, local cache and data partitioning
|
||||||
|
Redisson provides various Spring Cache managers with two important features:
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
**local cache** - so called `near cache` used to speed up read operations and avoid network roundtrips. It caches Map entries on Redisson side and executes read operations up to **45x faster** in comparison with common implementation. Local cache instances with the same name connected to the same pub/sub channel. This channel is used for exchanging of update/invalidate events between all instances. Local cache store doesn't use `hashCode()`/`equals()` methods of key object, instead it uses hash of serialized state.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
**data partitioning** - although Map object is cluster compatible its content isn't scaled/partitioned across multiple Redis or Valkey master nodes in cluster. Data partitioning allows to scale available memory, read/write operations and entry eviction process for individual Map instance in cluster.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
**Scripted eviction**
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Allows to define `time to live` or `max idle time` parameters per map entry. Eviction is done on Redisson side through a custom scheduled task which removes expired entries using Lua script. Eviction task is started once per unique object name at the moment of getting Map instance. If instance isn't used and has expired entries it should be get again to start the eviction process. This leads to extra Redis or Valkey calls and eviction task per unique map object name.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Entries are cleaned time to time by `org.redisson.eviction.EvictionScheduler`. By default, it removes 100 expired entries at a time. This can be changed through [cleanUpKeysAmount](../configuration.md) setting. Task launch time tuned automatically and depends on expired entries amount deleted in previous time and varies between 5 second to 30 minutes by default. This time interval can be changed through [minCleanUpDelay](../configuration.md) and [maxCleanUpDelay](../configuration.md). For example, if clean task deletes 100 entries each time it will be executed every 5 seconds (minimum execution delay). But if current expired entries amount is lower than previous one then execution delay will be increased by 1.5 times and decreased otherwise.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Available implementations:
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|Class name | Local<br/>cache | Data<br/>partitioning | Ultra-fast<br/>read/write |
|
||||||
|
| ------------- | :-----------: | :----------:| :----------:|
|
||||||
|
|RedissonSpringCacheManager<br/><sub><i>open-source version</i></sub> | ❌ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||||
|
|RedissonSpringCacheManager<br/><sub><i>[Redisson PRO](https://redisson.pro) version</i></sub> | ❌ | ❌ | ✔️ |
|
||||||
|
|RedissonSpringLocalCachedCacheManager<br/><sub><i>available only in [Redisson PRO](https://redisson.pro)</i></sub> | ✔️ | ❌ | ✔️ |
|
||||||
|
|RedissonClusteredSpringCacheManager<br/><sub><i>available only in [Redisson PRO](https://redisson.pro)</i></sub> | ❌ | ✔️ | ✔️ |
|
||||||
|
|RedissonClusteredSpringLocalCachedCacheManager<br/><sub><i>available only in [Redisson PRO](https://redisson.pro)</i></sub> | ✔️ | ✔️ | ✔️ |
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
**Advanced eviction**
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Allows to define `time to live` parameter per map entry. Doesn't use an entry eviction task, entries are cleaned on Redis or Valkey side.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Available implementations:
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|Class name | Local<br/>cache | Data<br/>partitioning | Ultra-fast<br/>read/write |
|
||||||
|
| ------------- | :-----------: | :----------:| :----------:|
|
||||||
|
|RedissonSpringCacheV2Manager<br/><sub><i>available only in [Redisson PRO](https://redisson.pro)</i></sub> | ❌ | ✔️ | ✔️ |
|
||||||
|
|RedissonSpringLocalCachedCacheV2Manager<br/><sub><i>available only in [Redisson PRO](https://redisson.pro)</i></sub> | ✔️ | ✔️ | ✔️ |
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
**Native eviction**
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Allows to define `time to live` parameter per map entry. Doesn't use an entry eviction task, entries are cleaned on Redis side.
|
||||||
|
Requires **Redis 7.4+**.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Available implementations:
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|Class name | Local<br/>cache | Data<br/>partitioning | Ultra-fast<br/>read/write |
|
||||||
|
| ------------- | :-----------: | :----------:| :----------:|
|
||||||
|
|RedissonSpringCacheNativeManager<br/><sub><i>open-source version</i></sub> | ❌ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||||
|
|RedissonSpringCacheNativeManager<br/><sub><i>[Redisson PRO](https://redisson.pro) version</i></sub> | ❌ | ❌ | ✔️ |
|
||||||
|
|RedissonSpringLocalCachedCacheNativeManager<br/><sub><i>available only in [Redisson PRO](https://redisson.pro)</i></sub> | ✔️ | ❌ | ✔️ |
|
||||||
|
|RedissonClusteredSpringCacheNativeManager<br/><sub><i>available only in [Redisson PRO](https://redisson.pro)</i></sub> | ❌ | ✔️ | ✔️ |
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
**Local cache**
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Follow options object can be supplied during local cached managers initialization:
|
||||||
|
```java
|
||||||
|
LocalCachedMapOptions options = LocalCachedMapOptions.defaults()
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
// Defines whether to store a cache miss into the local cache.
|
||||||
|
// Default value is false.
|
||||||
|
.storeCacheMiss(false);
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
// Defines store mode of cache data.
|
||||||
|
// Follow options are available:
|
||||||
|
// LOCALCACHE - store data in local cache only.
|
||||||
|
// LOCALCACHE_REDIS - store data in both Redis or Valkey and local cache.
|
||||||
|
.storeMode(StoreMode.LOCALCACHE_REDIS)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
// Defines Cache provider used as local cache store.
|
||||||
|
// Follow options are available:
|
||||||
|
// REDISSON - uses Redisson own implementation
|
||||||
|
// CAFFEINE - uses Caffeine implementation
|
||||||
|
.cacheProvider(CacheProvider.REDISSON)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
// Defines local cache eviction policy.
|
||||||
|
// Follow options are available:
|
||||||
|
// LFU - Counts how often an item was requested. Those that are used least often are discarded first.
|
||||||
|
// LRU - Discards the least recently used items first
|
||||||
|
// SOFT - Uses weak references, entries are removed by GC
|
||||||
|
// WEAK - Uses soft references, entries are removed by GC
|
||||||
|
// NONE - No eviction
|
||||||
|
.evictionPolicy(EvictionPolicy.NONE)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
// If cache size is 0 then local cache is unbounded.
|
||||||
|
.cacheSize(1000)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
// Used to load missed updates during any connection failures to Redis.
|
||||||
|
// Since, local cache updates can't be get in absence of connection to Redis.
|
||||||
|
// Follow reconnection strategies are available:
|
||||||
|
// CLEAR - Clear local cache if map instance has been disconnected for a while.
|
||||||
|
// LOAD - Store invalidated entry hash in invalidation log for 10 minutes
|
||||||
|
// Cache keys for stored invalidated entry hashes will be removed
|
||||||
|
// if LocalCachedMap instance has been disconnected less than 10 minutes
|
||||||
|
// or whole cache will be cleaned otherwise.
|
||||||
|
// NONE - Default. No reconnection handling
|
||||||
|
.reconnectionStrategy(ReconnectionStrategy.NONE)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
// Used to synchronize local cache changes.
|
||||||
|
// Follow sync strategies are available:
|
||||||
|
// INVALIDATE - Default. Invalidate cache entry across all LocalCachedMap instances on map entry change
|
||||||
|
// UPDATE - Insert/update cache entry across all LocalCachedMap instances on map entry change
|
||||||
|
// NONE - No synchronizations on map changes
|
||||||
|
.syncStrategy(SyncStrategy.INVALIDATE)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
// time to live for each map entry in local cache
|
||||||
|
.timeToLive(10000)
|
||||||
|
// or
|
||||||
|
.timeToLive(10, TimeUnit.SECONDS)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
// max idle time for each map entry in local cache
|
||||||
|
.maxIdle(10000)
|
||||||
|
// or
|
||||||
|
.maxIdle(10, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Each Spring Cache instance has two important parameters: `ttl` and `maxIdleTime` and stores data infinitely if they are not defined or equal to `0`.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Complete config example:
|
||||||
|
```java
|
||||||
|
@Configuration
|
||||||
|
@ComponentScan
|
||||||
|
@EnableCaching
|
||||||
|
public static class Application {
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
@Bean(destroyMethod="shutdown")
|
||||||
|
RedissonClient redisson() throws IOException {
|
||||||
|
Config config = new Config();
|
||||||
|
config.useClusterServers()
|
||||||
|
.addNodeAddress("redis://127.0.0.1:7004", "redis://127.0.0.1:7001");
|
||||||
|
return Redisson.create(config);
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
@Bean
|
||||||
|
CacheManager cacheManager(RedissonClient redissonClient) {
|
||||||
|
Map<String, CacheConfig> config = new HashMap<String, CacheConfig>();
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
// define local cache settings for "testMap" cache.
|
||||||
|
// ttl = 48 minutes and maxIdleTime = 24 minutes for local cache entries
|
||||||
|
LocalCachedMapOptions options = LocalCachedMapOptions.defaults()
|
||||||
|
.evictionPolicy(EvictionPolicy.LFU)
|
||||||
|
.timeToLive(48, TimeUnit.MINUTES)
|
||||||
|
.maxIdle(24, TimeUnit.MINUTES);
|
||||||
|
.cacheSize(1000);
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
// create "testMap" Redis or Valkey cache with ttl = 24 minutes and maxIdleTime = 12 minutes
|
||||||
|
LocalCachedCacheConfig cfg = new LocalCachedCacheConfig(24*60*1000, 12*60*1000, options);
|
||||||
|
// Max size of map stored in Redis
|
||||||
|
cfg.setMaxSize(2000);
|
||||||
|
config.put("testMap", cfg);
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
return new RedissonSpringLocalCachedCacheManager(redissonClient, config);
|
||||||
|
// or
|
||||||
|
return new RedissonSpringLocalCachedCacheNativeManager(redissonClient, config);
|
||||||
|
// or
|
||||||
|
return new RedissonSpringLocalCachedCacheV2Manager(redissonClient, config);
|
||||||
|
// or
|
||||||
|
return new RedissonClusteredSpringLocalCachedCacheManager(redissonClient, config);
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Cache configuration could be read from YAML configuration files:
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
```java
|
||||||
|
@Configuration
|
||||||
|
@ComponentScan
|
||||||
|
@EnableCaching
|
||||||
|
public static class Application {
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
@Bean(destroyMethod="shutdown")
|
||||||
|
RedissonClient redisson(@Value("classpath:/redisson.yaml") Resource configFile) throws IOException {
|
||||||
|
Config config = Config.fromYAML(configFile.getInputStream());
|
||||||
|
return Redisson.create(config);
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
@Bean
|
||||||
|
CacheManager cacheManager(RedissonClient redissonClient) throws IOException {
|
||||||
|
return new RedissonSpringLocalCachedCacheManager(redissonClient, "classpath:/cache-config.yaml");
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
### YAML config format
|
||||||
|
Below is the configuration of Spring Cache with name `testMap` in YAML format:
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
```yaml
|
||||||
|
---
|
||||||
|
testMap:
|
||||||
|
ttl: 1440000
|
||||||
|
maxIdleTime: 720000
|
||||||
|
localCacheOptions:
|
||||||
|
invalidationPolicy: "ON_CHANGE"
|
||||||
|
evictionPolicy: "NONE"
|
||||||
|
cacheSize: 0
|
||||||
|
timeToLiveInMillis: 0
|
||||||
|
maxIdleInMillis: 0
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
_Please note: `localCacheOptions` settings are available for `org.redisson.spring.cache.RedissonSpringLocalCachedCacheManager` and `org.redisson.spring.cache.RedissonSpringClusteredLocalCachedCacheManager` classes only._
|
||||||
@ -0,0 +1,37 @@
|
|||||||
|
Client tracking listener is invoked when an invalidation message is received if the data previously requested has been changed. Next listener invocation will be made only if a new data request has been made and another change has occurred since then.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Available for [RBucket](data-and-services/objects.md/#object-holder), [RStream](data-and-services/objects.md/#stream), [RSet](data-and-services/objects.md/#set), [RMap](data-and-services/objects.md/#map), [RScoredSortedSet](data-and-services/collections.md/#scoredsortedset), [RList](data-and-services/collections.md/#list), [RQueue](data-and-services/collections.md/#queue), [RDeque](data-and-services/collections.md/#deque), [RBlockingQueue](data-and-services/collections.md/#blocking-queue), [RBlockingDeque](data-and-services/collections.md/#blocking-deque), [RDelayedQueue](data-and-services/collections.md/#delayed-queue), [RRingBuffer](data-and-services/collections.md/#ring-buffer) objects.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Requires [protocol](configuration.md) setting value set to `RESP3`.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Code usage example.
|
||||||
|
```java
|
||||||
|
RBucket<String> b = redisson.getBucket("test");
|
||||||
|
int listenerId = b.addListener(new TrackingListener() {
|
||||||
|
@Override
|
||||||
|
public void onChange(String name) {
|
||||||
|
// ...
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
});
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
// data requested and change is now tracked
|
||||||
|
b.get();
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
// ...
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
// stop tracking
|
||||||
|
b.removeListener(listenerId);
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
**Flush listener**
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Flush listener is executed on flushall/flushdb commands execution.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
```java
|
||||||
|
redisson.getKeys().addListener(new FlushListener() {
|
||||||
|
@Override
|
||||||
|
public void onFlush(InetSocketAddress address) {
|
||||||
|
// ...
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
});
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
@ -0,0 +1,209 @@
|
|||||||
|
Redis or Valkey command|Sync / Async API<br/><sub>Redisson.create(config)</sub>|Reactive API<br/><sub>redisson.reactive()</sub>|RxJava3 API<br/><sub>redisson.rxJava()</sub>|
|
||||||
|
| --- | --- | --- | --- |
|
||||||
|
AUTH | Config.setPassword() | - | - |
|
||||||
|
APPEND | RBinaryStream.<br/>getOutputStream().write() | - | - |
|
||||||
|
BZPOPMAX|RScoredSortedSet.<br/>pollLast()<br/>pollLastAsync() | RScoredSortedSetReactive.<br/>pollLast()| RScoredSortedSetRx.<br/>pollLast() |
|
||||||
|
BZPOPMIN|RScoredSortedSet.<br/>pollFirst()<br/>pollFirstAsync() | RScoredSortedSetReactive.<br/>pollFirst() | RScoredSortedSetRx.<br/>pollFirst() |
|
||||||
|
BZMPOP|RScoredSortedSet.<br/>pollLast()<br/>pollLastAsync()<br/>pollLastFromAny()<br/>pollLastEntriesFromAny() | RScoredSortedSetReactive.<br/>pollLast()<br/>pollLastFromAny()<br/>pollLastEntriesFromAny()| RScoredSortedSetRx.<br/>pollLast()<br/>pollLastFromAny()<br/>pollLastEntriesFromAny() |
|
||||||
|
BITCOUNT|RBitSet.<br/>cardinality()<br/>cardinalityAsync() | RBitSetReactive.<br/>cardinality() | RBitSetRx.<br/>cardinality() |
|
||||||
|
BITOP|RBitSet.<br/>or()<br/>and()<br/>xor()<br/>orAsync()<br/>andAsync()<br/>xorAsync() | RBitSetReactive.<br/>or()<br/>and()<br/>xor() | RBitSetRx.<br/>or()<br/>and()<br/>xor() |
|
||||||
|
BITPOS|RBitSet.<br/>length()<br/>lengthAsync() | RBitSetReactive.<br/>length() | RBitSetRx.<br/>length() |
|
||||||
|
BITFIELD|RBitSet.<br/>getByte()<br/>setByte()<br/>incrementAndGetByte()<br/><br/>getShort()<br/>setShort()<br/>incrementAndGetShort()<br/><br/>getInteger()<br/>setInteger()<br/>incrementAndGetInteger()<br/><br/>getLong()<br/>setLong()<br/>incrementAndGetLong() | RBitSetReactive.<br/>getByte()<br/>setByte()<br/>incrementAndGetByte()<br/><br/>getShort()<br/>setShort()<br/>incrementAndGetShort()<br/><br/>getInteger()<br/>setInteger()<br/>incrementAndGetInteger()<br/><br/>getLong()<br/>setLong()<br/>incrementAndGetLong() | RBitSetRx.<br/>getByte()<br/>setByte()<br/>incrementAndGetByte()<br/><br/>getShort()<br/>setShort()<br/>incrementAndGetShort()<br/><br/>getInteger()<br/>setInteger()<br/>incrementAndGetInteger()<br/><br/>getLong()<br/>setLong()<br/>incrementAndGetLong() |
|
||||||
|
BLMPOP|RBlockingQueue.<br/>pollLastFromAny()<br/>pollFirstFromAny()<br/>pollLastFromAnyAsync()<br/>pollFirstFromAnyAsync() | RBlockingQueueReactive.<br/>pollLastFromAny()<br/>pollFirstFromAny() |RBlockingQueueRx.<br/>pollLastFromAny()<br/>pollFirstFromAny() |
|
||||||
|
BLPOP|RBlockingQueue.<br/>take()<br/>poll()<br/>pollFromAny()<br/>takeAsync()<br/>pollAsync()<br/>pollFromAnyAsync() | RBlockingQueueReactive.<br/>take()<br/>poll()<br/>pollFromAny() |RBlockingQueueRx.<br/>take()<br/>poll()<br/>pollFromAny() |
|
||||||
|
BLMOVE|RBlockingDeque.<br/>move()<br/>moveAsync()| RBlockingDequeReactive.<br/>move()|RBlockingDequeRx.<br/>move()|
|
||||||
|
BRPOP|RBlockingDeque.<br/>takeLast()<br/>takeLastAsync() | RBlockingDequeReactive.<br/>takeLast() | RBlockingDequeRx.<br/>takeLast() |
|
||||||
|
BRPOPLPUSH|RBlockingQueue.<br/>pollLastAndOfferFirstTo()<br/>pollLastAndOfferFirstToAsync() | RBlockingQueueReactive.<br/>pollLastAndOfferFirstTo()| RBlockingQueueRx.<br/>pollLastAndOfferFirstTo()|
|
||||||
|
CONFIG GET|RedisNode.<br/>setConfig()<br/>setConfigAsync() | - | - |
|
||||||
|
CONFIG SET|RedisNode.<br/>getConfig()<br/>getConfigAsync() | - | - |
|
||||||
|
COPY|RObject.<br/>copy()<br/>copyAsync() | RObjectReactive.<br/>copy() | RObjectRx.<br/>copy() |
|
||||||
|
CLIENT SETNAME|Config.setClientName() | - | - |
|
||||||
|
CLIENT REPLY|BatchOptions.skipResult() | - | - |
|
||||||
|
CLIENT TRACKING|RBucket<br/>.addListener(TrackingListener)<br/>RStream<br/>.addListener(TrackingListener)<br/>RScoredSortedSet<br/>.addListener(TrackingListener)<br/>RSet<br/>.addListener(TrackingListener)<br/>RMap<br/>.addListener(TrackingListener) | RBucketReactive<br/>.addListener(TrackingListener)<br/>RStreamReactive<br/>.addListener(TrackingListener)<br/>RScoredSortedSetReactive<br/>.addListener(TrackingListener)<br/>RSetReactive<br/>.addListener(TrackingListener)<br/>RMapReactive<br/>.addListener(TrackingListener) | RBucketRx<br/>.addListener(TrackingListener)<br/>RStreamRx<br/>.addListener(TrackingListener)<br/>RScoredSortedSetRx<br/>.addListener(TrackingListener)<br/>RSetRx<br/>.addListener(TrackingListener)<br/>RMapRx<br/>.addListener(TrackingListener) |
|
||||||
|
CLUSTER INFO| ClusterNode.info() | - | - |
|
||||||
|
CLUSTER KEYSLOT|RKeys.<br/>getSlot()<br/>getSlotAsync() | RKeysReactive.<br/>getSlot() | RKeysRx.<br/>getSlot() |
|
||||||
|
CLUSTER NODES|Used in ClusterConnectionManager |
|
||||||
|
DECRBY|RAtomicLong.<br/>addAndGet()<br/>addAndGetAsync() | RAtomicLongReactive.<br/>addAndGet() |RAtomicLongRx.<br/>addAndGet() |
|
||||||
|
DUMP|RObject.<br/>dump()<br/>dumpAsync()| RObjectReactive.<br/>dump()| RObjectRx.<br/>dump()|
|
||||||
|
DBSIZE|RKeys.<br/>count()<br/>countAsync()| RKeysReactive.<br/>count()| RKeysRx.count()|
|
||||||
|
DECR|RAtomicLong.<br/>decrementAndGet()<br/>decrementAndGetAsync()| RAtomicLongReactive.<br/>decrementAndGet()| RAtomicLongRx.<br/>decrementAndGet()|
|
||||||
|
DEL|RObject.<br/>delete()<br/>deleteAsync()<br/><br/>RKeys.<br/>delete()<br/>deleteAsync()| RObjectReactive.<br/>delete()<br/><br/>RKeysReactive.<br/>delete()|RObjectRx.<br/>delete()<br/><br/>RKeysRx.<br/>delete()|
|
||||||
|
STRLEN|RBucket.<br/>size()<br/>sizeAsync()| RBucketReactive.<br/>size()| RBucketRx.<br/>size()|
|
||||||
|
EVAL|RScript.<br/>eval()<br/>evalAsync()| RScriptReactive.<br/>eval()| RScriptRx.<br/>eval()|
|
||||||
|
EVALSHA|RScript.<br/>evalSha()<br/>evalShaAsync()| RScriptReactive.<br/>evalSha()| RScriptRx.<br/>evalSha()|
|
||||||
|
EXEC|RBatch.<br/>execute()<br/>executeAsync()| RBatchReactive.<br/>execute()| RBatchRx.<br/>execute()|
|
||||||
|
EXISTS|RObject.<br/>isExists()<br/>isExistsAsync()| RObjectReactive.<br/>isExists()| RObjectRx.<br/>isExists()|
|
||||||
|
FLUSHALL|RKeys.<br/>flushall()<br/>flushallAsync()| RKeysReactive.<br/>flushall()| RKeysRx.<br/>flushall()|
|
||||||
|
FLUSHDB|RKeys.<br/>flushdb()<br/>flushdbAsync()| RKeysReactive.<br/>flushdb()| RKeysRx.<br/>flushdb()|
|
||||||
|
GETRANGE|RBinaryStream.<br/>getChannel().read()|RBinaryStreamReactive.<br/>read()|RBinaryStreamRx.<br/>read()|
|
||||||
|
GEOADD|RGeo.<br/>add()<br/>addAsync()| RGeoReactive.<br/>add()| RGeoRx.<br/>add()|
|
||||||
|
GEODIST|RGeo.<br/>dist()<br/>distAsync()| RGeoReactive.<br/>dist()| RGeoRx.<br/>dist()|
|
||||||
|
GEOHASH|RGeo.<br/>hash()<br/>hashAsync()| RGeoReactive.<br/>hash()| RGeoRx.<br/>hash()|
|
||||||
|
GEOPOS|RGeo.<br/>pos()<br/>posAsync()| RGeoReactive.<br/>pos()| RGeoRx.<br/>pos()|
|
||||||
|
GEORADIUS|RGeo.<br/>radius()<br/>radiusAsync()<br/>radiusWithDistance()<br/>radiusWithDistanceAsync()<br/>radiusWithPosition()<br/>radiusWithPositionAsync()|RGeoReactive.<br/>radius()<br/>radiusWithDistance()<br/>radiusWithPosition()|RGeoRx.<br/>radius()<br/>radiusWithDistance()<br/>radiusWithPosition()|
|
||||||
|
GEOSEARCH|RGeo.<br/>search()<br/>searchAsync()| RGeoReactive.<br/>search()| RGeoRx.<br/>search()|
|
||||||
|
GEOSEARCHSTORE|RGeo.<br/>storeSearchTo()<br/>storeSearchToAsync()| RGeoReactive.<br/>storeSearchTo()| RGeoRx.<br/>storeSearchTo()|
|
||||||
|
GET|RBucket.<br/>get()<br/>getAsync()<br/><br/>RBinaryStream.<br/>get()<br/>getAsync()| RBucketReactive.<br/>get()<br/><br/>RBinaryStreamReactive.<br/>get()| RBucketRx.<br/>get()<br/><br/>RBinaryStreamRx.<br/>get()|
|
||||||
|
GETEX|RBucket.<br/>getAndExpire()<br/>getAndExpireAsync()<br/>getAndClearExpire()<br/>getAndClearExpireAsync()| RBucketReactive.<br/>getAndExpire()<br/>getAndClearExpire()| RBucketRx.<br/>getAndExpire()<br/>getAndClearExpire()|
|
||||||
|
GETBIT|RBitSet.<br/>get()<br/>getAsync()| RBitSetReactive.<br/>get()| RBitSetRx.<br/>get() |
|
||||||
|
GETSET|RBucket.<br/>getAndSet()<br/>getAndSetAsync()<br/><br/>RAtomicLong.<br/>getAndSet()<br/>getAndSetAsync()<br/><br/>RAtomicDouble.<br/>getAndSet()<br/>getAndSetAsync()|RBucketReactive.<br/>getAndSet()<br/><br/>RAtomicLongReactive.<br/>getAndSet()<br/><br/>RAtomicDoubleReactive.<br/>getAndSet()|RBucketRx.<br/>getAndSet()<br/><br/>RAtomicLongRx.<br/>getAndSet()<br/><br/>RAtomicDoubleRx.<br/>getAndSet()
|
||||||
|
HDEL|RMap.<br/>fastRemove()<br/>fastRemoveAsync()| RMapReactive.<br/>fastRemove()| RMapRx.<br/>fastRemove()|
|
||||||
|
HEXISTS|RMap.<br/>containsKey()<br/>containsKeyAsync()| RMapReactive.<br/>containsKey()| RMapRx.<br/>containsKey()|
|
||||||
|
HGET|RMap.<br/>get()<br/>getAsync()|RMapReactive.<br/>get()|RMapRx.<br/>get()|
|
||||||
|
HSTRLEN|RMap.<br/>valueSize()<br/>valueSizeAsync()|RMapReactive.<br/>valueSize()| RMapRx.<br/>valueSize()|
|
||||||
|
HGETALL|RMap.<br/>readAllEntrySet()<br/>readAllEntrySetAsync()|RMapReactive.<br/>readAllEntrySet()| RMapRx.<br/>readAllEntrySet()|
|
||||||
|
HINCRBY|RMap.<br/>addAndGet()<br/>addAndGetAsync()| RMapReactive.<br/>addAndGet()| RMapRx.<br/>addAndGet()|
|
||||||
|
HINCRBYFLOAT|RMap.<br/>addAndGet()<br/>addAndGetAsync()| RMapReactive.<br/>addAndGet()| RMapRx.<br/>addAndGet()|
|
||||||
|
HKEYS|RMap.<br/>readAllKeySet()<br/>readAllKeySetAsync()| RMapReactive.<br/>readAllKeySet()| RMapRx.<br/>readAllKeySet()|
|
||||||
|
HLEN|RMap.<br/>size()<br/>sizeAsync()| RMapReactive.<br/>size()| RMapRx.<br/>size()|
|
||||||
|
HMGET|RMap.<br/>getAll()<br/>getAllAsync()| RMapReactive.<br/>getAll()| RMapRx.<br/>getAll()|
|
||||||
|
HMSET|RMap.<br/>putAll()<br/>putAllAsync()| RMapReactive.<br/>putAll()| RMapRx.<br/>putAll()|
|
||||||
|
HRANDFIELD|RMap.<br/>putAll()<br/>putAllAsync()| RMapReactive.<br/>putAll()| RMapRx.<br/>putAll()|
|
||||||
|
HSCAN|RMap.<br/>keySet().iterator()<br/>values().iterator()<br/>entrySet().iterator()|RMapReactive.<br/>keyIterator()<br/>valueIterator()<br/>entryIterator()|RMapRx.<br/>keyIterator()<br/>valueIterator()<br/>entryIterator()|
|
||||||
|
HSET|RMap.<br/>randomEntries()<br/>randomKeys()<br/>randomEntriesAsync()<br/>randomKeysAsync()| RMapReactive.<br/>randomEntries()<br/>randomKeys()| RMapRx.<br/>randomEntries()<br/>randomKeys()|
|
||||||
|
HSETNX|RMap.<br/>fastPutIfAbsent()<br/>fastPutIfAbsentAsync()| RMapReactive.<br/>fastPutIfAbsent()| RMapRx.<br/>fastPutIfAbsent()|
|
||||||
|
HVALS|RMap.<br/>readAllValues()<br/>readAllValuesAsync()| RMapReactive.<br/>readAllValues()| RMapRx.<br/>readAllValues()|
|
||||||
|
HPEXPIRE|RMapCacheNative.<br/>put()<br/>fastPut()<br/>putIfAbsent()<br/>fastPutIfAbsent()<br/>putAll()<br/>expireEntry()<br/>putAsync()<br/>fastPutAsync()<br/>putIfAbsentAsync()<br/>fastPutIfAbsentAsync()<br/>putAllAsync()<br/>expireEntryAsync()| RMapCacheNativeReactive.<br/><br/>put()<br/>fastPut()<br/>putIfAbsent()<br/>fastPutIfAbsent()<br/>putAll()<br/>expireEntry()| RMapCacheNativeRx.<br/><br/>put()<br/>fastPut()<br/>putIfAbsent()<br/>fastPutIfAbsent()<br/>putAll()<br/>expireEntry()|
|
||||||
|
HPEXPIREAT|RMapCacheNative.<br/>put()<br/>fastPut()<br/>putIfAbsent()<br/>fastPutIfAbsent()<br/>putAll()<br/>expireEntry()<br/>putAsync()<br/>fastPutAsync()<br/>putIfAbsentAsync()<br/>fastPutIfAbsentAsync()<br/>putAllAsync()<br/>expireEntryAsync()| RMapCacheNativeReactive.<br/><br/>put()<br/>fastPut()<br/>putIfAbsent()<br/>fastPutIfAbsent()<br/>putAll()<br/>expireEntry()| RMapCacheNativeRx.<br/><br/>put()<br/>fastPut()<br/>putIfAbsent()<br/>fastPutIfAbsent()<br/>putAll()<br/>expireEntry()|
|
||||||
|
HEXPIRE|RMapCacheNative.<br/>put()<br/>fastPut()<br/>putIfAbsent()<br/>fastPutIfAbsent()<br/>putAll()<br/>expireEntry()<br/>putAsync()<br/>fastPutAsync()<br/>putIfAbsentAsync()<br/>fastPutIfAbsentAsync()<br/>putAllAsync()<br/>expireEntryAsync()| RMapCacheNativeReactive.<br/><br/>put()<br/>fastPut()<br/>putIfAbsent()<br/>fastPutIfAbsent()<br/>putAll()<br/>expireEntry()| RMapCacheNativeRx.<br/><br/>put()<br/>fastPut()<br/>putIfAbsent()<br/>fastPutIfAbsent()<br/>putAll()<br/>expireEntry()|
|
||||||
|
HEXPIREAT|RMapCacheNative.<br/>put()<br/>fastPut()<br/>putIfAbsent()<br/>fastPutIfAbsent()<br/>putAll()<br/>expireEntry()<br/>putAsync()<br/>fastPutAsync()<br/>putIfAbsentAsync()<br/>fastPutIfAbsentAsync()<br/>putAllAsync()<br/>expireEntryAsync()| RMapCacheNativeReactive.<br/><br/>put()<br/>fastPut()<br/>putIfAbsent()<br/>fastPutIfAbsent()<br/>putAll()<br/>expireEntry()| RMapCacheNativeRx.<br/><br/>put()<br/>fastPut()<br/>putIfAbsent()<br/>fastPutIfAbsent()<br/>putAll()<br/>expireEntry()|
|
||||||
|
HPERSIST|RMapCacheNative.<br/>clearExpire()<br/>clearExpireAsync()| RMapCacheNativeReactive.<br/>clearExpire()| RMapCacheNativeRx.<br/>clearExpire()|
|
||||||
|
HPTTL|RMapCacheNative.<br/>remainTimeToLive()<br/>remainTimeToLiveAsync()| RMapCacheNativeReactive.<br/>remainTimeToLive()| RMapCacheNativeRx.<br/>remainTimeToLive()|
|
||||||
|
INCR|RAtomicLong.<br/>incrementAndGet()<br/>incrementAndGetAsync()| RAtomicLongReactive.<br/>incrementAndGet()| RAtomicLongRx.<br/>incrementAndGet()|
|
||||||
|
INCRBY|RAtomicLong.<br/>addAndGet()<br/>addAndGetAsync()| RAtomicLongReactive.<br/>addAndGet()| RAtomicLongRx.<br/>addAndGet()|
|
||||||
|
INCRBYFLOAT|RAtomicDouble.<br/>addAndGet()<br/>addAndGetAsync()| RAtomicDoubleReactive.<br/>addAndGet()| RAtomicDoubleRx.<br/>addAndGet()|
|
||||||
|
JSON.ARRAPPEND|RJsonBucket.<br/>arrayAppend()<br/>arrayAppendAsync()| RJsonBucketReactive.<br/>arrayAppend()| RJsonBucketRx.<br/>arrayAppend()|
|
||||||
|
JSON.ARRINDEX|RJsonBucket.<br/>arrayIndex()<br/>arrayIndexAsync()| RJsonBucketReactive.<br/>arrayIndex()| RJsonBucketRx.<br/>arrayIndex()|
|
||||||
|
JSON.ARRINSERT|RJsonBucket.<br/>arrayInsert()<br/>arrayInsertAsync()| RJsonBucketReactive.<br/>arrayInsert()| RJsonBucketRx.<br/>arrayInsert()|
|
||||||
|
JSON.ARRLEN|RJsonBucket.<br/>arraySize()<br/>arraySizeAsync()| RJsonBucketReactive.<br/>arraySize()| RJsonBucketRx.<br/>arraySize()|
|
||||||
|
JSON.ARRPOP|RJsonBucket.<br/>arrayPollLast()<br/>arrayPollFirst()<br/>arrayPop()<br/>arrayPollLastAsync()<br/>arrayPollFirstAsync()<br/>arrayPopAsync()| RJsonBucketReactive.<br/>arrayPollLast()<br/>arrayPollFirst()<br/>arrayPop()| RJsonBucketRx.<br/>arrayPollLast()<br/>arrayPollFirst()<br/>arrayPop()|
|
||||||
|
JSON.ARRTRIM|RJsonBucket.<br/>arrayTrim()<br/>arrayTrimAsync()| RJsonBucketReactive.<br/>arrayTrim()| RJsonBucketRx.<br/>arrayTrim()|
|
||||||
|
JSON.CLEAR|RJsonBucket.<br/>clear()<br/>clearAsync()| RJsonBucketReactive.<br/>clear()| RJsonBucketRx.<br/>clear()|
|
||||||
|
JSON.GET|RJsonBucket.<br/>get()<br/>getAsync()| RJsonBucketReactive.<br/>get()| RJsonBucketRx.<br/>get()|
|
||||||
|
JSON.MERGE|RJsonBucket.<br/>merge()<br/>mergeAsync()| RJsonBucketReactive.<br/>merge()| RJsonBucketRx.<br/>merge()|
|
||||||
|
JSON.NUMINCRBY|RJsonBucket.<br/>incrementAndGet()<br/>incrementAndGetAsync()| RJsonBucketReactive.<br/>incrementAndGet()| RJsonBucketRx.<br/>incrementAndGet()|
|
||||||
|
JSON.OBJLEN|RJsonBucket.<br/>countKeys()<br/>countKeysAsync()| RJsonBucketReactive.<br/>countKeys()| RJsonBucketRx.<br/>countKeys()|
|
||||||
|
JSON.OBJKEYS|RJsonBucket.<br/>getKeys()<br/>getKeysAsync()| RJsonBucketReactive.<br/>getKeys()| RJsonBucketRx.<br/>getKeys()|
|
||||||
|
JSON.SET|RJsonBucket.<br/>set()<br/>setAsync()| RJsonBucketReactive.<br/>set()| RJsonBucketRx.<br/>set()|
|
||||||
|
JSON.STRAPPEND|RJsonBucket.<br/>stringAppend()<br/>stringAppendAsync()| RJsonBucketReactive.<br/>stringAppend()| RJsonBucketRx.<br/>stringAppend()|
|
||||||
|
JSON.STRLEN|RJsonBucket.<br/>stringSize()<br/>stringSizeAsync()| RJsonBucketReactive.<br/>stringSize()| RJsonBucketRx.<br/>stringSize()|
|
||||||
|
JSON.TOGGLE|RJsonBucket.<br/>toggle()<br/>toggleAsync()| RJsonBucketReactive.<br/>toggle()| RJsonBucketRx.<br/>toggle()|
|
||||||
|
JSON.TYPE|RJsonBucket.<br/>type()<br/>typeAsync()| RJsonBucketReactive.<br/>type()| RJsonBucketRx.<br/>type()|
|
||||||
|
KEYS|RKeys.<br/>getKeysByPattern()<br/>getKeysByPatternAsync()| RKeysReactive.<br/>getKeysByPattern()| RKeysRx.<br/>getKeysByPattern()|
|
||||||
|
LINDEX|RList.<br/>get()<br/>getAsync()| RListReactive.<br/>get()|RListRx.<br/>get()|
|
||||||
|
LLEN|RList.<br/>size()<br/>sizeAsync()| RListReactive.<br/>size()|RListRx.<br/>size()|
|
||||||
|
LMOVE|RDeque.<br/>move()<br/>moveAsync()| RDequeReactive.<br/>move()|RDequeRx.<br/>move()|
|
||||||
|
LPOP|RQueue.<br/>poll()<br/>pollAsync()| RQueueReactive.<br/>poll()|RQueueRx.<br/>poll()|
|
||||||
|
LPUSH|RDeque.<br/>addFirst()<br/>addFirstAsync()|RDequeReactive.<br/>addFirst()||RDequeRx.<br/>addFirst()|
|
||||||
|
LRANGE|RList.<br/>readAll()<br/>readAllAsync()|RListReactive.readAll()|RListRx.readAll()|
|
||||||
|
LPUSHX|RDeque.<br/>addFirstIfExists()<br/>addFirstIfExistsAsync()|RDequeReactive.<br/>addFirstIfExists()|RDequeRx.<br/>addFirstIfExists()|
|
||||||
|
LREM|RList.<br/>fastRemove()<br/>fastRemoveAsync()|RListReactive.<br/>fastRemove()|RListRx.<br/>fastRemove()|
|
||||||
|
LSET|RList.<br/>fastSet()<br/>fastSetAsync()|RListReactive.<br/>fastSet()|RListRx.<br/>fastSet()|
|
||||||
|
LTRIM|RList.<br/>trim()<br/>trimAsync()|RListReactive.<br/>trim()|RListRx.<br/>trim()|
|
||||||
|
LINSERT|RList.<br/>addBefore()<br/>addAfter()<br/>addBeforeAsync()<br/>addAfterAsync()|RListReactive.<br/>addBefore()<br/>addAfter()|RListRx.<br/>addBefore()<br/>addAfter()|
|
||||||
|
MULTI|RBatch.<br/>execute()<br/>executeAsync()|RBatchReactive.<br/>execute()|RBatchRx.<br/>execute()|
|
||||||
|
MGET|RBuckets.<br/>get()<br/>getAsync()|RBucketsReactive.<br/>get()|RBucketsRx.<br/>get()|
|
||||||
|
MSETNX|RBuckets.<br/>trySet()<br/>trySetAsync()|RBucketsReactive.<br/>trySet()|RBucketsRx.<br/>trySet()|
|
||||||
|
MIGRATE|RObject.<br/>migrate()<br/>migrateAsync()|RObjectReactive.<br/>migrate()|RObjectRx.<br/>migrate()|
|
||||||
|
MOVE|RObject.<br/>move()<br/>moveAsync()|RObjectReactive.<br/>move()|RObjectRx.<br/>move()|
|
||||||
|
MSET|RBuckets.<br/>set()<br/>setAsync()|RBucketsReactive.<br/>set()|RBucketsRx.<br/>set()|
|
||||||
|
PERSIST|RExpirable.<br/>clearExpire()<br/>clearExpireAsync()|RExpirableReactive.<br/>clearExpire()|RExpirableRx.<br/>clearExpire()|
|
||||||
|
PEXPIRE|RExpirable.<br/>expire()<br/>expireAsync()|RExpirableReactive.<br/>expire()|RExpirableRx.<br/>expire()|
|
||||||
|
PEXPIREAT|RExpirable.<br/>expireAt()<br/>expireAtAsync()|RExpirableReactive.<br/>expireAt()|RExpirableRx.<br/>expireAt()|
|
||||||
|
PEXPIRETIME|RExpirable.<br/>expireTime()<br/>expireTimeAsync()|RExpirableReactive.<br/>expireTime()|RExpirableRx.<br/>expireTime()|
|
||||||
|
PFADD|RHyperLogLog.<br/>add()<br/>addAsync()<br/>addAll()<br/>addAllAsync()|RHyperLogLogReactive.<br/>add()<br/><br/>addAll()|RHyperLogLogRx.<br/>add()<br/><br/>addAll()|
|
||||||
|
PFCOUNT|RHyperLogLog.<br/>count()<br/>countAsync()<br/>countWith()<br/>countWithAsync()|RHyperLogLogReactive.<br/>count()<br/>countWith()|RHyperLogLogRx.<br/>count()<br/>countWith()|
|
||||||
|
PFMERGE|RHyperLogLog.<br/>mergeWith()<br/>mergeWithAsync()|RHyperLogLogReactive.<br/>mergeWith()|RHyperLogLogRx.<br/>mergeWith()|
|
||||||
|
PING|Node.ping()<br/>NodesGroup.pingAll()| - | - |
|
||||||
|
PSUBSCRIBE|RPatternTopic.<br/>addListener()|RPatternTopicReactive.<br/>addListener()|RPatternTopicRx.<br/>addListener()|
|
||||||
|
PSETEX|RBucket.<br/>set()<br/>setAsync()|RBucketReactive.<br/>set()|RBucketRx.<br/>set()|
|
||||||
|
PTTL|RExpirable.<br/>remainTimeToLive()<br/>remainTimeToLiveAsync()|RExpirableReactive.<br/>remainTimeToLive()|RExpirableRx.<br/>remainTimeToLive()|
|
||||||
|
PUBLISH|RTopic.<br/>publish()|RTopicReactive.<br/>publish()|RTopicRx.<br/>publish()|
|
||||||
|
PUBSUB NUMSUB|RTopic.<br/>countSubscribers()<br/>countSubscribersAsync()|RTopicReactive.<br/>countSubscribers()|RTopicRx.<br/>countSubscribers()|
|
||||||
|
PUNSUBSCRIBE|RPatternTopic.<br/>removeListener()|RPatternTopicReactive.<br/>removeListener()|RPatternTopicRx.<br/>removeListener()|
|
||||||
|
RANDOMKEY|RKeys.<br/>randomKey()<br/>randomKeyAsync()|RKeysReactive.<br/>randomKey()|RKeysRx.<br/>randomKey()|
|
||||||
|
RESTORE|RObject.<br/>restore()<br/>restoreAsync()|RObjectReactive.<br/>restore()|RObjectRx.<br/>restore()|
|
||||||
|
RENAME|RObject.<br/>rename()<br/>renameAsync()|RObjectReactive.<br/>rename()|RObjectRx.<br/>rename()|
|
||||||
|
RPOP|RDeque.<br/>pollLast()<br/>removeLast()<br/>pollLastAsync()<br/>removeLastAsync()|RDequeReactive.<br/>pollLast()<br/>removeLast()|RDequeRx.<br/>pollLast()<br/>removeLast()|
|
||||||
|
RPOPLPUSH|RDeque.<br/>pollLastAndOfferFirstTo()<br/>pollLastAndOfferFirstToAsync()|RDequeReactive.<br/>pollLastAndOfferFirstTo()|RDequeRx.<br/>pollLastAndOfferFirstTo()|
|
||||||
|
RPUSH|RList.<br/>add()<br/>addAsync()|RListReactive.<br/>add()|RListRx.<br/>add()|
|
||||||
|
RPUSHX|RDeque.<br/>addLastIfExists()<br/>addLastIfExistsAsync()|RListReactive.<br/>addLastIfExists()|RListRx.<br/>addLastIfExists()|
|
||||||
|
SADD|RSet.<br/>add()<br/>addAsync()|RSetReactive.<br/>add()|RSetRx.<br/>add()|
|
||||||
|
SETRANGE|RBinaryStream.<br/>getChannel().write()|RBinaryStreamReactive.<br/>write()|RBinaryStreamRx.<br/>write()|
|
||||||
|
SCAN|RKeys.<br/>getKeys()|RKeysReactive.<br/>getKeys()|RKeysRx.<br/>getKeys()|
|
||||||
|
SCARD|RSet.<br/>size()<br/>sizeAsync()|RSetReactive.<br/>size()|RSetRx.<br/>size()|
|
||||||
|
SCRIPT EXISTS|RScript.<br/>scriptExists()<br/>scriptExistsAsync()|RScriptReactive.<br/>scriptExists()|RScriptRx.<br/>scriptExists()|
|
||||||
|
SCRIPT FLUSH|RScript.<br/>scriptFlush()<br/>scriptFlushAsync()|RScriptReactive.<br/>scriptFlush()|RScriptRx.<br/>scriptFlush()|
|
||||||
|
SCRIPT KILL|RScript.<br/>scriptKill()<br/>scriptKillAsync()|RScriptReactive.<br/>scriptKill()|RScriptRx.<br/>scriptKill()|
|
||||||
|
SCRIPT LOAD|RScript.<br/>scriptLoad()<br/>scriptLoadAsync()|RScriptReactive.<br/>scriptLoad()|RScriptRx.<br/>scriptLoad()|
|
||||||
|
SDIFFSTORE|RSet.<br/>diff()<br/>diffAsync()|RSetReactive.<br/>diff()|RSetRx.<br/>diff()|
|
||||||
|
SDIFF|RSet.<br/>readDiff()<br/>readDiffAsync()|RSetReactive.<br/>readDiff()|RSetRx.<br/>readDiff()|
|
||||||
|
SRANDMEMBER|RSet.<br/>random()<br/>randomAsync()|RSetReactive.<br/>random()|RSetRx.<br/>random()|
|
||||||
|
SELECT|Config.setDatabase()| - | - |
|
||||||
|
SET|RBucket.<br/>set()<br/>setAsync()|RBucketReactive.<br/>set()|RBucketRx.<br/>set()|
|
||||||
|
SETBIT|RBitSet.<br/>set()<br/>clear()<br/>setAsync()<br/>clearAsync()|RBitSetReactive.<br/>set()<br/>clear()|RBitSetRx.<br/>set()<br/>clear()|
|
||||||
|
SETEX|RBucket.<br/>set()<br/>setAsync()|RBucketReactive.<br/>set()|RBucketRx.<br/>set()|
|
||||||
|
SETNX|RBucket.<br/>setIfAbsent()<br/>setIfAbsentAsync()|RBucketReactive.<br/>setIfAbsent()|RBucketRx.<br/>setIfAbsent()|
|
||||||
|
SISMEMBER|RSet.<br/>contains()<br/>containsAsync()|RSetReactive.<br/>contains()|RSetRx.<br/>contains()|
|
||||||
|
SINTERSTORE|RSet.<br/>intersection()<br/>intersectionAsync()|RSetReactive.<br/>intersection()|RSetRx.<br/>intersection()|
|
||||||
|
SINTER|RSet.<br/>readIntersection()<br/>readIntersectionAsync()|RSetReactive.<br/>readIntersection()|RSetRx.<br/>readIntersection()|
|
||||||
|
SMEMBERS|RSet.<br/>readAll()<br/>readAllAsync()|RSetReactive.<br/>readAll()|RSetRx.<br/>readAll()|
|
||||||
|
SMOVE|RSet.<br/>move()<br/>moveAsync()|RSetReactive.<br/>move()|RSetRx.<br/>move()|
|
||||||
|
SORT|RList.<br/>readSort()<br/>sortTo()<br/>readSortAsync()<br/>sortToAsync()|RListReactive.<br/>readSort()<br/>sortTo()|RListRx.<br/>readSort()<br/>sortTo()|
|
||||||
|
SPOP|RSet.<br/>removeRandom()<br/>removeRandomAsync()|RSetReactive.<br/>removeRandom()|RSetRx.<br/>removeRandom()|
|
||||||
|
SREM|RSet.<br/>remove()<br/>removeAsync()|RSetReactive.<br/>remove()|RSetRx.<br/>remove()|
|
||||||
|
SSCAN|RSet.<br/>iterator()|RSetReactive.<br/>iterator()|RSetRx.<br/>iterator()|
|
||||||
|
SUBSCRIBE|RTopic.<br/>addListener()|RTopicReactive.<br/>addListener()|RTopicRx.<br/>addListener()|
|
||||||
|
SUNION|RSet.<br/>readUnion()<br/>readUnionAsync()|RSetReactive.<br/>readUnion()|RSetRx.<br/>readUnion()|
|
||||||
|
SUNIONSTORE|RSet.<br/>union()<br/>unionAsync()|RSetReactive.<br/>union()|RSetRx.<br/>union()|
|
||||||
|
SWAPDB|RKeys.<br/>swapdb()<br/>swapdbAsync()|RKeysReactive.<br/>swapdb()|RKeysRx.<br/>swapdb()|
|
||||||
|
TTL|RExpirable.<br/>remainTimeToLive()<br/>remainTimeToLiveAsync()|RExpirableReactive.<br/>remainTimeToLive()|RExpirableRx.<br/>remainTimeToLive()|
|
||||||
|
TYPE|RKeys.<br/>getType()<br/>getTypeAsync()|RKeysReactive.<br/>getType()|RKeysRx.<br/>getType()|
|
||||||
|
TOUCH|RObject.<br/>touch()<br/>touchAsync()|RObjectReactive.<br/>touch()|RObjectRx.<br/>touch()|
|
||||||
|
UNSUBSCRIBE|RTopic.<br/>removeListener()|RTopicReactive.<br/>removeListener()|RTopicRx.<br/>removeListener()|
|
||||||
|
UNLINK|RObject.<br/>unlink()<br/>unlinkAsync()|RObjectReactive.<br/>unlink()|RObjectRx.<br/>unlink()|
|
||||||
|
WAIT|BatchOptions.<br/>sync()|BatchOptions.<br/>sync()|BatchOptions.<br/>sync()|
|
||||||
|
WAITAOF|BatchOptions.<br/>syncAOF()|BatchOptions.<br/>syncAOF()|BatchOptions.<br/>syncAOF()|
|
||||||
|
ZADD|RScoredSortedSet.<br/>add()<br/>addAsync()<br/>addAll()<br/>addAllAsync()|RScoredSortedSetReactive.<br/>add()<br/>addAll()|RScoredSortedSetRx.<br/>add()<br/>addAll()|
|
||||||
|
ZCARD|RScoredSortedSet.<br/>size()<br/>sizeAsync()|RScoredSortedSetReactive.<br/>size()|RScoredSortedSetRx.<br/>size()|
|
||||||
|
ZCOUNT|RScoredSortedSet.<br/>count()<br/>countAsync()|RScoredSortedSetReactive.<br/>count()|RScoredSortedSetRx.<br/>count()|
|
||||||
|
ZDIFF|RScoredSortedSet.<br/>readDiff()<br/>readDiffAsync()|RScoredSortedSetReactive.<br/>readDiff()|RScoredSortedSetRx.<br/>readDiff()|
|
||||||
|
ZDIFFSTORE|RScoredSortedSet.<br/>diff()<br/>diffAsync()|RScoredSortedSetReactive.<br/>diff()|RScoredSortedSetRx.<br/>diff()|
|
||||||
|
ZINCRBY|RScoredSortedSet.<br/>addScore()<br/>addScoreAsync()|RScoredSortedSetReactive.<br/>addScore()|RScoredSortedSetRx.<br/>addScore()|
|
||||||
|
ZINTER|RScoredSortedSet.<br/>readIntersection()<br/>readIntersectionAsync()|RScoredSortedSetReactive.<br/>readIntersection()|RScoredSortedSetRx.<br/>readIntersection()|
|
||||||
|
ZREMRANGEBYRANK|RScoredSortedSet.<br/>removeRangeByRank()<br/>removeRangeByRankAsync()|RScoredSortedSetReactive.<br/>removeRangeByRank()|RScoredSortedSetRx.<br/>removeRangeByRank()|
|
||||||
|
ZREVRANGEBYLEX|RLexSortedSet.<br/>rangeReversed()<br/>rangeReversedAsync()|RLexSortedSetReactive.<br/>rangeReversed()|RLexSortedSetSetRx.<br/>rangeReversed()|
|
||||||
|
ZLEXCOUNT|RLexSortedSet.<br/>lexCount()<br/>lexCountHead()<br/>lexCountTail()<br/>lexCountAsync()<br/>lexCountHeadAsync()<br/>lexCountTailAsync()|RLexSortedSetReactive.<br/>lexCount()<br/>lexCountHead()<br/>lexCountTail()|RLexSortedSetRx.<br/>lexCount()<br/>lexCountHead()<br/>lexCountTail()|
|
||||||
|
ZRANGE|RScoredSortedSet.<br/>valueRange()<br/>valueRangeAsync()|RScoredSortedSetReactive.<br/>valueRange()|RScoredSortedSetRx.<br/>valueRange()|
|
||||||
|
ZRANDMEMBER|RScoredSortedSet.<br/>random()<br/>randomAsync()|RScoredSortedSetReactive.<br/>random()|RScoredSortedSetRx.<br/>random()|
|
||||||
|
ZREVRANGE|RScoredSortedSet.<br/>valueRangeReversed()<br/>valueRangeReversedAsync()|RScoredSortedSetReactive.<br/>valueRangeReversed()|RScoredSortedSetRx.<br/>valueRangeReversed()|
|
||||||
|
ZUNION|RScoredSortedSet.<br/>readUnion()<br/>readUnionAsync()|RScoredSortedSetReactive.<br/>readUnion()|RScoredSortedSetRx.<br/>readUnion()|
|
||||||
|
ZUNIONSTORE|RScoredSortedSet.<br/>union()<br/>unionAsync()|RScoredSortedSetReactive.<br/>union()|RScoredSortedSetRx.<br/>union()|
|
||||||
|
ZINTERSTORE|RScoredSortedSet.<br/>intersection()<br/>intersectionAsync()|RScoredSortedSetReactive.<br/>intersection()|RScoredSortedSetRx.<br/>intersection()|
|
||||||
|
ZPOPMAX|RScoredSortedSet.<br/>pollLast()<br/>pollLastAsync()|RScoredSortedSetReactive.<br/>pollLast()|RScoredSortedSetRx.<br/>pollLast()|
|
||||||
|
ZPOPMIN|RScoredSortedSet.<br/>pollFirst()<br/>pollFirstAsync()|RScoredSortedSetReactive.<br/>pollFirst()|RScoredSortedSetRx.<br/>pollFirst()|
|
||||||
|
ZMPOP|RScoredSortedSet.<br/>pollFirstEntriesFromAny()<br/>pollFirstEntriesFromAnyAsync()<br/>pollLastFromAny()<br/>pollLastFromAnyAsync()<br/>pollFirstFromAny()<br/>pollFirstFromAnyAsync()|RScoredSortedSetReactive.<br/>pollFirstEntriesFromAny()<br/>pollLastFromAny()<br/>pollFirstFromAny()|RScoredSortedSetRx.<br/>pollFirstEntriesFromAny()<br/>pollLastFromAny()<br/>pollFirstFromAny()|
|
||||||
|
ZRANGEBYLEX|RLexSortedSet.<br/>range()<br/>rangeHead()<br/>rangeTail()<br/>rangeAsync()<br/>rangeHeadAsync()<br/>rangeTailAsync()|RLexSortedSetReactive.<br/>range()<br/>rangeHead()<br/>rangeTail()|RLexSortedSetRx.<br/>range()<br/>rangeHead()<br/>rangeTail()|
|
||||||
|
ZRANGEBYSCORE|RScoredSortedSet.<br/>valueRange()<br/>entryRange()<br/>valueRangeAsync()<br/>entryRangeAsync()|RScoredSortedSetReactive.<br/>valueRange()<br/>entryRange()|RScoredSortedSetRx.<br/>valueRange()<br/>entryRange()|
|
||||||
|
TIME|RedissonClient.<br/>getNodesGroup().<br/>getNode().time()<br/>getClusterNodesGroup().<br/>getNode().time()| - | - |
|
||||||
|
ZRANK|RScoredSortedSet.<br/>rank()<br/>rankAsync()|RScoredSortedSetReactive.<br/>rank()|RScoredSortedSetRx.<br/>rank()|
|
||||||
|
ZREM|RScoredSortedSet.<br/>remove()<br/>removeAll()<br/>removeAsync()<br/>removeAllAsync()|RScoredSortedSetReactive.<br/>remove()<br/>removeAll()|RScoredSortedSetRx.<br/>remove()<br/>removeAll()|
|
||||||
|
ZREMRANGEBYLEX|RLexSortedSet.<br/>removeRange()<br/>removeRangeHead()<br/>removeRangeTail()<br/>removeRangeAsync()<br/>removeRangeHeadAsync()<br/>removeRangeTailAsync()|RLexSortedSetReactive.<br/>removeRange()<br/>removeRangeHead()<br/>removeRangeTail()|RLexSortedSetRx.<br/>removeRange()<br/>removeRangeHead()<br/>removeRangeTail()|
|
||||||
|
ZREMRANGEBYSCORE|RScoredSortedSet.<br/>removeRangeByScore()<br/>removeRangeByScoreAsync()|RScoredSortedSetReactive.<br/>removeRangeByScore()|RScoredSortedSetRx.<br/>removeRangeByScore()|
|
||||||
|
ZREVRANGEBYSCORE|RScoredSortedSet.<br/>valueRangeReversed()<br/>entryRangeReversed()<br/>valueRangeReversedAsync()<br/>entryRangeReversedAsync()|RScoredSortedSetReactive.<br/>entryRangeReversed()<br/>valueRangeReversed()|RScoredSortedSetRx.<br/>entryRangeReversed()<br/>valueRangeReversed()|
|
||||||
|
ZREVRANK|RScoredSortedSet.<br/>revRank()<br/>revRankAsync()|RScoredSortedSetReactive.<br/>revRank()|RScoredSortedSetRx.<br/>revRank()|
|
||||||
|
ZSCORE|RScoredSortedSet.<br/>getScore()<br/>getScoreAsync()|RScoredSortedSetReactive.<br/>getScore()|RScoredSortedSetRx.<br/>getScore()|
|
||||||
|
XACK|RStream.<br/>ack()<br/>ackAsync()|RStreamReactive.<br/>ack()|RStreamRx.<br/>ack()|
|
||||||
|
XADD|RStream.<br/>add()<br/>addAsync()|RStreamReactive.<br/>add()|RStreamRx.<br/>add()|
|
||||||
|
XAUTOCLAIM|RStream.<br/>autoClaim()<br/>autoClaimAsync()|RStreamReactive.<br/>autoClaim()|RStreamRx.<br/>autoClaim()|
|
||||||
|
XCLAIM|RStream.<br/>claim()<br/>claimAsync()|RStreamReactive.<br/>claim()|RStreamRx.<br/>claim()|
|
||||||
|
XDEL|RStream.<br/>remove()<br/>removeAsync()|RStreamReactive.<br/>remove()|RStreamRx.<br/>remove()|
|
||||||
|
XGROUP|RStream.<br/>createGroup()<br/>removeGroup()<br/>updateGroup()<br/>createGroupAsync()<br/>removeGroupAsync()<br/>updateGroupAsync()|RStreamReactive.<br/>createGroup()<br/>removeGroup()<br/>updateGroup()|RStreamRx.<br/>createGroup()<br/>removeGroup()<br/>updateGroup()|
|
||||||
|
XINFO|RStream.<br/>getInfo()<br/>listGroups()<br/>listConsumers()<br/>getInfoAsync()<br/>listGroupsAsync()<br/>listConsumersAsync()|RStreamReactive.<br/>getInfo()<br/>listGroups()<br/>listConsumers()|RStreamRx.<br/>getInfo()<br/>listGroups()<br/>listConsumers()|
|
||||||
|
XLEN|RStream.<br/>size()<br/>sizeAsync()|RStreamReactive.<br/>size()|RStreamRx.<br/>size()|
|
||||||
|
XPENDING|RStream.<br/>listPending()<br/>listPendingAsync()|RStreamReactive.<br/>listPending()|RStreamRx.<br/>listPending()|
|
||||||
|
XRANGE|RStream.<br/>range()<br/>rangeAsync()|RStreamReactive.<br/>range()|RStreamRx.<br/>range()|
|
||||||
|
XREAD|RStream.<br/>read()<br/>readAsync()|RStreamReactive.<br/>read()|RStreamRx.<br/>read()|
|
||||||
|
XREADGROUP|RStream.<br/>readGroup()<br/>readGroupAsync()|RStreamReactive.<br/>readGroup()|RStreamRx.<br/>readGroup()|
|
||||||
|
XREVRANGE|RStream.<br/>rangeReversed()<br/>rangeReversedAsync()|RStreamReactive.<br/>rangeReversed()|RStreamRx.<br/>rangeReversed()|
|
||||||
|
XTRIM|RStream.<br/>trim()<br/>trimAsync()|RStreamReactive.<br/>trim()|RStreamRx.<br/>trim()|
|
||||||
File diff suppressed because it is too large
Load Diff
File diff suppressed because it is too large
Load Diff
@ -0,0 +1,140 @@
|
|||||||
|
**1. Object name**
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Name of Redisson object stored as a key in Redis or Valkey.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Example:
|
||||||
|
```java
|
||||||
|
RMap map = redisson.getMap("mymap");
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
map.getName(); // = mymap
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
**2. Common methods**
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Each Redisson object implements [RObject](https://static.javadoc.io/org.redisson/redisson/latest/org/redisson/api/RObject.html) and [RExpirable](https://static.javadoc.io/org.redisson/redisson/latest/org/redisson/api/RExpirable.html) interfaces.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Below are the most commonly used methods.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
```java
|
||||||
|
RObject object = ...
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
// Copy methods
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
object.copy("myNewCopy");
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
object.copyAndReplace("myNewCopy");
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
// Delete methods
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
object.delete();
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
object.unlink(); // works faster because it's executed on the database side in a different thread
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
// Rename methods
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
object.rename("myNewName");
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
object.renamenx("myNewName"); // rename only if the new key doesn't exist
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
// Dump and restore methods
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
byte[] state = object.dump();
|
||||||
|
object.restore(state);
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
**3. Listeners per Redisson object instance**
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Listeners can be attached per Redisson object instance. Base listeners are `ExpiredObjectListener` and `DeletedObjectListener`. Redisson objects may support specific listeners. Like [RScoredSortedSet](https://www.javadoc.io/doc/org.redisson/redisson/latest/org/redisson/api/RScoredSortedSet.html#addListener(org.redisson.api.ObjectListener)), [RStream](https://www.javadoc.io/doc/org.redisson/redisson/latest/org/redisson/api/RStream.html#addListener(org.redisson.api.ObjectListener)) and others.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
```java
|
||||||
|
RObject object = ...
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
// listening to expired events
|
||||||
|
object.addListener((ExpiredObjectListener) name -> {
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
//...
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
});
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
// listening to delete events
|
||||||
|
object.addListener((DeletedObjectListener) name -> {
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
//...
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
});
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
**4. Operations over all Redisson object instances**
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Operations over all objects are exposed by [RKeys](https://static.javadoc.io/org.redisson/redisson/latest/org/redisson/api/RKeys.html) interface.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Usage example:
|
||||||
|
```java
|
||||||
|
RKeys keys = redisson.getKeys();
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
// Keys iteration
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Iterable<String> allKeys = keys.getKeys();
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Iterable<String> foundedKeys = keys.getKeys(KeysScanOptions.defaults().pattern("key*"));
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
String randomKey = keys.randomKey();
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
long keysAmount = keys.count();
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
long keysAmount = keys.countExists("obj1", "obj2", "obj3"); // amount of existing keys
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
// Delete methods
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
long delKeys = keys.delete("obj1", "obj2", "obj3");
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
long delKeys = keys.deleteByPattern("test?");
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
long delKeys = keys.unlink("obj1", "obj2", "obj3"); // works faster because it's executed on the database side in a different thread
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
long delKeys = keys.unlinkByPattern("test?"); // works faster because it's executed on the database side in a different thread
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
keys.flushall(); // Delete all keys of all existing databases
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
keys.flushallParallel(); // Delete all keys of all existing databases in background without blocking server
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
keys.flushdb(); // Delete all keys of currently selected database
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
**5. Global listeners**
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Global listeners are attached to all Redisson object instances.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Available listeners:
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
- [TrackingListener](https://www.javadoc.io/doc/org.redisson/redisson/latest/org/redisson/api/listener/TrackingListener.html),
|
||||||
|
- [SetObjectListener](https://www.javadoc.io/doc/org.redisson/redisson/latest/org/redisson/api/listener/SetObjectListener.html),
|
||||||
|
- [NewObjectListener](https://www.javadoc.io/doc/org.redisson/redisson/latest/org/redisson/api/listener/NewObjectListener.html),
|
||||||
|
- [ExpiredObjectListener](https://www.javadoc.io/doc/org.redisson/redisson/latest/org/redisson/api/ExpiredObjectListener.html),
|
||||||
|
- [DeletedObjectListener](https://www.javadoc.io/doc/org.redisson/redisson/latest/org/redisson/api/DeletedObjectListener.html),
|
||||||
|
- [FlushListener](https://www.javadoc.io/doc/org.redisson/redisson/latest/org/redisson/api/listener/FlushListener.html)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Usage example:
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
```java
|
||||||
|
RKeys keys = redisson.getKeys();
|
||||||
|
int id = keys.addListener((NewObjectListener) name -> {
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
//...
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
});
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
int id = keys.addListener((DeletedObjectListener) name -> {
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
//...
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
});
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
int id = keys.addListener((FlushListener) address -> {
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
//...
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
});
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
keys.removeListener(id);
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
@ -0,0 +1,167 @@
|
|||||||
|
## Id generator
|
||||||
|
Redis or Valkey based Java Id generator [RIdGenerator](https://static.javadoc.io/org.redisson/redisson/latest/org/redisson/api/RIdGenerator.html) generates unique numbers but not monotonically increased. At first request, batch of id numbers is allocated and cached on Java side till it's exhausted. This approach allows to generate ids faster than [RAtomicLong](#atomiclong).
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Default allocation size is 5000.
|
||||||
|
Default start value is 0.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Code example:
|
||||||
|
```java
|
||||||
|
RIdGenerator generator = redisson.getIdGenerator("generator");
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
// Initialize with start value = 12 and allocation size = 20000
|
||||||
|
generator.tryInit(12, 20000);
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
long id = generator.nextId();
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Code example of **[Async](https://static.javadoc.io/org.redisson/redisson/latest/org/redisson/api/RIdGeneratorAsync.html) interface** usage:
|
||||||
|
```java
|
||||||
|
RIdGenerator generator = redisson.getIdGenerator("generator");
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
// Initialize with start value = 12 and allocation size = 20000
|
||||||
|
RFuture<Boolean> initFuture = generator.tryInitAsync(12, 20000);
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
RFuture<Long> idFuture = generator.nextIdAsync();
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Code example of **[Reactive](https://static.javadoc.io/org.redisson/redisson/latest/org/redisson/api/RIdGeneratorReactive.html) interface** usage:
|
||||||
|
```java
|
||||||
|
RedissonReactiveClient redisson = redissonClient.reactive();
|
||||||
|
RIdGenerator generator = redisson.getIdGenerator("generator");
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
// Initialize with start value = 12 and allocation size = 20000
|
||||||
|
Mono<Boolean> initMono = generator.tryInit(12, 20000);
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Mono<Long> idMono = generator.nextId();
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Code example of **[RxJava3](https://static.javadoc.io/org.redisson/redisson/latest/org/redisson/api/RIdGeneratorRx.html) interface** usage:
|
||||||
|
```java
|
||||||
|
RedissonRxClient redisson = redissonClient.rxJava();
|
||||||
|
RIdGenerator generator = redisson.getIdGenerator("generator");
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
// Initialize with start value = 12 and allocation size = 20000
|
||||||
|
Single<Boolean> initRx = generator.tryInit(12, 20000);
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Single<Long> idRx = generator.nextId();
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
## AtomicLong
|
||||||
|
Java implementation of Redis or Valkey based [AtomicLong](https://static.javadoc.io/org.redisson/redisson/latest/org/redisson/api/RAtomicLong.html) object provides API similar to [java.util.concurrent.atomic.AtomicLong](https://docs.oracle.com/javase/8/docs/api/java/util/concurrent/atomic/AtomicLong.html) object.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Code example:
|
||||||
|
```java
|
||||||
|
RAtomicLong atomicLong = redisson.getAtomicLong("myAtomicLong");
|
||||||
|
atomicLong.set(3);
|
||||||
|
atomicLong.incrementAndGet();
|
||||||
|
atomicLong.get();
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Code example of **[Async](https://static.javadoc.io/org.redisson/redisson/latest/org/redisson/api/RAtomicLongAsync.html) interface** usage:
|
||||||
|
```java
|
||||||
|
RAtomicLongAsync atomicLong = redisson.getAtomicLong("myAtomicLong");
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
RFuture<Void> setFuture = atomicLong.setAsync(3);
|
||||||
|
RFuture<Long> igFuture = atomicLong.incrementAndGetAsync();
|
||||||
|
RFuture<Long> getFuture = atomicLong.getAsync();
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Code example of **[Reactive](https://static.javadoc.io/org.redisson/redisson/latest/org/redisson/api/RAtomicLongReactive.html) interface** usage:
|
||||||
|
```java
|
||||||
|
RedissonReactiveClient redisson = redissonClient.reactive();
|
||||||
|
RAtomicLongReactive atomicLong = redisson.getAtomicLong("myAtomicLong");
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Mono<Void> setMono = atomicLong.set(3);
|
||||||
|
Mono<Long> igMono = atomicLong.incrementAndGet();
|
||||||
|
RFuture<Long> getMono = atomicLong.getAsync();
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Code example of **[RxJava3](https://static.javadoc.io/org.redisson/redisson/latest/org/redisson/api/RAtomicLongRx.html) interface** usage:
|
||||||
|
```java
|
||||||
|
RedissonRxClient redisson = redissonClient.rxJava();
|
||||||
|
RAtomicLongRx atomicLong = redisson.getAtomicLong("myAtomicLong");
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Completable setMono = atomicLong.set(3);
|
||||||
|
Single<Long> igMono = atomicLong.incrementAndGet();
|
||||||
|
Single<Long> getMono = atomicLong.getAsync();
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
## AtomicDouble
|
||||||
|
Java implementation of Redis or Valkey based [AtomicDouble](https://static.javadoc.io/org.redisson/redisson/latest/org/redisson/api/RAtomicDouble.html) object.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Code example:
|
||||||
|
```java
|
||||||
|
RAtomicDouble atomicDouble = redisson.getAtomicDouble("myAtomicDouble");
|
||||||
|
atomicDouble.set(2.81);
|
||||||
|
atomicDouble.addAndGet(4.11);
|
||||||
|
atomicDouble.get();
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Code example of **[Async](https://static.javadoc.io/org.redisson/redisson/latest/org/redisson/api/RAtomicDoubleAsync.html) interface** usage:
|
||||||
|
```java
|
||||||
|
RAtomicDoubleAsync atomicDouble = redisson.getAtomicDouble("myAtomicDouble");
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
RFuture<Void> setFuture = atomicDouble.setAsync(2.81);
|
||||||
|
RFuture<Double> agFuture = atomicDouble.addAndGetAsync(4.11);
|
||||||
|
RFuture<Double> getFuture = atomicDouble.getAsync();
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Code example of **[Reactive](https://static.javadoc.io/org.redisson/redisson/latest/org/redisson/api/RAtomicDoubleReactive.html) interface** usage:
|
||||||
|
```java
|
||||||
|
RedissonReactiveClient redisson = redissonClient.reactive();
|
||||||
|
RAtomicDoubleReactive atomicDouble = redisson.getAtomicDouble("myAtomicDouble");
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Mono<Void> setMono = atomicDouble.set(2.81);
|
||||||
|
Mono<Double> agMono = atomicDouble.addAndGet(4.11);
|
||||||
|
Mono<Double> getMono = atomicDouble.get();
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Code example of **[RxJava3](https://static.javadoc.io/org.redisson/redisson/latest/org/redisson/api/RAtomicDoubleRx.html) interface** usage:
|
||||||
|
```java
|
||||||
|
RedissonRxClient redisson = redissonClient.rxJava();
|
||||||
|
RAtomicDoubleRx atomicDouble = redisson.getAtomicDouble("myAtomicDouble");
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Completable setMono = atomicDouble.set(2.81);
|
||||||
|
Single<Double> igMono = atomicDouble.addAndGet(4.11);
|
||||||
|
Single<Double> getMono = atomicDouble.get();
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
## LongAdder
|
||||||
|
Java implementation of Redis or Valkey based [LongAdder](https://static.javadoc.io/org.redisson/redisson/latest/org/redisson/api/RLongAdder.html) object provides API similar to [java.util.concurrent.atomic.LongAdder](https://docs.oracle.com/javase/8/docs/api/java/util/concurrent/atomic/LongAdder.html) object.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
It maintains internal LongAdder object on client side and provides superior performance for both increment and decrement operations. Up to __12000x__ faster than similar `AtomicLong` object. Suitable for distributed metric objects.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Code example:
|
||||||
|
```java
|
||||||
|
RLongAdder atomicLong = redisson.getLongAdder("myLongAdder");
|
||||||
|
atomicLong.add(12);
|
||||||
|
atomicLong.increment();
|
||||||
|
atomicLong.decrement();
|
||||||
|
atomicLong.sum();
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Object should be destroyed if it's not used anymore, but it's not necessary to call destroy method if Redisson goes shutdown.
|
||||||
|
```java
|
||||||
|
RLongAdder atomicLong = ...
|
||||||
|
atomicLong.destroy();
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
## DoubleAdder
|
||||||
|
Java implementation of Redis or Valkey based [DoubleAdder](https://static.javadoc.io/org.redisson/redisson/latest/org/redisson/api/RDoubleAdder.html) object provides API similar to [java.util.concurrent.atomic.DoubleAdder](https://docs.oracle.com/javase/8/docs/api/java/util/concurrent/atomic/DoubleAdder.html) object.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
It maintains internal DoubleAdder object on client side and provides superior performance for both increment and decrement operations. Up to __12000x__ faster than similar `AtomicDouble` object. Suitable for distributed metric objects.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Code example:
|
||||||
|
```java
|
||||||
|
RLongDouble atomicDouble = redisson.getLongDouble("myLongDouble");
|
||||||
|
atomicDouble.add(12);
|
||||||
|
atomicDouble.increment();
|
||||||
|
atomicDouble.decrement();
|
||||||
|
atomicDouble.sum();
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Object should be destroyed if it's not used anymore, but it's not necessary to call destroy method if Redisson goes shutdown.
|
||||||
|
```java
|
||||||
|
RLongDouble atomicDouble = ...
|
||||||
|
atomicDouble.destroy();
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
@ -0,0 +1,22 @@
|
|||||||
|
All Redisson Java objects are Redis or Valkey cluster compatible, but their state isn't scaled/partitioned to multiple master nodes in cluster. [Redisson PRO](https://redisson.pro/) offers data partitioning for some of them. This feature offers several advantages:
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
1. State of single Redisson object evenly distributed across master nodes instead of single master node. This allows to avoid Redis or Valkey OutOfMemory problem.
|
||||||
|
2. Scaling read/write operations to all master nodes.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Redisson splits data to **231 partitions by default**. Minimal number of partition is **3**. Partitions are uniformly distributed across all cluster nodes. This means that each node contains nearly equal amount of partitions. For default partitions amount (231) and 4 master nodes in cluster, each node contains nearly 57 data partitions. 46 data partitions per node for 5 master nodes cluster and so on. This feature achieved thanks to special slot distribution algorithm used in Redisson.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Data partitioning supported for [Set](collections.md/#set), [Map](collections.md/#map), [BitSet](objects.md/#bitset), [Bloom filter](objects.md/#bloom-filter), [Spring Cache](../integration-with-spring.md/#spring-cache), [Hibernate Cache](../cache-api-implementations.md/#hibernate-cache), [JCache](../cache-api-implementations.md/#jcache-api-jsr-107), [Quarkus Cache](../cache-api-implementations.md/#quarkus-cache) and [Micronaut Cache](../cache-api-implementations.md/#micronaut-cache) structures.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
**Joined Redis deployments**
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Multiple Redis deployments could be joined and used as a single partitioned (sharded) Redis deployment.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
```java
|
||||||
|
RedissonClient redisson1 = ...;
|
||||||
|
RedissonClient redisson2 = ...;
|
||||||
|
RedissonClient redisson3 = ...;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
RedissonClient redisson = ShardedRedisson.create(redisson1, redisson2, redisson3);
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
_This feature available only in [Redisson PRO](https://redisson.pro) edition._
|
||||||
@ -0,0 +1,23 @@
|
|||||||
|
Data serialization is extensively used by Redisson to marshall and unmarshall bytes received or sent over network link with Redis or Valkey server. Many popular codecs are available for usage:
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Codec class name| Description
|
||||||
|
--- | ---
|
||||||
|
`org.redisson.codec.Kryo5Codec`| [Kryo 5](https://github.com/EsotericSoftware/kryo) binary codec<br/>(**Android** compatible) __Default codec__
|
||||||
|
`org.redisson.codec.KryoCodec`| [Kryo 4](https://github.com/EsotericSoftware/kryo) binary codec
|
||||||
|
`org.redisson.codec.JsonJacksonCodec`| [Jackson JSON](https://github.com/FasterXML/jackson) codec.<br/>Stores type information in `@class` field<br/>(**Android** compatible)
|
||||||
|
`org.redisson.codec.TypedJsonJacksonCodec`| Jackson JSON codec which doesn't store type id (`@class` field)
|
||||||
|
`org.redisson.codec.AvroJacksonCodec`| [Avro](http://avro.apache.org/) binary json codec
|
||||||
|
`org.redisson.codec.ProtobufCodec`| [Protobuf](https://github.com/protocolbuffers/protobuf) codec
|
||||||
|
`org.redisson.codec.FuryCodec`| [Apache Fury](https://github.com/apache/fury) codec
|
||||||
|
`org.redisson.codec.SmileJacksonCodec`| [Smile](http://wiki.fasterxml.com/SmileFormatSpec) binary json codec
|
||||||
|
`org.redisson.codec.CborJacksonCodec`| [CBOR](http://cbor.io/) binary json codec
|
||||||
|
`org.redisson.codec.MsgPackJacksonCodec`| [MsgPack](http://msgpack.org/) binary json codec
|
||||||
|
`org.redisson.codec.IonJacksonCodec`| [Amazon Ion](https://amzn.github.io/ion-docs/) codec
|
||||||
|
`org.redisson.codec.SerializationCodec`| JDK Serialization binary codec<br/>(**Android** compatible)
|
||||||
|
`org.redisson.codec.LZ4Codec`| [LZ4](https://github.com/jpountz/lz4-java) compression codec.<br/> Uses `Kryo5Codec` for serialization by default
|
||||||
|
`org.redisson.codec.LZ4CodecV2`| [LZ4 Apache Commons](https://github.com/apache/commons-compress) compression codec.<br/> Uses `Kryo5Codec` for serialization by default
|
||||||
|
`org.redisson.codec.SnappyCodecV2` | Snappy compression codec based on [snappy-java](https://github.com/xerial/snappy-java) project.<br/> Uses `Kryo5Codec` for serialization by default
|
||||||
|
`org.redisson.client.codec.StringCodec`| String codec
|
||||||
|
`org.redisson.client.codec.LongCodec`| Long codec
|
||||||
|
`org.redisson.client.codec.ByteArrayCodec` | Byte array codec
|
||||||
|
`org.redisson.codec.CompositeCodec` | Allows to mix different codecs as one
|
||||||
@ -0,0 +1,946 @@
|
|||||||
|
## Lock
|
||||||
|
Redis or Valkey based distributed reentrant [Lock](https://static.javadoc.io/org.redisson/redisson/latest/org/redisson/api/RLock.html) object for Java and implements [Lock](https://docs.oracle.com/javase/8/docs/api/java/util/concurrent/locks/Lock.html) interface. Uses pub/sub channel to notify other threads across all Redisson instances waiting to acquire a lock.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
If Redisson instance which acquired lock crashes then such lock could hang forever in acquired state. To avoid this Redisson maintains lock watchdog, it prolongs lock expiration while lock holder Redisson instance is alive. By default lock watchdog timeout is 30 seconds and can be changed through [Config.lockWatchdogTimeout](../configuration.md) setting.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
`leaseTime` parameter during lock acquisition can be defined. After specified time interval locked lock will be released automatically.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
`RLock` object behaves according to the Java Lock specification. It means only lock owner thread can unlock it otherwise `IllegalMonitorStateException` would be thrown. Otherwise consider to use [RSemaphore](#semaphore) object.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Code example:
|
||||||
|
```java
|
||||||
|
RLock lock = redisson.getLock("myLock");
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
// traditional lock method
|
||||||
|
lock.lock();
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
// or acquire lock and automatically unlock it after 10 seconds
|
||||||
|
lock.lock(10, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
// or wait for lock aquisition up to 100 seconds
|
||||||
|
// and automatically unlock it after 10 seconds
|
||||||
|
boolean res = lock.tryLock(100, 10, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
|
||||||
|
if (res) {
|
||||||
|
try {
|
||||||
|
...
|
||||||
|
} finally {
|
||||||
|
lock.unlock();
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Code example of **[Async](https://static.javadoc.io/org.redisson/redisson/latest/org/redisson/api/RLockAsync.html) interface** usage:
|
||||||
|
```java
|
||||||
|
RLock lock = redisson.getLock("myLock");
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
long threadId = Thread.currentThread().getId();
|
||||||
|
RFuture<Void> lockFuture = lock.lockAsync(threadId);
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
// or acquire lock and automatically unlock it after 10 seconds
|
||||||
|
RFuture<Void> lockFuture = lock.lockAsync(10, TimeUnit.SECONDS, threadId);
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
// or wait for lock aquisition up to 100 seconds
|
||||||
|
// and automatically unlock it after 10 seconds
|
||||||
|
RFuture<Boolean> lockFuture = lock.tryLockAsync(100, 10, TimeUnit.SECONDS, threadId);
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
lockFuture.whenComplete((res, exception) -> {
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
// ...
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
lock.unlockAsync(threadId);
|
||||||
|
});
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Code example of **[Reactive](https://static.javadoc.io/org.redisson/redisson/latest/org/redisson/api/RLockReactive.html) interface** usage:
|
||||||
|
```java
|
||||||
|
RedissonReactiveClient redisson = redissonClient.reactive();
|
||||||
|
RLockReactive lock = redisson.getLock("myLock");
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
long threadId = Thread.currentThread().getId();
|
||||||
|
Mono<Void> lockMono = lock.lock(threadId);
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
// or acquire lock and automatically unlock it after 10 seconds
|
||||||
|
Mono<Void> lockMono = lock.lock(10, TimeUnit.SECONDS, threadId);
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
// or wait for lock aquisition up to 100 seconds
|
||||||
|
// and automatically unlock it after 10 seconds
|
||||||
|
Mono<Boolean> lockMono = lock.tryLock(100, 10, TimeUnit.SECONDS, threadId);
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
lockMono.doOnSuccess(res -> {
|
||||||
|
// ...
|
||||||
|
})
|
||||||
|
.doFinally(r -> lock.unlock(threadId).subscribe())
|
||||||
|
.subscribe();
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Code example of **[RxJava3](https://static.javadoc.io/org.redisson/redisson/latest/org/redisson/api/RLockRx.html) interface** usage:
|
||||||
|
```java
|
||||||
|
RedissonRxClient redisson = redissonClient.rxJava();
|
||||||
|
RLockRx lock = redisson.getLock("myLock");
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
long threadId = Thread.currentThread().getId();
|
||||||
|
Completable lockRes = lock.lock(threadId);
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
// or acquire lock and automatically unlock it after 10 seconds
|
||||||
|
Completable lockRes = lock.lock(10, TimeUnit.SECONDS, threadId);
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
// or wait for lock aquisition up to 100 seconds
|
||||||
|
// and automatically unlock it after 10 seconds
|
||||||
|
Single<Boolean> lockRes = lock.tryLock(100, 10, TimeUnit.SECONDS, threadId);
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
lockRes.doOnSuccess(res -> {
|
||||||
|
// ...
|
||||||
|
})
|
||||||
|
.doFinally(() -> lock.unlock(threadId).subscribe())
|
||||||
|
.subscribe();
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
## Fair Lock
|
||||||
|
Redis or Valkey based distributed reentrant fair [Lock](https://static.javadoc.io/org.redisson/redisson/latest/org/redisson/api/RLock.html) object for Java implements [Lock](https://docs.oracle.com/javase/8/docs/api/java/util/concurrent/locks/Lock.html) interface.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Fair lock guarantees that threads will acquire it in is same order they requested it. All waiting threads are queued and if some thread has died then Redisson waits its return for 5 seconds. For example, if 5 threads are died for some reason then delay will be 25 seconds.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
If Redisson instance which acquired lock crashes then such lock could hang forever in acquired state. To avoid this Redisson maintains lock watchdog, it prolongs lock expiration while lock holder Redisson instance is alive. By default lock watchdog timeout is 30 seconds and can be changed through [Config.lockWatchdogTimeout](../configuration.md) setting.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
`leaseTime` parameter during lock acquisition can be defined. After specified time interval locked lock will be released automatically.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
`RLock` object behaves according to the Java Lock specification. It means only lock owner thread can unlock it otherwise `IllegalMonitorStateException` would be thrown. Otherwise consider to use [RSemaphore](#semaphore) object.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Code example:
|
||||||
|
```java
|
||||||
|
RLock lock = redisson.getFairLock("myLock");
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
// traditional lock method
|
||||||
|
lock.lock();
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
// or acquire lock and automatically unlock it after 10 seconds
|
||||||
|
lock.lock(10, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
// or wait for lock aquisition up to 100 seconds
|
||||||
|
// and automatically unlock it after 10 seconds
|
||||||
|
boolean res = lock.tryLock(100, 10, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
|
||||||
|
if (res) {
|
||||||
|
try {
|
||||||
|
...
|
||||||
|
} finally {
|
||||||
|
lock.unlock();
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Code example of **[Async](https://static.javadoc.io/org.redisson/redisson/latest/org/redisson/api/RLockAsync.html) interface** usage:
|
||||||
|
```java
|
||||||
|
RLock lock = redisson.getFairLock("myLock");
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
RFuture<Void> lockFuture = lock.lockAsync();
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
// or acquire lock and automatically unlock it after 10 seconds
|
||||||
|
RFuture<Void> lockFuture = lock.lockAsync(10, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
// or wait for lock aquisition up to 100 seconds
|
||||||
|
// and automatically unlock it after 10 seconds
|
||||||
|
RFuture<Boolean> lockFuture = lock.tryLockAsync(100, 10, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
lockFuture.whenComplete((res, exception) -> {
|
||||||
|
// ...
|
||||||
|
lock.unlockAsync();
|
||||||
|
});
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Code example of **[Reactive](https://static.javadoc.io/org.redisson/redisson/latest/org/redisson/api/RLockReactive.html) interface** usage:
|
||||||
|
```java
|
||||||
|
RedissonReactiveClient redisson = redissonClient.reactive();
|
||||||
|
RLockReactive lock = redisson.getFairLock("myLock");
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
long threadId = Thread.currentThread().getId();
|
||||||
|
Mono<Void> lockMono = lock.lock(threadId);
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
// or acquire lock and automatically unlock it after 10 seconds
|
||||||
|
Mono<Void> lockMono = lock.lock(10, TimeUnit.SECONDS, threadId);
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
// or wait for lock aquisition up to 100 seconds
|
||||||
|
// and automatically unlock it after 10 seconds
|
||||||
|
Mono<Boolean> lockMono = lock.tryLock(100, 10, TimeUnit.SECONDS, threadId);
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
lockMono.doOnSuccess(res -> {
|
||||||
|
// ...
|
||||||
|
})
|
||||||
|
.doFinally(r -> lock.unlock(threadId).subscribe())
|
||||||
|
.subscribe();
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Code example of **[RxJava3](https://static.javadoc.io/org.redisson/redisson/latest/org/redisson/api/RLockRx.html) interface** usage:
|
||||||
|
```java
|
||||||
|
RedissonRxClient redisson = redissonClient.rxJava();
|
||||||
|
RLockRx lock = redisson.getFairLock("myLock");
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
long threadId = Thread.currentThread().getId();
|
||||||
|
Completable lockRes = lock.lock(threadId);
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
// or acquire lock and automatically unlock it after 10 seconds
|
||||||
|
Completable lockRes = lock.lock(10, TimeUnit.SECONDS, threadId);
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
// or wait for lock aquisition up to 100 seconds
|
||||||
|
// and automatically unlock it after 10 seconds
|
||||||
|
Single<Boolean> lockRes = lock.tryLock(100, 10, TimeUnit.SECONDS, threadId);
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
lockRes.doOnSuccess(res -> {
|
||||||
|
// ...
|
||||||
|
})
|
||||||
|
.doFinally(() -> lock.unlock(threadId).subscribe())
|
||||||
|
.subscribe();
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
## MultiLock
|
||||||
|
Redis or Valkey based distributed `MultiLock` object allows to group [Lock](https://static.javadoc.io/org.redisson/redisson/latest/org/redisson/api/RLock.html) objects and handle them as a single lock. Each `RLock` object may belong to different Redisson instances.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
If Redisson instance which acquired `MultiLock` crashes then such `MultiLock` could hang forever in acquired state. To avoid this Redisson maintains lock watchdog, it prolongs lock expiration while lock holder Redisson instance is alive. By default lock watchdog timeout is 30 seconds and can be changed through [Config.lockWatchdogTimeout](../configuration.md) setting.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
`leaseTime` parameter during lock acquisition can be defined. After specified time interval locked lock will be released automatically.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
`MultiLock` object behaves according to the Java Lock specification. It means only lock owner thread can unlock it otherwise `IllegalMonitorStateException` would be thrown. Otherwise consider to use [RSemaphore](#semaphore) object.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Code example:
|
||||||
|
```java
|
||||||
|
RLock lock1 = redisson1.getLock("lock1");
|
||||||
|
RLock lock2 = redisson2.getLock("lock2");
|
||||||
|
RLock lock3 = redisson3.getLock("lock3");
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
RLock multiLock = anyRedisson.getMultiLock(lock1, lock2, lock3);
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
// traditional lock method
|
||||||
|
multiLock.lock();
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
// or acquire lock and automatically unlock it after 10 seconds
|
||||||
|
multiLock.lock(10, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
// or wait for lock aquisition up to 100 seconds
|
||||||
|
// and automatically unlock it after 10 seconds
|
||||||
|
boolean res = multiLock.tryLock(100, 10, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
|
||||||
|
if (res) {
|
||||||
|
try {
|
||||||
|
...
|
||||||
|
} finally {
|
||||||
|
multiLock.unlock();
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Code example of **[Async](https://static.javadoc.io/org.redisson/redisson/latest/org/redisson/api/RLockAsync.html) interface** usage:
|
||||||
|
```java
|
||||||
|
RLock lock1 = redisson1.getLock("lock1");
|
||||||
|
RLock lock2 = redisson2.getLock("lock2");
|
||||||
|
RLock lock3 = redisson3.getLock("lock3");
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
RLock multiLock = anyRedisson.getMultiLock(lock1, lock2, lock3);
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
long threadId = Thread.currentThread().getId();
|
||||||
|
RFuture<Void> lockFuture = multiLock.lockAsync(threadId);
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
// or acquire lock and automatically unlock it after 10 seconds
|
||||||
|
RFuture<Void> lockFuture = multiLock.lockAsync(10, TimeUnit.SECONDS, threadId);
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
// or wait for lock aquisition up to 100 seconds
|
||||||
|
// and automatically unlock it after 10 seconds
|
||||||
|
RFuture<Boolean> lockFuture = multiLock.tryLockAsync(100, 10, TimeUnit.SECONDS, threadId);
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
lockFuture.whenComplete((res, exception) -> {
|
||||||
|
// ...
|
||||||
|
multiLock.unlockAsync(threadId);
|
||||||
|
});
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Code example of **[Reactive](https://static.javadoc.io/org.redisson/redisson/latest/org/redisson/api/RLockReactive.html) interface** usage:
|
||||||
|
```java
|
||||||
|
RedissonReactiveClient anyRedisson = redissonClient.reactive();
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
RLockReactive lock1 = redisson1.getLock("lock1");
|
||||||
|
RLockReactive lock2 = redisson2.getLock("lock2");
|
||||||
|
RLockReactive lock3 = redisson3.getLock("lock3");
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
RLockReactive multiLock = anyRedisson.getMultiLock(lock1, lock2, lock3);
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
long threadId = Thread.currentThread().getId();
|
||||||
|
Mono<Void> lockMono = multiLock.lock(threadId);
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
// or acquire lock and automatically unlock it after 10 seconds
|
||||||
|
Mono<Void> lockMono = multiLock.lock(10, TimeUnit.SECONDS, threadId);
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
// or wait for lock aquisition up to 100 seconds
|
||||||
|
// and automatically unlock it after 10 seconds
|
||||||
|
Mono<Boolean> lockMono = multiLock.tryLock(100, 10, TimeUnit.SECONDS, threadId);
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
lockMono.doOnSuccess(res -> {
|
||||||
|
// ...
|
||||||
|
})
|
||||||
|
.doFinally(r -> multiLock.unlock(threadId).subscribe())
|
||||||
|
.subscribe();
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Code example of **[RxJava3](https://static.javadoc.io/org.redisson/redisson/latest/org/redisson/api/RLockRx.html) interface** usage:
|
||||||
|
```java
|
||||||
|
RedissonRxClient anyRedisson = redissonClient.rxJava();
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
RLockRx lock1 = redisson1.getLock("lock1");
|
||||||
|
RLockRx lock2 = redisson2.getLock("lock2");
|
||||||
|
RLockRx lock3 = redisson3.getLock("lock3");
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
RLockRx multiLock = anyRedisson.getMultiLock(lock1, lock2, lock3);
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
long threadId = Thread.currentThread().getId();
|
||||||
|
Completable lockRes = multiLock.lock(threadId);
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
// or acquire lock and automatically unlock it after 10 seconds
|
||||||
|
Completable lockRes = multiLock.lock(10, TimeUnit.SECONDS, threadId);
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
// or wait for lock aquisition up to 100 seconds
|
||||||
|
// and automatically unlock it after 10 seconds
|
||||||
|
Single<Boolean> lockRes = multiLock.tryLock(100, 10, TimeUnit.SECONDS, threadId);
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
lockRes.doOnSuccess(res -> {
|
||||||
|
// ...
|
||||||
|
})
|
||||||
|
.doFinally(() -> multiLock.unlock(threadId).subscribe())
|
||||||
|
.subscribe();
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
## RedLock
|
||||||
|
_This object is deprecated. Use [RLock](#81-lock) or [RFencedLock](#810-fenced-lock) instead._
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
## ReadWriteLock
|
||||||
|
Redis or Valkey based distributed reentrant [ReadWriteLock](https://static.javadoc.io/org.redisson/redisson/latest/org/redisson/api/RReadWriteLock.html) object for Java implements [ReadWriteLock](https://docs.oracle.com/javase/8/docs/api/java/util/concurrent/locks/ReadWriteLock.html) interface. Both Read and Write locks implement [RLock](#lock) interface.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Multiple ReadLock owners and only one WriteLock owner are allowed.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
If Redisson instance which acquired lock crashes then such lock could hang forever in acquired state. To avoid this Redisson maintains lock watchdog, it prolongs lock expiration while lock holder Redisson instance is alive. By default lock watchdog timeout is 30 seconds and can be changed through [Config.lockWatchdogTimeout](../configuration.md) setting.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Also Redisson allow to specify `leaseTime` parameter during lock acquisition. After specified time interval locked lock will be released automatically.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
`RLock` object behaves according to the Java Lock specification. It means only lock owner thread can unlock it otherwise `IllegalMonitorStateException` would be thrown. Otherwise consider to use [RSemaphore](#semaphore) object.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Code example:
|
||||||
|
```java
|
||||||
|
RReadWriteLock rwlock = redisson.getReadWriteLock("myLock");
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
RLock lock = rwlock.readLock();
|
||||||
|
// or
|
||||||
|
RLock lock = rwlock.writeLock();
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
// traditional lock method
|
||||||
|
lock.lock();
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
// or acquire lock and automatically unlock it after 10 seconds
|
||||||
|
lock.lock(10, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
// or wait for lock aquisition up to 100 seconds
|
||||||
|
// and automatically unlock it after 10 seconds
|
||||||
|
boolean res = lock.tryLock(100, 10, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
|
||||||
|
if (res) {
|
||||||
|
try {
|
||||||
|
...
|
||||||
|
} finally {
|
||||||
|
lock.unlock();
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Code example of **[Async](https://static.javadoc.io/org.redisson/redisson/latest/org/redisson/api/RLockAsync.html) interface** usage:
|
||||||
|
```java
|
||||||
|
RReadWriteLock rwlock = redisson.getReadWriteLock("myLock");
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
long threadId = Thread.currentThread().getId();
|
||||||
|
RLock lock = rwlock.readLock();
|
||||||
|
// or
|
||||||
|
RLock lock = rwlock.writeLock();
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
RFuture<Void> lockFuture = lock.lockAsync(threadId);
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
// or acquire lock and automatically unlock it after 10 seconds
|
||||||
|
RFuture<Void> lockFuture = lock.lockAsync(10, TimeUnit.SECONDS, threadId);
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
// or wait for lock aquisition up to 100 seconds
|
||||||
|
// and automatically unlock it after 10 seconds
|
||||||
|
RFuture<Boolean> lockFuture = lock.tryLockAsync(100, 10, TimeUnit.SECONDS, threadId);
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
lockFuture.whenComplete((res, exception) -> {
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
// ...
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
lock.unlockAsync(threadId);
|
||||||
|
});
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Code example of **[Reactive](https://static.javadoc.io/org.redisson/redisson/latest/org/redisson/api/RLockReactive.html) interface** usage:
|
||||||
|
```java
|
||||||
|
RedissonReactiveClient redisson = redissonClient.reactive();
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
RReadWriteLockReactive rwlock = redisson.getReadWriteLock("myLock");
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
RLockReactive lock = rwlock.readLock();
|
||||||
|
// or
|
||||||
|
RLockReactive lock = rwlock.writeLock();
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
long threadId = Thread.currentThread().getId();
|
||||||
|
Mono<Void> lockMono = lock.lock(threadId);
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
// or acquire lock and automatically unlock it after 10 seconds
|
||||||
|
Mono<Void> lockMono = lock.lock(10, TimeUnit.SECONDS, threadId);
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
// or wait for lock aquisition up to 100 seconds
|
||||||
|
// and automatically unlock it after 10 seconds
|
||||||
|
Mono<Boolean> lockMono = lock.tryLock(100, 10, TimeUnit.SECONDS, threadId);
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
lockMono.doOnSuccess(res -> {
|
||||||
|
// ...
|
||||||
|
})
|
||||||
|
.doFinally(r -> lock.unlock(threadId).subscribe())
|
||||||
|
.subscribe();
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Code example of **[RxJava3](https://static.javadoc.io/org.redisson/redisson/latest/org/redisson/api/RLockRx.html) interface** usage:
|
||||||
|
```java
|
||||||
|
RedissonRxClient redisson = redissonClient.rxJava();
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
RReadWriteLockRx rwlock = redisson.getReadWriteLock("myLock");
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
RLockRx lock = rwlock.readLock();
|
||||||
|
// or
|
||||||
|
RLockRx lock = rwlock.writeLock();
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
long threadId = Thread.currentThread().getId();
|
||||||
|
Completable lockRes = lock.lock(threadId);
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
// or acquire lock and automatically unlock it after 10 seconds
|
||||||
|
Completable lockRes = lock.lock(10, TimeUnit.SECONDS, threadId);
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
// or wait for lock aquisition up to 100 seconds
|
||||||
|
// and automatically unlock it after 10 seconds
|
||||||
|
Single<Boolean> lockRes = lock.tryLock(100, 10, TimeUnit.SECONDS, threadId);
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
lockRes.doOnSuccess(res -> {
|
||||||
|
// ...
|
||||||
|
})
|
||||||
|
.doFinally(() -> lock.unlock(threadId).subscribe())
|
||||||
|
.subscribe();
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
## Semaphore
|
||||||
|
Redis or Valkey based distributed [Semaphore](https://static.javadoc.io/org.redisson/redisson/latest/org/redisson/api/RSemaphore.html) object for Java similar to [Semaphore](https://docs.oracle.com/javase/8/docs/api/java/util/concurrent/Semaphore.html) object.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Could be initialized before usage, but it's not requirement, with available permits amount through `trySetPermits(permits)` method.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Code example:
|
||||||
|
```java
|
||||||
|
RSemaphore semaphore = redisson.getSemaphore("mySemaphore");
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
// acquire single permit
|
||||||
|
semaphore.acquire();
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
// or acquire 10 permits
|
||||||
|
semaphore.acquire(10);
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
// or try to acquire permit
|
||||||
|
boolean res = semaphore.tryAcquire();
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
// or try to acquire permit or wait up to 15 seconds
|
||||||
|
boolean res = semaphore.tryAcquire(15, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
// or try to acquire 10 permit
|
||||||
|
boolean res = semaphore.tryAcquire(10);
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
// or try to acquire 10 permits or wait up to 15 seconds
|
||||||
|
boolean res = semaphore.tryAcquire(10, 15, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
|
||||||
|
if (res) {
|
||||||
|
try {
|
||||||
|
...
|
||||||
|
} finally {
|
||||||
|
semaphore.release();
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Code example of **[Async](https://static.javadoc.io/org.redisson/redisson/latest/org/redisson/api/RSemaphoreAsync.html) interface** usage:
|
||||||
|
```java
|
||||||
|
RSemaphore semaphore = redisson.getSemaphore("mySemaphore");
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
// acquire single permit
|
||||||
|
RFuture<Void> acquireFuture = semaphore.acquireAsync();
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
// or acquire 10 permits
|
||||||
|
RFuture<Void> acquireFuture = semaphore.acquireAsync(10);
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
// or try to acquire permit
|
||||||
|
RFuture<Boolean> acquireFuture = semaphore.tryAcquireAsync();
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
// or try to acquire permit or wait up to 15 seconds
|
||||||
|
RFuture<Boolean> acquireFuture = semaphore.tryAcquireAsync(15, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
// or try to acquire 10 permit
|
||||||
|
RFuture<Boolean> acquireFuture = semaphore.tryAcquireAsync(10);
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
// or try to acquire 10 permits or wait up to 15 seconds
|
||||||
|
RFuture<Boolean> acquireFuture = semaphore.tryAcquireAsync(10, 15, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
acquireFuture.whenComplete((res, exception) -> {
|
||||||
|
// ...
|
||||||
|
semaphore.releaseAsync();
|
||||||
|
});
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Code example of **[Reactive](https://static.javadoc.io/org.redisson/redisson/latest/org/redisson/api/RSemaphoreReactive.html) interface** usage:
|
||||||
|
```java
|
||||||
|
RedissonReactiveClient redisson = redissonClient.reactive();
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
RSemaphoreReactive semaphore = redisson.getSemaphore("mySemaphore");
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
// acquire single permit
|
||||||
|
Mono<Void> acquireMono = semaphore.acquire();
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
// or acquire 10 permits
|
||||||
|
Mono<Void> acquireMono = semaphore.acquire(10);
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
// or try to acquire permit
|
||||||
|
Mono<Boolean> acquireMono = semaphore.tryAcquire();
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
// or try to acquire permit or wait up to 15 seconds
|
||||||
|
Mono<Boolean> acquireMono = semaphore.tryAcquire(15, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
// or try to acquire 10 permit
|
||||||
|
Mono<Boolean> acquireMono = semaphore.tryAcquire(10);
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
// or try to acquire 10 permits or wait up to 15 seconds
|
||||||
|
Mono<Boolean> acquireMono = semaphore.tryAcquire(10, 15, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
acquireMono.doOnSuccess(res -> {
|
||||||
|
// ...
|
||||||
|
})
|
||||||
|
.doFinally(r -> semaphore.release().subscribe())
|
||||||
|
.subscribe();
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Code example of **[RxJava3](https://static.javadoc.io/org.redisson/redisson/latest/org/redisson/api/RSemaphoreRx.html) interface** usage:
|
||||||
|
```java
|
||||||
|
RedissonRxClient redisson = redissonClient.rxJava();
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
RSemaphoreRx semaphore = redisson.getSemaphore("mySemaphore");
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
// acquire single permit
|
||||||
|
Completable acquireRx = semaphore.acquire();
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
// or acquire 10 permits
|
||||||
|
Completable acquireRx = semaphore.acquire(10);
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
// or try to acquire permit
|
||||||
|
Single<Boolean> acquireRx = semaphore.tryAcquire();
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
// or try to acquire permit or wait up to 15 seconds
|
||||||
|
Single<Boolean> acquireRx = semaphore.tryAcquire(15, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
// or try to acquire 10 permit
|
||||||
|
Single<Boolean> acquireRx = semaphore.tryAcquire(10);
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
// or try to acquire 10 permits or wait up to 15 seconds
|
||||||
|
Single<Boolean> acquireRx = semaphore.tryAcquire(10, 15, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
acquireRx.doOnSuccess(res -> {
|
||||||
|
// ...
|
||||||
|
})
|
||||||
|
.doFinally(() -> semaphore.release().subscribe())
|
||||||
|
.subscribe();
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
## PermitExpirableSemaphore
|
||||||
|
Redis or Valkey based distributed [Semaphore](https://static.javadoc.io/org.redisson/redisson/latest/org/redisson/api/RPermitExpirableSemaphore.html) object for Java with lease time parameter support for each acquired permit. Each permit identified by own id and could be released only using its id.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Should be initialized before usage with available permits amount through `trySetPermits(permits)` method. Allows to increase/decrease number of available permits through `addPermits(permits)` method.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Code example:
|
||||||
|
```java
|
||||||
|
RPermitExpirableSemaphore semaphore = redisson.getPermitExpirableSemaphore("mySemaphore");
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
semaphore.trySetPermits(23);
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
// acquire permit
|
||||||
|
String id = semaphore.acquire();
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
// or acquire permit with lease time in 10 seconds
|
||||||
|
String id = semaphore.acquire(10, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
// or try to acquire permit
|
||||||
|
String id = semaphore.tryAcquire();
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
// or try to acquire permit or wait up to 15 seconds
|
||||||
|
String id = semaphore.tryAcquire(15, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
// or try to acquire permit with least time 15 seconds or wait up to 10 seconds
|
||||||
|
String id = semaphore.tryAcquire(10, 15, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
|
||||||
|
if (id != null) {
|
||||||
|
try {
|
||||||
|
...
|
||||||
|
} finally {
|
||||||
|
semaphore.release(id);
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Code example of **[Async](https://static.javadoc.io/org.redisson/redisson/latest/org/redisson/api/RPermitExpirableSemaphoreAsync.html) interface** usage:
|
||||||
|
```java
|
||||||
|
RPermitExpirableSemaphore semaphore = redisson.getPermitExpirableSemaphore("mySemaphore");
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
RFuture<Boolean> setFuture = semaphore.trySetPermitsAsync(23);
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
// acquire permit
|
||||||
|
RFuture<String> acquireFuture = semaphore.acquireAsync();
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
// or acquire permit with lease time in 10 seconds
|
||||||
|
RFuture<String> acquireFuture = semaphore.acquireAsync(10, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
// or try to acquire permit
|
||||||
|
RFuture<String> acquireFuture = semaphore.tryAcquireAsync();
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
// or try to acquire permit or wait up to 15 seconds
|
||||||
|
RFuture<String> acquireFuture = semaphore.tryAcquireAsync(15, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
// or try to acquire permit with least time 15 seconds or wait up to 10 seconds
|
||||||
|
RFuture<String> acquireFuture = semaphore.tryAcquireAsync(10, 15, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
|
||||||
|
acquireFuture.whenComplete((id, exception) -> {
|
||||||
|
// ...
|
||||||
|
semaphore.releaseAsync(id);
|
||||||
|
});
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Code example of **[Reactive](https://static.javadoc.io/org.redisson/redisson/latest/org/redisson/api/RPermitExpirableSemaphoreReactive.html) interface** usage:
|
||||||
|
```java
|
||||||
|
RedissonReactiveClient redisson = redissonClient.reactive();
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
RPermitExpirableSemaphoreReactive semaphore = redisson.getPermitExpirableSemaphore("mySemaphore");
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Mono<Boolean> setMono = semaphore.trySetPermits(23);
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
// acquire permit
|
||||||
|
Mono<String> acquireMono = semaphore.acquire();
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
// or acquire permit with lease time in 10 seconds
|
||||||
|
Mono<String> acquireMono = semaphore.acquire(10, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
// or try to acquire permit
|
||||||
|
Mono<String> acquireMono = semaphore.tryAcquire();
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
// or try to acquire permit or wait up to 15 seconds
|
||||||
|
Mono<String> acquireMono = semaphore.tryAcquire(15, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
// or try to acquire permit with least time 15 seconds or wait up to 10 seconds
|
||||||
|
Mono<String> acquireMono = semaphore.tryAcquire(10, 15, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
acquireMono.flatMap(id -> {
|
||||||
|
// ...
|
||||||
|
return semaphore.release(id);
|
||||||
|
}).subscribe();
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Code example of **[RxJava3](https://static.javadoc.io/org.redisson/redisson/latest/org/redisson/api/RPermitExpirableSemaphoreRx.html) interface** usage:
|
||||||
|
```java
|
||||||
|
RedissonRxClient redisson = redissonClient.rxJava();
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
RPermitExpirableSemaphoreRx semaphore = redisson.getPermitExpirableSemaphore("mySemaphore");
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Single<Boolean> setRx = semaphore.trySetPermits(23);
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
// acquire permit
|
||||||
|
Single<String> acquireRx = semaphore.acquire();
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
// or acquire permit with lease time in 10 seconds
|
||||||
|
Single<String> acquireRx = semaphore.acquire(10, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
// or try to acquire permit
|
||||||
|
Maybe<String> acquireRx = semaphore.tryAcquire();
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
// or try to acquire permit or wait up to 15 seconds
|
||||||
|
Maybe<String> acquireRx = semaphore.tryAcquire(15, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
// or try to acquire permit with least time 15 seconds or wait up to 10 seconds
|
||||||
|
Maybe<String> acquireRx = semaphore.tryAcquire(10, 15, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
acquireRx.flatMap(id -> {
|
||||||
|
// ...
|
||||||
|
return semaphore.release(id);
|
||||||
|
}).subscribe();
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
## CountDownLatch
|
||||||
|
Redis or Valkey based distributed [CountDownLatch](https://static.javadoc.io/org.redisson/redisson/latest/org/redisson/api/RCountDownLatch.html) object for Java has structure similar to [CountDownLatch](https://docs.oracle.com/javase/8/docs/api/java/util/concurrent/CountDownLatch.html) object.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Should be initialized with count by `trySetCount(count)` method before usage.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Code example:
|
||||||
|
```java
|
||||||
|
RCountDownLatch latch = redisson.getCountDownLatch("myCountDownLatch");
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
latch.trySetCount(1);
|
||||||
|
// await for count down
|
||||||
|
latch.await();
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
// in other thread or JVM
|
||||||
|
RCountDownLatch latch = redisson.getCountDownLatch("myCountDownLatch");
|
||||||
|
latch.countDown();
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Code example of **[Async](https://static.javadoc.io/org.redisson/redisson/latest/org/redisson/api/RCountDownLatchAsync.html) interface** usage:
|
||||||
|
```java
|
||||||
|
RCountDownLatch latch = redisson.getCountDownLatch("myCountDownLatch");
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
RFuture<Boolean> setFuture = lock.trySetCountAsync(1);
|
||||||
|
// await for count down
|
||||||
|
RFuture<Void> awaitFuture = latch.awaitAsync();
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
// in other thread or JVM
|
||||||
|
RCountDownLatch latch = redisson.getCountDownLatch("myCountDownLatch");
|
||||||
|
RFuture<Void> countFuture = latch.countDownAsync();
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Code example of **[Reactive](https://static.javadoc.io/org.redisson/redisson/latest/org/redisson/api/RCountDownLatchReactive.html) interface** usage:
|
||||||
|
```java
|
||||||
|
RedissonReactiveClient redisson = redissonClient.reactive();
|
||||||
|
RCountDownLatchReactive latch = redisson.getCountDownLatch("myCountDownLatch");
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Mono<Boolean> setMono = latch.trySetCount(1);
|
||||||
|
// await for count down
|
||||||
|
Mono<Void> awaitMono = latch.await();
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
// in other thread or JVM
|
||||||
|
RCountDownLatchReactive latch = redisson.getCountDownLatch("myCountDownLatch");
|
||||||
|
Mono<Void> countMono = latch.countDown();
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Code example of **[RxJava3](https://static.javadoc.io/org.redisson/redisson/latest/org/redisson/api/RCountDownLatchRx.html) interface** usage:
|
||||||
|
```java
|
||||||
|
RedissonRxClient redisson = redissonClient.rxJava();
|
||||||
|
RCountDownLatchRx latch = redisson.getCountDownLatch("myCountDownLatch");
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Single<Boolean> setRx = latch.trySetCount(1);
|
||||||
|
// await for count down
|
||||||
|
Completable awaitRx = latch.await();
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
// in other thread or JVM
|
||||||
|
RCountDownLatchRx latch = redisson.getCountDownLatch("myCountDownLatch");
|
||||||
|
Completable countRx = latch.countDown();
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
## Spin Lock
|
||||||
|
Redis or Valkey based distributed reentrant [SpinLock](https://static.javadoc.io/org.redisson/redisson/latest/org/redisson/api/RLock.html) object for Java and implements [Lock](https://docs.oracle.com/javase/8/docs/api/java/util/concurrent/locks/Lock.html) interface.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Thousands or more locks acquired/released per short time interval may cause reaching of network throughput limit and Redis or Valkey CPU overload because of pubsub usage in [Lock](#lock) object. This occurs due to nature of pubsub - messages are distributed to all nodes in cluster. Spin Lock uses Exponential Backoff strategy by default for lock acquisition instead of pubsub channel.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
If Redisson instance which acquired lock crashes then such lock could hang forever in acquired state. To avoid this Redisson maintains lock watchdog, it prolongs lock expiration while lock holder Redisson instance is alive. By default lock watchdog timeout is 30 seconds and can be changed through [Config.lockWatchdogTimeout](../configuration.md) setting.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
`leaseTime` parameter during lock acquisition can be defined. After specified time interval locked lock will be released automatically.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
`RLock` object behaves according to the Java Lock specification. It means only lock owner thread can unlock it otherwise `IllegalMonitorStateException` would be thrown. Otherwise consider to use [RSemaphore](#semaphore) object.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Code example:
|
||||||
|
```java
|
||||||
|
RLock lock = redisson.getSpinLock("myLock");
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
// traditional lock method
|
||||||
|
lock.lock();
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
// or acquire lock and automatically unlock it after 10 seconds
|
||||||
|
lock.lock(10, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
// or wait for lock aquisition up to 100 seconds
|
||||||
|
// and automatically unlock it after 10 seconds
|
||||||
|
boolean res = lock.tryLock(100, 10, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
|
||||||
|
if (res) {
|
||||||
|
try {
|
||||||
|
...
|
||||||
|
} finally {
|
||||||
|
lock.unlock();
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Code example of **[Async](https://static.javadoc.io/org.redisson/redisson/latest/org/redisson/api/RLockAsync.html) interface** usage:
|
||||||
|
```java
|
||||||
|
RLock lock = redisson.getSpinLock("myLock");
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
long threadId = Thread.currentThread().getId();
|
||||||
|
RFuture<Void> lockFuture = lock.lockAsync(threadId);
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
// or acquire lock and automatically unlock it after 10 seconds
|
||||||
|
RFuture<Void> lockFuture = lock.lockAsync(10, TimeUnit.SECONDS, threadId);
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
// or wait for lock aquisition up to 100 seconds
|
||||||
|
// and automatically unlock it after 10 seconds
|
||||||
|
RFuture<Boolean> lockFuture = lock.tryLockAsync(100, 10, TimeUnit.SECONDS, threadId);
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
lockFuture.whenComplete((res, exception) -> {
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
// ...
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
lock.unlockAsync(threadId);
|
||||||
|
});
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Code example of **[Reactive](https://static.javadoc.io/org.redisson/redisson/latest/org/redisson/api/RLockReactive.html) interface** usage:
|
||||||
|
```java
|
||||||
|
RedissonReactiveClient redisson = redissonClient.reactive();
|
||||||
|
RLockReactive lock = redisson.getSpinLock("myLock");
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
long threadId = Thread.currentThread().getId();
|
||||||
|
Mono<Void> lockMono = lock.lock(threadId);
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
// or acquire lock and automatically unlock it after 10 seconds
|
||||||
|
Mono<Void> lockMono = lock.lock(10, TimeUnit.SECONDS, threadId);
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
// or wait for lock aquisition up to 100 seconds
|
||||||
|
// and automatically unlock it after 10 seconds
|
||||||
|
Mono<Boolean> lockMono = lock.tryLock(100, 10, TimeUnit.SECONDS, threadId);
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
lockMono.doOnSuccess(res -> {
|
||||||
|
// ...
|
||||||
|
})
|
||||||
|
.doFinally(r -> lock.unlock(threadId).subscribe())
|
||||||
|
.subscribe();
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Code example of **[RxJava3](https://static.javadoc.io/org.redisson/redisson/latest/org/redisson/api/RLockRx.html) interface** usage:
|
||||||
|
```java
|
||||||
|
RedissonRxClient redisson = redissonClient.rxJava();
|
||||||
|
RLockRx lock = redisson.getSpinLock("myLock");
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
long threadId = Thread.currentThread().getId();
|
||||||
|
Completable lockRes = lock.lock(threadId);
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
// or acquire lock and automatically unlock it after 10 seconds
|
||||||
|
Completable lockRes = lock.lock(10, TimeUnit.SECONDS, threadId);
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
// or wait for lock aquisition up to 100 seconds
|
||||||
|
// and automatically unlock it after 10 seconds
|
||||||
|
Single<Boolean> lockRes = lock.tryLock(100, 10, TimeUnit.SECONDS, threadId);
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
lockRes.doOnSuccess(res -> {
|
||||||
|
// ...
|
||||||
|
})
|
||||||
|
.doFinally(() -> lock.unlock(threadId).subscribe())
|
||||||
|
.subscribe();
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
## Fenced Lock
|
||||||
|
Redis or Valkey based distributed reentrant [FencedLock](https://static.javadoc.io/org.redisson/redisson/latest/org/redisson/api/RFencedLock.html) object for Java and implements [Lock](https://docs.oracle.com/javase/8/docs/api/java/util/concurrent/locks/Lock.html) interface.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
This type of lock maintains the fencing token to avoid cases when Client acquired the lock was delayed due to long GC pause or other reason and can't detect that it doesn't own the lock anymore. To resolve this issue token is returned by locking methods or `getToken()` method. Token should be checked if it's greater or equal with the previous one by the service guarded by this lock and reject operation if condition is false.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
If Redisson instance which acquired lock crashes then such lock could hang forever in acquired state. To avoid this Redisson maintains lock watchdog, it prolongs lock expiration while lock holder Redisson instance is alive. By default lock watchdog timeout is 30 seconds and can be changed through [Config.lockWatchdogTimeout](../configuration.md) setting.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
`leaseTime` parameter during lock acquisition can be defined. After specified time interval locked lock will be released automatically.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
`RLock` object behaves according to the Java Lock specification. It means only lock owner thread can unlock it otherwise `IllegalMonitorStateException` would be thrown. Otherwise consider to use [RSemaphore](#semaphore) object.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Code example:
|
||||||
|
```java
|
||||||
|
RFencedLock lock = redisson.getFencedLock("myLock");
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
// traditional lock method
|
||||||
|
Long token = lock.lockAndGetToken();
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
// or acquire lock and automatically unlock it after 10 seconds
|
||||||
|
token = lock.lockAndGetToken(10, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
// or wait for lock aquisition up to 100 seconds
|
||||||
|
// and automatically unlock it after 10 seconds
|
||||||
|
Long token = lock.tryLockAndGetToken(100, 10, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
|
||||||
|
if (token != null) {
|
||||||
|
try {
|
||||||
|
// check if token >= old token
|
||||||
|
...
|
||||||
|
} finally {
|
||||||
|
lock.unlock();
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Code example of **[Async](https://static.javadoc.io/org.redisson/redisson/latest/org/redisson/api/RLockAsync.html) interface** usage:
|
||||||
|
```java
|
||||||
|
RFencedLock lock = redisson.getFencedLock("myLock");
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
RFuture<Long> lockFuture = lock.lockAndGetTokenAsync();
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
// or acquire lock and automatically unlock it after 10 seconds
|
||||||
|
RFuture<Long> lockFuture = lock.lockAndGetTokenAsync(10, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
// or wait for lock aquisition up to 100 seconds
|
||||||
|
// and automatically unlock it after 10 seconds
|
||||||
|
RFuture<Long> lockFuture = lock.tryLockAndGetTokenAsync(100, 10, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
long threadId = Thread.currentThread().getId();
|
||||||
|
lockFuture.whenComplete((token, exception) -> {
|
||||||
|
if (token != null) {
|
||||||
|
try {
|
||||||
|
// check if token >= old token
|
||||||
|
...
|
||||||
|
} finally {
|
||||||
|
lock.unlockAsync(threadId);
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
});
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Code example of **[Reactive](https://static.javadoc.io/org.redisson/redisson/latest/org/redisson/api/RLockReactive.html) interface** usage:
|
||||||
|
```java
|
||||||
|
RedissonReactiveClient redisson = redissonClient.reactive();
|
||||||
|
RFencedLockReactive lock = redisson.getFencedLock("myLock");
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
long threadId = Thread.currentThread().getId();
|
||||||
|
Mono<Long> lockMono = lock.lockAndGetToken();
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
// or acquire lock and automatically unlock it after 10 seconds
|
||||||
|
Mono<Long> lockMono = lock.lockAndGetToken(10, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
// or wait for lock aquisition up to 100 seconds
|
||||||
|
// and automatically unlock it after 10 seconds
|
||||||
|
Mono<Long> lockMono = lock.tryLockAndGetToken(100, 10, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
lockMono.doOnSuccess(token -> {
|
||||||
|
if (token != null) {
|
||||||
|
try {
|
||||||
|
// check if token >= old token
|
||||||
|
...
|
||||||
|
} finally {
|
||||||
|
lock.unlock(threadId).subscribe();
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
})
|
||||||
|
.subscribe();
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Code example of **[RxJava3](https://static.javadoc.io/org.redisson/redisson/latest/org/redisson/api/RLockRx.html) interface** usage:
|
||||||
|
```java
|
||||||
|
RedissonRxClient redisson = redissonClient.rxJava();
|
||||||
|
RFencedLockRx lock = redisson.getFencedLock("myLock");
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Single<Long> lockRes = lock.lockAndGetToken();
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
// or acquire lock and automatically unlock it after 10 seconds
|
||||||
|
Single<Long> lockRes = lock.lockAndGetToken(10, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
// or wait for lock aquisition up to 100 seconds
|
||||||
|
// and automatically unlock it after 10 seconds
|
||||||
|
Single<Long> lockRes = lock.tryLock(100, 10, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
long threadId = Thread.currentThread().getId();
|
||||||
|
lockRes.doOnSuccess(token -> {
|
||||||
|
if (token != null) {
|
||||||
|
try {
|
||||||
|
// check if token >= old token
|
||||||
|
...
|
||||||
|
} finally {
|
||||||
|
lock.unlock(threadId).subscribe();
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
})
|
||||||
|
.subscribe();
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
@ -0,0 +1,16 @@
|
|||||||
|
It's possible to use a Redisson object inside another Redisson object in any combination. In this case a special reference object will be used and handled by Redisson.
|
||||||
|
Usage example:
|
||||||
|
```java
|
||||||
|
RMap<RSet<RList>, RList<RMap>> map = redisson.getMap("myMap");
|
||||||
|
RSet<RList> set = redisson.getSet("mySet");
|
||||||
|
RList<RMap> list = redisson.getList("myList");
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
map.put(set, list);
|
||||||
|
// With the help of the special reference object, we can even create a circular
|
||||||
|
// reference which is impossible to achieve if we were to serialize its content
|
||||||
|
set.add(list);
|
||||||
|
list.add(map);
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
As you may have noticed there is no need to re "save/persist" the map object after its elements have changed. Because it does not contain any value but merely a reference, this makes Redisson objects behaves much more like standard Java objects. In effect, making Redis or Valkey becomes part of JVM's memory rather than just a simple repository.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
One Redis HASH, one Redis SET and one Redis LIST will be created in the example above.
|
||||||
@ -0,0 +1,626 @@
|
|||||||
|
## Object holder
|
||||||
|
Java implementation of Redis or Valkey based [RBucket](https://static.javadoc.io/org.redisson/redisson/latest/org/redisson/api/RBucket.html) object is a holder for any type of object. Size is limited to 512Mb.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Code example:
|
||||||
|
```java
|
||||||
|
RBucket<AnyObject> bucket = redisson.getBucket("anyObject");
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
bucket.set(new AnyObject(1));
|
||||||
|
AnyObject obj = bucket.get();
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
bucket.trySet(new AnyObject(3));
|
||||||
|
bucket.compareAndSet(new AnyObject(4), new AnyObject(5));
|
||||||
|
bucket.getAndSet(new AnyObject(6));
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Code example of **[Async](https://static.javadoc.io/org.redisson/redisson/latest/org/redisson/api/RBucketAsync.html) interface** usage:
|
||||||
|
```java
|
||||||
|
RBucket<AnyObject> bucket = redisson.getBucket("anyObject");
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
RFuture<Void> future = bucket.setAsync(new AnyObject(1));
|
||||||
|
RFuture<AnyObject> objfuture = bucket.getAsync();
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
RFuture<Boolean> tsFuture = bucket.trySetAsync(new AnyObject(3));
|
||||||
|
RFuture<Boolean> csFuture = bucket.compareAndSetAsync(new AnyObject(4), new AnyObject(5));
|
||||||
|
RFuture<AnyObject> gsFuture = bucket.getAndSetAsync(new AnyObject(6));
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Code example of **[Reactive](https://static.javadoc.io/org.redisson/redisson/latest/org/redisson/api/RBucketReactive.html) interface** usage:
|
||||||
|
```java
|
||||||
|
RedissonReactiveClient redisson = redissonClient.reactive();
|
||||||
|
RBucketReactive<AnyObject> bucket = redisson.getBucket("anyObject");
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Mono<Void> mono = bucket.set(new AnyObject(1));
|
||||||
|
Mono<AnyObject> objMono = bucket.get();
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Mono<Boolean> tsMono = bucket.trySet(new AnyObject(3));
|
||||||
|
Mono<Boolean> csMono = bucket.compareAndSet(new AnyObject(4), new AnyObject(5));
|
||||||
|
Mono<AnyObject> gsMono = bucket.getAndSet(new AnyObject(6));
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Code example of **[RxJava3](https://static.javadoc.io/org.redisson/redisson/latest/org/redisson/api/RBucketRx.html) interface** usage:
|
||||||
|
```java
|
||||||
|
RedissonRxClient redisson = redissonClient.rxJava();
|
||||||
|
RBucketRx<AnyObject> bucket = redisson.getBucket("anyObject");
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Completable rx = bucket.set(new AnyObject(1));
|
||||||
|
Maybe<AnyObject> objRx = bucket.get();
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Single<Boolean> tsRx = bucket.trySet(new AnyObject(3));
|
||||||
|
Single<Boolean> csRx = bucket.compareAndSet(new AnyObject(4), new AnyObject(5));
|
||||||
|
Maybe<AnyObject> gsRx = bucket.getAndSet(new AnyObject(6));
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
<br/>
|
||||||
|
<br/>
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Use [RBuckets](https://static.javadoc.io/org.redisson/redisson/latest/org/redisson/api/RBuckets.html) interface to execute operations over multiple [RBucket](https://static.javadoc.io/org.redisson/redisson/latest/org/redisson/api/RBucket.html) objects:
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Code example:
|
||||||
|
```java
|
||||||
|
RBuckets buckets = redisson.getBuckets();
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
// get all bucket values
|
||||||
|
Map<String, V> loadedBuckets = buckets.get("myBucket1", "myBucket2", "myBucket3");
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Map<String, Object> map = new HashMap<>();
|
||||||
|
map.put("myBucket1", new MyObject());
|
||||||
|
map.put("myBucket2", new MyObject());
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
// sets all or nothing if some bucket is already exists
|
||||||
|
buckets.trySet(map);
|
||||||
|
// store all at once
|
||||||
|
buckets.set(map);
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Code example of **[Async](https://static.javadoc.io/org.redisson/redisson/latest/org/redisson/api/RBucketsAsync.html) interface** usage:
|
||||||
|
```java
|
||||||
|
RBuckets buckets = redisson.getBuckets();
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
// get all bucket values
|
||||||
|
RFuture<Map<String, V>> bucketsFuture = buckets.getAsync("myBucket1", "myBucket2", "myBucket3");
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Map<String, Object> map = new HashMap<>();
|
||||||
|
map.put("myBucket1", new MyObject());
|
||||||
|
map.put("myBucket2", new MyObject());
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
// sets all or nothing if some bucket is already exists
|
||||||
|
RFuture<Boolean> tsFuture = buckets.trySetAsync(map);
|
||||||
|
// store all at once
|
||||||
|
RFuture<Void> sFuture = buckets.setAsync(map);
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Code example of **[Reactive](https://static.javadoc.io/org.redisson/redisson/latest/org/redisson/api/RBucketsReactive.html) interface** usage:
|
||||||
|
```java
|
||||||
|
RedissonReactiveClient redisson = redissonClient.reactive();
|
||||||
|
RBucketsReactive buckets = redisson.getBuckets();
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
// get all bucket values
|
||||||
|
Mono<Map<String, V>> bucketsMono = buckets.getAsync("myBucket1", "myBucket2", "myBucket3");
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Map<String, Object> map = new HashMap<>();
|
||||||
|
map.put("myBucket1", new MyObject());
|
||||||
|
map.put("myBucket2", new MyObject());
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
// sets all or nothing if some bucket is already exists
|
||||||
|
Mono<Boolean> tsMono = buckets.trySet(map);
|
||||||
|
// store all at once
|
||||||
|
Mono<Void> sMono = buckets.set(map);
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Code example of **[RxJava](https://static.javadoc.io/org.redisson/redisson/latest/org/redisson/api/RBucketsRx.html) interface** usage:
|
||||||
|
```java
|
||||||
|
RedissonRxClient redisson = redissonClient.rxJava();
|
||||||
|
RBucketsRx buckets = redisson.getBuckets();
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
// get all bucket values
|
||||||
|
Single<Map<String, V>> bucketsRx = buckets.get("myBucket1", "myBucket2", "myBucket3");
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Map<String, Object> map = new HashMap<>();
|
||||||
|
map.put("myBucket1", new MyObject());
|
||||||
|
map.put("myBucket2", new MyObject());
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
// sets all or nothing if some bucket is already exists
|
||||||
|
Single<Boolean> tsRx = buckets.trySet(map);
|
||||||
|
// store all at once
|
||||||
|
Completable sRx = buckets.set(map);
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
### Listeners
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Redisson allows to bind listeners per `RBucket` object.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|Listener class name|Event description |
|
||||||
|
|:--:|:--:|
|
||||||
|
|org.redisson.api.listener.TrackingListener|Data created/updated after read operation|
|
||||||
|
|org.redisson.api.listener.SetObjectListener|Data created/updated|
|
||||||
|
|org.redisson.api.ExpiredObjectListener|`RBucket` object expired|
|
||||||
|
|org.redisson.api.DeletedObjectListener|`RBucket` object deleted|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Usage example:
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
```java
|
||||||
|
RBucket<String> set = redisson.getBucket("anyObject");
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
int listenerId = set.addListener(new SetObjectListener() {
|
||||||
|
@Override
|
||||||
|
public void onSet(String name) {
|
||||||
|
// ...
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
});
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
int listenerId = set.addListener(new DeletedObjectListener() {
|
||||||
|
@Override
|
||||||
|
public void onDeleted(String name) {
|
||||||
|
// ...
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
});
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
// ...
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
set.removeListener(listenerId);
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
## Binary stream holder
|
||||||
|
Java implementation of Redis or Valkey based [RBinaryStream](https://www.javadoc.io/doc/org.redisson/redisson/latest/org/redisson/api/RBinaryStream.html) object holds sequence of bytes. It extends [RBucket](#object-holder) interface and size is limited to 512Mb.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Code example:
|
||||||
|
```java
|
||||||
|
RBinaryStream stream = redisson.getBinaryStream("anyStream");
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
byte[] content = ...
|
||||||
|
stream.set(content);
|
||||||
|
stream.getAndSet(content);
|
||||||
|
stream.trySet(content);
|
||||||
|
stream.compareAndSet(oldContent, content);
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Code example of **[Async](https://static.javadoc.io/org.redisson/redisson/latest/org/redisson/api/RBucketAsync.html) interface** usage:
|
||||||
|
```java
|
||||||
|
RBinaryStream stream = redisson.getBinaryStream("anyStream");
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
byte[] content = ...
|
||||||
|
RFuture<Void> future = stream.set(content);
|
||||||
|
RFuture<byte[]> future = stream.getAndSet(content);
|
||||||
|
RFuture<Boolean> future = stream.trySet(content);
|
||||||
|
RFuture<Boolean> future = stream.compareAndSet(oldContent, content);
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Code example of **[Reactive](https://static.javadoc.io/org.redisson/redisson/latest/org/redisson/api/RBinaryStreamReactive.html) interface** usage:
|
||||||
|
```java
|
||||||
|
RedissonReactiveClient redisson = redissonClient.reactive();
|
||||||
|
RBinaryStreamReactive stream = redisson.getBinaryStream("anyStream");
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
ByteBuffer content = ...
|
||||||
|
Mono<Void> mono = stream.set(content);
|
||||||
|
Mono<byte[]> mono = stream.getAndSet(content);
|
||||||
|
Mono<Boolean> mono = stream.trySet(content);
|
||||||
|
Mono<Boolean> mono = stream.compareAndSet(oldContent, content);
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Mono<Integer> mono = stream.write(content);
|
||||||
|
stream.position(0);
|
||||||
|
Mono<Integer> mono = stream.read(b);
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Code example of **[RxJava3](https://static.javadoc.io/org.redisson/redisson/latest/org/redisson/api/RBinaryStreamRx.html) interface** usage:
|
||||||
|
```java
|
||||||
|
RedissonRxClient redisson = redissonClient.rxJava();
|
||||||
|
RBinaryStreamRx stream = redisson.getBinaryStream("anyStream");
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
ByteBuffer content = ...
|
||||||
|
Completable rx = stream.set(content);
|
||||||
|
Maybe<byte[]> rx = stream.getAndSet(content);
|
||||||
|
Single<Boolean> rx = stream.trySet(content);
|
||||||
|
Single<Boolean> rx = stream.compareAndSet(oldContent, content);
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Single<Integer> rx = stream.write(content);
|
||||||
|
stream.position(0);
|
||||||
|
Single<Integer> rx = stream.read(b);
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Code example of [java.io.InputStream](https://docs.oracle.com/javase/8/docs/api/java/io/InputStream.html) and [java.io.OutputStream](https://docs.oracle.com/javase/8/docs/api/java/io/OutputStream.html) interfaces usage:
|
||||||
|
```java
|
||||||
|
RBinaryStream stream = redisson.getBinaryStream("anyStream");
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
InputStream is = stream.getInputStream();
|
||||||
|
byte[] readBuffer = ...
|
||||||
|
is.read(readBuffer);
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
OutputStream os = stream.getOuputStream();
|
||||||
|
byte[] contentToWrite = ...
|
||||||
|
os.write(contentToWrite);
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Code example of [java.nio.channels.SeekableByteChannel](https://docs.oracle.com/javase/8/docs/api/java/nio/channels/SeekableByteChannel.html) interface usage:
|
||||||
|
```java
|
||||||
|
RBinaryStream stream = redisson.getBinaryStream("anyStream");
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
SeekableByteChannel sbc = stream.getChannel();
|
||||||
|
ByteBuffer readBuffer = ...
|
||||||
|
sbc.read(readBuffer);
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
sbc.position(0);
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
ByteBuffer contentToWrite = ...
|
||||||
|
sbc.write(contentToWrite);
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
sbc.truncate(234);
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Code example of [java.nio.channels.AsynchronousByteChannel](https://docs.oracle.com/javase/8/docs/api/java/nio/channels/AsynchronousByteChannel.html) interface usage:
|
||||||
|
```java
|
||||||
|
RBinaryStream stream = redisson.getBinaryStream("anyStream");
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
AsynchronousByteChannel sbc = stream.getAsynchronousChannel();
|
||||||
|
ByteBuffer readBuffer = ...
|
||||||
|
sbc.read(readBuffer);
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
ByteBuffer contentToWrite = ...
|
||||||
|
sbc.write(contentToWrite);
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
### Listeners
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Redisson allows to bind listeners per `RBinaryStream` object.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|Listener class name|Event description |
|
||||||
|
|:--:|:--:|
|
||||||
|
|org.redisson.api.listener.TrackingListener|Data created/updated after read operation|
|
||||||
|
|org.redisson.api.listener.SetObjectListener|Data created/updated|
|
||||||
|
|org.redisson.api.ExpiredObjectListener|`RBinaryStream` object expired|
|
||||||
|
|org.redisson.api.DeletedObjectListener|`RBinaryStream` object deleted|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Usage example:
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
```java
|
||||||
|
RBinaryStream stream = redisson.getBinaryStream("anyObject");
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
int listenerId = set.addListener(new DeletedObjectListener() {
|
||||||
|
@Override
|
||||||
|
public void onDeleted(String name) {
|
||||||
|
// ...
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
});
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
// ...
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
set.removeListener(listenerId);
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
## JSON object holder
|
||||||
|
Java implementation of [RJsonBucket](https://static.javadoc.io/org.redisson/redisson/latest/org/redisson/api/RJsonBucket.html) object stores data in JSON format using `JSON.*` commands. JSON data encoding/decoding handled by `JsonCodec` which is a required parameter. Available implementation is `org.redisson.codec.JacksonCodec` which is thread-safe.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Use [JSON Store](collections.md/#json-store) for key-value implementation and local cache.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
### Local cache
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Redisson provides JSON object holder implementation with local cache.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
**local cache** - so called near cache used to speed up read operations and avoid network roundtrips. It caches whole JSON object on Redisson side and executes read operations up to **45x faster** in comparison with common implementation. Local cache instances with the same name connected to the same pub/sub channel. This channel is used to exchange invalidate events between instances.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|RedissonClient<br/>method name | Local cache | Ultra-fast<br/>read/write |
|
||||||
|
| ------------- | :-----------: | :---------:|
|
||||||
|
|getJsonBucket()<br/><sub><i>open-source version</i></sub> | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||||
|
|getJsonBucket()<br/><sub><i>[Redisson PRO](https://redisson.pro) version</i></sub> | ❌ | ✔️ |
|
||||||
|
|getLocalCachedJsonBucket()<br/><sub><i>[Redisson PRO](https://redisson.pro) version</i></sub> | ✔️ | ✔️ |
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Code example:
|
||||||
|
```java
|
||||||
|
RJsonBucket<AnyObject> bucket = redisson.getJsonBucket("anyObject", new JacksonCodec<>(AnyObject.class));
|
||||||
|
// or local cached instance
|
||||||
|
RLocalCachedJsonBucket<AnyObject> bucket = redisson.getLocalCachedJsonBucket("anyObject", new JacksonCodec<>(AnyObject.class));
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
bucket.set(new AnyObject(1));
|
||||||
|
AnyObject obj = bucket.get();
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
bucket.trySet(new AnyObject(3));
|
||||||
|
bucket.compareAndSet(new AnyObject(4), new AnyObject(5));
|
||||||
|
bucket.getAndSet(new AnyObject(6));
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
List<String> values = bucket.get(new JacksonCodec<>(new TypeReference<List<String>>() {}), "values");
|
||||||
|
long aa = bucket.arrayAppend("$.obj.values", "t3", "t4");
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Code example of **[Async](https://static.javadoc.io/org.redisson/redisson/latest/org/redisson/api/RJsonBucketAsync.html) interface** usage:
|
||||||
|
```java
|
||||||
|
RJsonBucket<AnyObject> bucket = redisson.getJsonBucket("anyObject", new JacksonCodec<>(AnyObject.class));
|
||||||
|
// or local cached instace
|
||||||
|
RLocalCachedJsonBucket<AnyObject> bucket = redisson.getLocalCachedJsonBucket("anyObject", new JacksonCodec<>(AnyObject.class));
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
RFuture<Void> future = bucket.setAsync(new AnyObject(1));
|
||||||
|
RFuture<AnyObject> objfuture = bucket.getAsync();
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
RFuture<Boolean> tsFuture = bucket.trySetAsync(new AnyObject(3));
|
||||||
|
RFuture<Boolean> csFuture = bucket.compareAndSetAsync(new AnyObject(4), new AnyObject(5));
|
||||||
|
RFuture<AnyObject> gsFuture = bucket.getAndSetAsync(new AnyObject(6));
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
RFutue<List<String>> gFuture = bucket.getAsync(new JacksonCodec<>(new TypeReference<List<String>>() {}), "obj.values");
|
||||||
|
RFutue<Long> aaFuture = bucket.arrayAppendAsync("$.obj.values", "t3", "t4");
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Code example of **[Reactive](https://static.javadoc.io/org.redisson/redisson/latest/org/redisson/api/RJsonBucketReactive.html) interface** usage:
|
||||||
|
```java
|
||||||
|
RedissonReactiveClient redisson = redissonClient.reactive();
|
||||||
|
RJsonBucketReactive<AnyObject> bucket = redisson.getJsonBucket("anyObject", new JacksonCodec<>(AnyObject.class));
|
||||||
|
// or local cached instance
|
||||||
|
RLocalCachedJsonBucketReactive<AnyObject> bucket = redisson.getLocalCachedJsonBucket("anyObject", new JacksonCodec<>(AnyObject.class));
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Mono<Void> mono = bucket.set(new AnyObject(1));
|
||||||
|
Mono<AnyObject> objMono = bucket.get();
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Mono<Boolean> tsMono = bucket.trySet(new AnyObject(3));
|
||||||
|
Mono<Boolean> csMono = bucket.compareAndSet(new AnyObject(4), new AnyObject(5));
|
||||||
|
Mono<AnyObject> gsMono = bucket.getAndSet(new AnyObject(6));
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Mono<List<String>> vsMono = bucket.get(new JacksonCodec<>(new TypeReference<List<String>>() {}), "values");
|
||||||
|
Mono<Long> aaMono = bucket.arrayAppend("$.obj.values", "t3", "t4");
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Code example of **[RxJava3](https://static.javadoc.io/org.redisson/redisson/latest/org/redisson/api/RJsonBucketRx.html) interface** usage:
|
||||||
|
```java
|
||||||
|
RedissonRxClient redisson = redissonClient.rxJava();
|
||||||
|
RJsonBucketRx<AnyObject> bucket = redisson.getJsonBucket("anyObject", new JacksonCodec<>(AnyObject.class));
|
||||||
|
// or local cached instance
|
||||||
|
RLocalCachedJsonBucketRx<AnyObject> bucket = redisson.getLocalCachedJsonBucket("anyObject", new JacksonCodec<>(AnyObject.class));
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Completable rx = bucket.set(new AnyObject(1));
|
||||||
|
Maybe<AnyObject> objRx = bucket.get();
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Single<Boolean> tsRx = bucket.trySet(new AnyObject(3));
|
||||||
|
Single<Boolean> csRx = bucket.compareAndSet(new AnyObject(4), new AnyObject(5));
|
||||||
|
Maybe<AnyObject> gsRx = bucket.getAndSet(new AnyObject(6));
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Single<List<String>> valuesRx = bucket.get(new JacksonCodec<>(new TypeReference<List<String>>() {}), "values");
|
||||||
|
Single<Long> aaRx = bucket.arrayAppend("$.obj.values", "t3", "t4");
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
## Geospatial holder
|
||||||
|
Java implementation of Redis or Valkey based [RGeo](https://static.javadoc.io/org.redisson/redisson/latest/org/redisson/api/RGeo.html) object is a holder for geospatial items.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Code example:
|
||||||
|
```java
|
||||||
|
RGeo<String> geo = redisson.getGeo("test");
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
geo.add(new GeoEntry(13.361389, 38.115556, "Palermo"),
|
||||||
|
new GeoEntry(15.087269, 37.502669, "Catania"));
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Double distance = geo.dist("Palermo", "Catania", GeoUnit.METERS);
|
||||||
|
Map<String, GeoPosition> positions = geo.pos("test2", "Palermo", "test3", "Catania", "test1");
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
List<String> cities = geo.search(GeoSearchArgs.from(15, 37).radius(200, GeoUnit.KILOMETERS));
|
||||||
|
Map<String, GeoPosition> citiesWithPositions = geo.searchWithPosition(GeoSearchArgs.from(15, 37).radius(200, GeoUnit.KILOMETERS));
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Code example of **[Async](https://static.javadoc.io/org.redisson/redisson/latest/org/redisson/api/RGeoAsync.html) interface** usage:
|
||||||
|
```java
|
||||||
|
RGeo<String> geo = redisson.getGeo("test");
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
RFuture<Long> addFuture = geo.addAsync(new GeoEntry(13.361389, 38.115556, "Palermo"),
|
||||||
|
new GeoEntry(15.087269, 37.502669, "Catania"));
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
RFuture<Double> distanceFuture = geo.distAsync("Palermo", "Catania", GeoUnit.METERS);
|
||||||
|
RFuture<Map<String, GeoPosition>> positionsFuture = geo.posAsync("test2", "Palermo", "test3", "Catania", "test1");
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
RFuture<List<String>> citiesFuture = geo.searchAsync(GeoSearchArgs.from(15, 37).radius(200, GeoUnit.KILOMETERS));
|
||||||
|
RFuture<Map<String, GeoPosition>> citiesWithPositions = geo.searchWithPositionAsync(GeoSearchArgs.from(15, 37).radius(200, GeoUnit.KILOMETERS));
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Code example of **[Reactive](https://static.javadoc.io/org.redisson/redisson/latest/org/redisson/api/RGeoReactive.html) interface** usage:
|
||||||
|
```java
|
||||||
|
RedissonReactiveClient redisson = redissonClient.reactive();
|
||||||
|
RGeoReactive<String> bucket = redisson.getGeo("test");
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Mono<Long> addFuture = geo.add(new GeoEntry(13.361389, 38.115556, "Palermo"),
|
||||||
|
new GeoEntry(15.087269, 37.502669, "Catania"));
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Mono<Double> distanceFuture = geo.dist("Palermo", "Catania", GeoUnit.METERS);
|
||||||
|
Mono<Map<String, GeoPosition>> positionsFuture = geo.pos("test2", "Palermo", "test3", "Catania", "test1");
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Mono<List<String>> citiesFuture = geo.search(GeoSearchArgs.from(15, 37).radius(200, GeoUnit.KILOMETERS));
|
||||||
|
Mono<Map<String, GeoPosition>> citiesWithPositions = geo.searchWithPosition(GeoSearchArgs.from(15, 37).radius(200, GeoUnit.KILOMETERS));
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Code example of **[RxJava3](https://static.javadoc.io/org.redisson/redisson/latest/org/redisson/api/RGeoRx.html) interface** usage:
|
||||||
|
```java
|
||||||
|
RedissonRxClient redisson = redissonClient.rxJava();
|
||||||
|
RGeoRx<String> bucket = redisson.getGeo("test");
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Single<Long> addFuture = geo.add(new GeoEntry(13.361389, 38.115556, "Palermo"),
|
||||||
|
new GeoEntry(15.087269, 37.502669, "Catania"));
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Single<Double> distanceFuture = geo.dist("Palermo", "Catania", GeoUnit.METERS);
|
||||||
|
Single<Map<String, GeoPosition>> positionsFuture = geo.pos("test2", "Palermo", "test3", "Catania", "test1");
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Single<List<String>> citiesFuture = geo.search(GeoSearchArgs.from(15, 37).radius(200, GeoUnit.KILOMETERS));
|
||||||
|
Single<Map<String, GeoPosition>> citiesWithPositions = geo.searchWithPosition(GeoSearchArgs.from(15, 37).radius(200, GeoUnit.KILOMETERS));
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
## BitSet
|
||||||
|
Java implementation of Redis or Valkey based [RBitSet](https://static.javadoc.io/org.redisson/redisson/latest/org/redisson/api/RBitSet.html) object provides API similar to [java.util.BitSet](https://docs.oracle.com/javase/8/docs/api/java/util/BitSet.html). It represents vector of bits that grows as needed. Size limited to `4 294 967 295` bits.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Code example:
|
||||||
|
```java
|
||||||
|
RBitSet set = redisson.getBitSet("simpleBitset");
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
set.set(0, true);
|
||||||
|
set.set(1812, false);
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
set.clear(0);
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
set.and("anotherBitset");
|
||||||
|
set.xor("anotherBitset");
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Code example of **[Async](https://static.javadoc.io/org.redisson/redisson/latest/org/redisson/api/RBitSetAsync.html) interface** usage:
|
||||||
|
```java
|
||||||
|
RBitSetAsync set = redisson.getBitSet("simpleBitset");
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
RFuture<Boolean> setFuture = set.setAsync(0, true);
|
||||||
|
RFuture<Boolean> setFuture = set.setAsync(1812, false);
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
RFuture<Void> clearFuture = set.clearAsync(0);
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
RFuture<Void> andFuture = set.andAsync("anotherBitset);
|
||||||
|
RFuture<Void> xorFuture = set.xorAsync("anotherBitset");
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Code example of **[Reactive](https://static.javadoc.io/org.redisson/redisson/latest/org/redisson/api/RBitSetReactive.html) interface** usage:
|
||||||
|
```java
|
||||||
|
RedissonReactiveClient redisson = redissonClient.reactive();
|
||||||
|
RBitSetReactive stream = redisson.getBitSet("simpleBitset");
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Mono<Boolean> setMono = set.set(0, true);
|
||||||
|
Mono<Boolean> setMono = set.set(1812, false);
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Mono<Void> clearMono = set.clear(0);
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Mono<Void> andMono = set.and("anotherBitset);
|
||||||
|
Mono<Void> xorMono = set.xor("anotherBitset");
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Code example of **[RxJava3](https://static.javadoc.io/org.redisson/redisson/latest/org/redisson/api/RBitSetRx.html) interface** usage:
|
||||||
|
```java
|
||||||
|
RedissonRxClient redisson = redissonClient.rxJava();
|
||||||
|
RBitSetRx stream = redisson.getBitSet("simpleBitset");
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Single<Boolean> setRx = set.set(0, true);
|
||||||
|
Single<Boolean> setRx = set.set(1812, false);
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Completable clearRx = set.clear(0);
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Completable andRx = set.and("anotherBitset);
|
||||||
|
Completable xorRx = set.xor("anotherBitset");
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
### Data partitioning
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Although 'RBitSet' object is cluster compatible its content isn't scaled across multiple master nodes. BitSet data partitioning available only in cluster mode and implemented by separate `RClusteredBitSet` object. It uses distributed implementation of roaring bitmap structure. Size is limited by whole Cluster memory. More details about partitioning [here](data-partitioning.md).
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Below is the list of all available BitSet implementations:
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|RedissonClient <br/> method name | Data partitioning <br/> support | Ultra-fast read/write |
|
||||||
|
| ------------- | :----------:| :----------:|
|
||||||
|
|getBitSet()<br/><sub><i>open-source version</i></sub> | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||||
|
|getBitSet()<br/><sub><i>[Redisson PRO](https://redisson.pro) version</i></sub> | ❌ | ✔️ |
|
||||||
|
|getClusteredBitSet()<br/><sub><i>available only in [Redisson PRO](https://redisson.pro)</i></sub> | ✔️ | ✔️ |
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Code example:
|
||||||
|
```java
|
||||||
|
RClusteredBitSet set = redisson.getClusteredBitSet("simpleBitset");
|
||||||
|
set.set(0, true);
|
||||||
|
set.set(1812, false);
|
||||||
|
set.clear(0);
|
||||||
|
set.addAsync("e");
|
||||||
|
set.xor("anotherBitset");
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
## Bloom filter
|
||||||
|
Redis or Valkey based distributed [RBloomFilter](https://static.javadoc.io/org.redisson/redisson/latest/org/redisson/api/RBloomFilter.html) bloom filter for Java. Number of contained bits is limited to `2^32` with [data partitioning](data-partitioning.md) to `2^63`
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Must be initialized with capacity size by `tryInit(expectedInsertions, falseProbability)` method before usage.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
```java
|
||||||
|
RBloomFilter<SomeObject> bloomFilter = redisson.getBloomFilter("sample");
|
||||||
|
// initialize bloom filter with
|
||||||
|
// expectedInsertions = 55000000
|
||||||
|
// falseProbability = 0.03
|
||||||
|
bloomFilter.tryInit(55000000L, 0.03);
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
bloomFilter.add(new SomeObject("field1Value", "field2Value"));
|
||||||
|
bloomFilter.add(new SomeObject("field5Value", "field8Value"));
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
bloomFilter.contains(new SomeObject("field1Value", "field8Value"));
|
||||||
|
bloomFilter.count();
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
### Data partitioning
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
_This feature available only in [Redisson PRO](https://redisson.pro) edition._
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Although 'RBloomFilter' object is cluster compatible its content isn't scaled across multiple master nodes. Bloom Filter data partitioning support available only in cluster mode and implemented by separate `RClusteredBloomFilter` object. This implementation uses more efficient distributed memory allocation algorithm. It allows to "shrink" memory space consumed by unused bits across all Redis or Valkey nodes. State of each instance is partitioned across all nodes in Redis or Valkey cluster. Number of contained bits is limited to `2^63`. More details about partitioning [here](data-partitioning.md).
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Below is the list of all available BloomFilter implementations:
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|RedissonClient <br/> method name | Data partitioning <br/> support | Ultra-fast read/write | Bits amount limit |
|
||||||
|
| ------------- | :----------:| :----------:| :----------:|
|
||||||
|
|getBloomFilter()<br/><sub><i>open-source version</i></sub> | ❌ | ❌ | 2^32 |
|
||||||
|
|getBloomFilter()<br/><sub><i>[Redisson PRO](https://redisson.pro) version</i></sub> | ❌ | ✔️ | 2^32 |
|
||||||
|
|getClusteredBloomFilter()<br/><sub><i>available only in [Redisson PRO](https://redisson.pro)</i></sub> | ✔️ | ✔️ | **2^63** |
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
```java
|
||||||
|
RClusteredBloomFilter<SomeObject> bloomFilter = redisson.getClusteredBloomFilter("sample");
|
||||||
|
// initialize bloom filter with
|
||||||
|
// expectedInsertions = 255000000
|
||||||
|
// falseProbability = 0.03
|
||||||
|
bloomFilter.tryInit(255000000L, 0.03);
|
||||||
|
bloomFilter.add(new SomeObject("field1Value", "field2Value"));
|
||||||
|
bloomFilter.add(new SomeObject("field5Value", "field8Value"));
|
||||||
|
bloomFilter.contains(new SomeObject("field1Value", "field8Value"));
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
## HyperLogLog
|
||||||
|
Redis or Valkey based distributed [RHyperLogLog](https://static.javadoc.io/org.redisson/redisson/latest/org/redisson/api/RHyperLogLog.html) object for Java. Probabilistic data structure that lets you maintain counts of millions of items with extreme space efficiency.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
It has [Async](https://static.javadoc.io/org.redisson/redisson/latest/org/redisson/api/RHyperLogLogAsync.html), [Reactive](https://static.javadoc.io/org.redisson/redisson/latest/org/redisson/api/RHyperLogLogReactive.html) and [RxJava3](https://static.javadoc.io/org.redisson/redisson/latest/org/redisson/api/RHyperLogLogRx.html) interfaces.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
```java
|
||||||
|
RHyperLogLog<Integer> log = redisson.getHyperLogLog("log");
|
||||||
|
log.add(1);
|
||||||
|
log.add(2);
|
||||||
|
log.add(3);
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
log.count();
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
## RateLimiter
|
||||||
|
Redis or Valkey based distributed [RateLimiter](https://static.javadoc.io/org.redisson/redisson/latest/org/redisson/api/RRateLimiter.html) object for Java restricts the total rate of calls either from all threads regardless of Redisson instance or from all threads working with the same Redisson instance. Doesn't guarantee fairness.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Code example:
|
||||||
|
```java
|
||||||
|
RRateLimiter limiter = redisson.getRateLimiter("myLimiter");
|
||||||
|
// Initialization required only once.
|
||||||
|
// 5 permits per 2 seconds
|
||||||
|
limiter.trySetRate(RateType.OVERALL, 5, 2, RateIntervalUnit.SECONDS);
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
// acquire 3 permits or block until they became available
|
||||||
|
limiter.acquire(3);
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Code example of **[Async](https://static.javadoc.io/org.redisson/redisson/latest/org/redisson/api/RRateLimiterAsync.html) interface** usage:
|
||||||
|
```java
|
||||||
|
RRateLimiter limiter = redisson.getRateLimiter("myLimiter");
|
||||||
|
// Initialization required only once.
|
||||||
|
// 5 permits per 2 seconds
|
||||||
|
RFuture<Boolean> setRateFuture = limiter.trySetRate(RateType.OVERALL, 5, 2, RateIntervalUnit.SECONDS);
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
// acquire 3 permits or block until they became available
|
||||||
|
RFuture<Void> aquireFuture = limiter.acquire(3);
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Code example of **[Reactive](https://static.javadoc.io/org.redisson/redisson/latest/org/redisson/api/RRateLimiterReactive.html) interface** usage:
|
||||||
|
```java
|
||||||
|
RedissonReactiveClient redisson = redissonClient.reactive();
|
||||||
|
RRateLimiterReactive limiter = redisson.getRateLimiter("myLimiter");
|
||||||
|
// Initialization required only once.
|
||||||
|
// 5 permits per 2 seconds
|
||||||
|
Mono<Boolean> setRateMono = limiter.trySetRate(RateType.OVERALL, 5, 2, RateIntervalUnit.SECONDS);
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
// acquire 3 permits or block until they became available
|
||||||
|
Mono<Void> aquireMono = limiter.acquire(3);
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Code example of **[RxJava3](https://static.javadoc.io/org.redisson/redisson/latest/org/redisson/api/RRateLimiterRx.html) interface** usage:
|
||||||
|
```java
|
||||||
|
RedissonRxClient redisson = redissonClient.rxJava();
|
||||||
|
RRateLimiterRx limiter = redisson.getRateLimiter("anyObject");
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
// Initialization required only once.
|
||||||
|
// 5 permits per 2 seconds
|
||||||
|
Single<Boolean> setRateRx = limiter.trySetRate(RateType.OVERALL, 5, 2, RateIntervalUnit.SECONDS);
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
// acquire 3 permits or block until they became available
|
||||||
|
Completable aquireRx = limiter.acquire(3);
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
@ -0,0 +1,262 @@
|
|||||||
|
## Topic
|
||||||
|
Java implementation of Redis or Valkey based [RTopic](https://static.javadoc.io/org.redisson/redisson/latest/org/redisson/api/RTopic.html) object implements Publish / Subscribe mechanism. It allows to subscribe on events published with multiple instances of `RTopic` object with the same name.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Listeners are re-subscribed automatically after reconnection or failover. All messages sent during absence of connection are lost. Use [Reliable Topic](#reliable-topic) for reliable delivery.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Code example:
|
||||||
|
```java
|
||||||
|
RTopic topic = redisson.getTopic("myTopic");
|
||||||
|
int listenerId = topic.addListener(SomeObject.class, new MessageListener<SomeObject>() {
|
||||||
|
@Override
|
||||||
|
public void onMessage(String channel, SomeObject message) {
|
||||||
|
//...
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
});
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
// in other thread or JVM
|
||||||
|
RTopic topic = redisson.getTopic("myTopic");
|
||||||
|
long clientsReceivedMessage = topic.publish(new SomeObject());
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Code example of **[Async](https://static.javadoc.io/org.redisson/redisson/latest/org/redisson/api/RTopicAsync.html) interface** usage:
|
||||||
|
```java
|
||||||
|
RTopicAsync topic = redisson.getTopic("myTopic");
|
||||||
|
RFuture<Integer> listenerFuture = topic.addListenerAsync(SomeObject.class, new MessageListener<SomeObject>() {
|
||||||
|
@Override
|
||||||
|
public void onMessage(String channel, SomeObject message) {
|
||||||
|
//...
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
});
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
// in other thread or JVM
|
||||||
|
RTopicAsync topic = redisson.getTopic("myTopic");
|
||||||
|
RFuture<Long> publishFuture = topic.publishAsync(new SomeObject());
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Code example of **[Reactive](https://static.javadoc.io/org.redisson/redisson/latest/org/redisson/api/RTopicReactive.html) interface** usage:
|
||||||
|
```java
|
||||||
|
RedissonReactiveClient redisson = redissonClient.reactive();
|
||||||
|
RTopicReactive topic = redisson.getTopic("myTopic");
|
||||||
|
Mono<Integer> listenerMono = topic.addListener(SomeObject.class, new MessageListener<SomeObject>() {
|
||||||
|
@Override
|
||||||
|
public void onMessage(String channel, SomeObject message) {
|
||||||
|
//...
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
});
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
// in other thread or JVM
|
||||||
|
RTopicReactive topic = redisson.getTopic("myTopic");
|
||||||
|
Mono<Long> publishMono = topic.publish(new SomeObject());
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Code example of **[RxJava3](https://static.javadoc.io/org.redisson/redisson/latest/org/redisson/api/RTopicRx.html) interface** usage:
|
||||||
|
```java
|
||||||
|
RedissonRxClient redisson = redissonClient.rxJava();
|
||||||
|
RTopicRx topic = redisson.getTopic("myTopic");
|
||||||
|
Single<Integer> listenerMono = topic.addListener(SomeObject.class, new MessageListener<SomeObject>() {
|
||||||
|
@Override
|
||||||
|
public void onMessage(String channel, SomeObject message) {
|
||||||
|
//...
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
});
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
// in other thread or JVM
|
||||||
|
RTopicRx topic = redisson.getTopic("myTopic");
|
||||||
|
Single<Long> publishMono = topic.publish(new SomeObject());
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
## Topic pattern
|
||||||
|
Java implementation of Redis or Valkey based [RPatternTopic](https://static.javadoc.io/org.redisson/redisson/latest/org/redisson/api/RPatternTopic.html) object. It allows to subscribe to multiple topics by specified glob-style pattern.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Listeners are re-subscribed automatically after reconnection to a server or failover.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Pattern examples:
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
* `topic?` subscribes to `topic1`, `topicA` ...
|
||||||
|
* `topic?_my` subscribes to `topic_my`, `topic123_my`, `topicTEST_my` ...
|
||||||
|
* `topic[ae]` subscribes to `topica` and `topice` only
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Code example:
|
||||||
|
```java
|
||||||
|
// subscribe to all topics by `topic*` pattern
|
||||||
|
RPatternTopic patternTopic = redisson.getPatternTopic("topic*");
|
||||||
|
int listenerId = patternTopic.addListener(Message.class, new PatternMessageListener<Message>() {
|
||||||
|
@Override
|
||||||
|
public void onMessage(String pattern, String channel, Message msg) {
|
||||||
|
//...
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
});
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Code example of **[Async](https://static.javadoc.io/org.redisson/redisson/latest/org/redisson/api/RPatternTopicAsync.html) interface** usage:
|
||||||
|
```java
|
||||||
|
RPatternTopicAsync patternTopic = redisson.getPatternTopic("topic*");
|
||||||
|
RFuture<Integer> listenerFuture = patternTopic.addListenerAsync(Message.class, new PatternMessageListener<Message>() {
|
||||||
|
@Override
|
||||||
|
public void onMessage(String pattern, String channel, Message msg) {
|
||||||
|
//...
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
});
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Code example of **[Reactive](https://static.javadoc.io/org.redisson/redisson/latest/org/redisson/api/RPatternTopicReactive.html) interface** usage:
|
||||||
|
```java
|
||||||
|
RedissonReactiveClient redisson = redissonClient.reactive();
|
||||||
|
RTopicReactive patternTopic = redisson.getPatternTopic("topic*");
|
||||||
|
Mono<Integer> listenerMono = patternTopic.addListener(Message.class, new PatternMessageListener<Message>() {
|
||||||
|
@Override
|
||||||
|
public void onMessage(String pattern, String channel, Message msg) {
|
||||||
|
//...
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
});
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Code example of **[RxJava3](https://static.javadoc.io/org.redisson/redisson/latest/org/redisson/api/RPatternTopicRx.html) interface** usage:
|
||||||
|
```java
|
||||||
|
RedissonRxClient redisson = redissonClient.rxJava();
|
||||||
|
RTopicRx patternTopic = redisson.getPatternTopic("topic*");
|
||||||
|
Single<Integer> listenerSingle = patternTopic.addListener(Message.class, new PatternMessageListener<Message>() {
|
||||||
|
@Override
|
||||||
|
public void onMessage(String pattern, String channel, Message msg) {
|
||||||
|
//...
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
});
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
## Sharded topic
|
||||||
|
Java implementation of Redis or Valkey based [RShardedTopic](https://static.javadoc.io/org.redisson/redisson/latest/org/redisson/api/RShardedTopic.html) object implements Sharded Publish / Subscribe mechanism. It allows to subscribe on events published with multiple instances of `RShardedTopic` object with the same name. Subscribe/publish operations are executed only on Redis or Valkey node in Cluster which is bounded to specific topic name. Published messages via `RShardedTopic` aren't broadcasted across all nodes as for `RTopic` object. Which reduces network bandwidth and Redis or Valkey load.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Listeners are re-subscribed automatically after reconnection to a server or failover. All messages sent during absence of connection are lost. Use [Reliable Topic](#reliable-topic) for reliable delivery.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Code example:
|
||||||
|
```java
|
||||||
|
RShardedTopic topic = redisson.getShardedTopic("myTopic");
|
||||||
|
int listenerId = topic.addListener(SomeObject.class, new MessageListener<SomeObject>() {
|
||||||
|
@Override
|
||||||
|
public void onMessage(String channel, SomeObject message) {
|
||||||
|
//...
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
});
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
// in other thread or JVM
|
||||||
|
RShardedTopic topic = redisson.getShardedTopic("myTopic");
|
||||||
|
long clientsReceivedMessage = topic.publish(new SomeObject());
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Code example of **[Async](https://static.javadoc.io/org.redisson/redisson/latest/org/redisson/api/RShardedTopicAsync.html) interface** usage:
|
||||||
|
```java
|
||||||
|
RShardedTopicAsync topic = redisson.getShardedTopic("myTopic");
|
||||||
|
RFuture<Integer> listenerFuture = topic.addListenerAsync(SomeObject.class, new MessageListener<SomeObject>() {
|
||||||
|
@Override
|
||||||
|
public void onMessage(String channel, SomeObject message) {
|
||||||
|
//...
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
});
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
// in other thread or JVM
|
||||||
|
RShardedTopicAsync topic = redisson.getShardedTopic("myTopic");
|
||||||
|
RFuture<Long> publishFuture = topic.publishAsync(new SomeObject());
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Code example of **[Reactive](https://static.javadoc.io/org.redisson/redisson/latest/org/redisson/api/RShardedTopicReactive.html) interface** usage:
|
||||||
|
```java
|
||||||
|
RedissonReactiveClient redisson = redissonClient.reactive();
|
||||||
|
RShardedTopicReactive topic = redisson.getShardedTopic("myTopic");
|
||||||
|
Mono<Integer> listenerMono = topic.addListener(SomeObject.class, new MessageListener<SomeObject>() {
|
||||||
|
@Override
|
||||||
|
public void onMessage(String channel, SomeObject message) {
|
||||||
|
//...
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
});
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
// in other thread or JVM
|
||||||
|
RShardedTopicReactive topic = redisson.getShardedTopic("myTopic");
|
||||||
|
Mono<Long> publishMono = topic.publish(new SomeObject());
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Code example of **[RxJava3](https://static.javadoc.io/org.redisson/redisson/latest/org/redisson/api/RShardedTopicRx.html) interface** usage:
|
||||||
|
```java
|
||||||
|
RedissonRxClient redisson = redissonClient.rxJava();
|
||||||
|
RShardedTopicRx topic = redisson.getShardedTopic("myTopic");
|
||||||
|
Single<Integer> listenerMono = topic.addListener(SomeObject.class, new MessageListener<SomeObject>() {
|
||||||
|
@Override
|
||||||
|
public void onMessage(String channel, SomeObject message) {
|
||||||
|
//...
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
});
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
// in other thread or JVM
|
||||||
|
RShardedTopicRx topic = redisson.getShardedTopic("myTopic");
|
||||||
|
Single<Long> publishMono = topic.publish(new SomeObject());
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
## Reliable Topic
|
||||||
|
Java implementation of Redis or Valkey based [RReliableTopic](https://static.javadoc.io/org.redisson/redisson/latest/org/redisson/api/RReliableTopic.html) object implements Publish / Subscribe mechanism with reliable delivery of messages. In case of Redis or Valkey connection interruption all missed messages are delivered after reconnection to Redis. Message considered as delivered when it was received by Redisson and submited for processing by topic listeners.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Each `RReliableTopic` object instance (subscriber) has own watchdog which is started when the first listener was registered. Subscriber expires after `org.redisson.config.Config#reliableTopicWatchdogTimeout` timeout if watchdog didn't extend it to the next timeout time interval. This prevents against infinity grow of stored messages in topic due to Redisson client crash or any other reason when subscriber unable to consume messages.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Topic listeners are resubscribed automatically after reconnection to a server or failover.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Code example:
|
||||||
|
```java
|
||||||
|
RReliableTopic topic = redisson.getReliableTopic("anyTopic");
|
||||||
|
topic.addListener(SomeObject.class, new MessageListener<SomeObject>() {
|
||||||
|
@Override
|
||||||
|
public void onMessage(CharSequence channel, SomeObject message) {
|
||||||
|
//...
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
});
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
// in other thread or JVM
|
||||||
|
RReliableTopic topic = redisson.getReliableTopic("anyTopic");
|
||||||
|
long subscribersReceivedMessage = topic.publish(new SomeObject());
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Code example of **[Async](https://static.javadoc.io/org.redisson/redisson/latest/org/redisson/api/RReliableTopicAsync.html) interface** usage:
|
||||||
|
```java
|
||||||
|
RReliableTopicAsync topic = redisson.getReliableTopic("anyTopic");
|
||||||
|
RFuture<String> listenerFuture = topic.addListenerAsync(SomeObject.class, new MessageListener<SomeObject>() {
|
||||||
|
@Override
|
||||||
|
public void onMessage(CharSequence channel, SomeObject message) {
|
||||||
|
//...
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
});
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
// in other thread or JVM
|
||||||
|
RReliableTopicAsync topic = redisson.getReliableTopic("anyTopic");
|
||||||
|
RFuture<Long> future = topic.publishAsync(new SomeObject());
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Code example of **[Reactive](https://static.javadoc.io/org.redisson/redisson/latest/org/redisson/api/RReliableTopicReactive.html) interface** usage:
|
||||||
|
```java
|
||||||
|
RedissonReactiveClient redisson = redissonClient.reactive();
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
RReliableTopicReactive topic = redisson.getReliableTopic("anyTopic");
|
||||||
|
Mono<String> listenerMono = topic.addListener(SomeObject.class, new MessageListener<SomeObject>() {
|
||||||
|
@Override
|
||||||
|
public void onMessage(CharSequence channel, SomeObject message) {
|
||||||
|
//...
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
});
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
// in other thread or JVM
|
||||||
|
RReliableTopicReactive topic = redisson.getReliableTopic("anyTopic");
|
||||||
|
Mono<Long> publishMono = topic.publish(new SomeObject());
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Code example of **[RxJava3](https://static.javadoc.io/org.redisson/redisson/latest/org/redisson/api/RReliableTopicRx.html) interface** usage:
|
||||||
|
```java
|
||||||
|
RedissonRxClient redisson = redissonClient.rxJava();
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
RReliableTopicRx topic = redisson.getReliableTopic("anyTopic");
|
||||||
|
Single<String> listenerRx = topic.addListener(SomeObject.class, new MessageListener<SomeObject>() {
|
||||||
|
@Override
|
||||||
|
public void onMessage(CharSequence channel, SomeObject message) {
|
||||||
|
//...
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
});
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
// in other thread or JVM
|
||||||
|
RReliableTopicRx topic = redisson.getReliableTopic("anyTopic");
|
||||||
|
Single<Long> publisRx = topic.publish(new SomeObject());
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
File diff suppressed because it is too large
Load Diff
@ -0,0 +1,26 @@
|
|||||||
|
Below is the libraries used by Redisson:
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
| Group id | Artifact Id | Version | Dependency |
|
||||||
|
| ------------- | ------------- | ------------| ------------|
|
||||||
|
| com.esotericsoftware | kryo | 5.4+| **required** (if Kryo is used as codec)|
|
||||||
|
| com.esotericsoftware | reflectasm | 1.11+ | **required** (if Kryo is used as codec)|
|
||||||
|
| com.esotericsoftware | minlog | 1.3+ | **required** (if Kryo is used as codec)|
|
||||||
|
| org.objenesis | objenesis| 3.3+ | **required** (if Kryo is used as codec)|
|
||||||
|
| io.netty | netty-common | 4.1+ | **required**|
|
||||||
|
| io.netty | netty-codec | 4.1+ | **required** |
|
||||||
|
| io.netty | netty-buffer | 4.1+ | **required** |
|
||||||
|
| io.netty | netty-transport | 4.1+ | **required** |
|
||||||
|
| io.netty | netty-handler | 4.1+ | **required** |
|
||||||
|
| io.netty | netty-resolver | 4.1+ | **required** |
|
||||||
|
| io.netty | netty-resolver-dns | 4.1+ | **required** |
|
||||||
|
| com.fasterxml.jackson.dataformat | jackson-core | 2.7+ | **required** |
|
||||||
|
| com.fasterxml.jackson.dataformat | jackson-databind | 2.7+ | **required** |
|
||||||
|
| com.fasterxml.jackson.dataformat | jackson-annotations | 2.7+ | **required** |
|
||||||
|
| com.fasterxml.jackson.dataformat | jackson-dataformat-yaml | 2.7+ | **required** |
|
||||||
|
| org.yaml | snakeyaml | 1.0+ | **required** |
|
||||||
|
| net.bytebuddy | byte-buddy | 1.6+ | _optional (used by LiveObject service)_ |
|
||||||
|
| org.jodd | jodd-bean | 3.7+ | _optional (used by LiveObject service)_ |
|
||||||
|
| javax.cache | cache-api | 1.1.1 | _optional (used by JCache implementation)_ |
|
||||||
|
| io.projectreactor | reactor-core | 3.1+ | _optional (used by RedissonReactiveClient)_ |
|
||||||
|
| io.reactivex.rxjava3 | rxjava | 3.0+ | _optional (used by RedissonRxClient)_ |
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
@ -0,0 +1,81 @@
|
|||||||
|
**1. Add dependency**
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
``` python
|
||||||
|
import tensorflow as tf
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Maven
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
```xml
|
||||||
|
<dependency>
|
||||||
|
<groupId>org.redisson</groupId>
|
||||||
|
<artifactId>redisson</artifactId>
|
||||||
|
<version>xVERSIONx</version>
|
||||||
|
</dependency>
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Gradle
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
```java
|
||||||
|
compile 'org.redisson:redisson:xVERSIONx'
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
SBT
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
```java
|
||||||
|
libraryDependencies += "org.redisson" % "redisson" % "xVERSIONx"
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
**2. Start development**
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
```java
|
||||||
|
// 1. Create config object
|
||||||
|
Config config = new Config();
|
||||||
|
config.useClusterServers()
|
||||||
|
// use "rediss://" for SSL connection
|
||||||
|
.addNodeAddress("redis://127.0.0.1:7181");
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
// or read config from file
|
||||||
|
config = Config.fromYAML(new File("config-file.yaml"));
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
```java
|
||||||
|
// 2. Create Redisson instance
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
// Sync and Async API
|
||||||
|
RedissonClient redisson = Redisson.create(config);
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
// Reactive API
|
||||||
|
RedissonReactiveClient redissonReactive = redisson.reactive();
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
// RxJava3 API
|
||||||
|
RedissonRxClient redissonRx = redisson.rxJava();
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
```java
|
||||||
|
// 3. Get Redis or Valkey based implementation of java.util.concurrent.ConcurrentMap
|
||||||
|
RMap<MyKey, MyValue> map = redisson.getMap("myMap");
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
RMapReactive<MyKey, MyValue> mapReactive = redissonReactive.getMap("myMap");
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
RMapRx<MyKey, MyValue> mapRx = redissonRx.getMap("myMap");
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
```java
|
||||||
|
// 4. Get Redis or Valkey based implementation of java.util.concurrent.locks.Lock
|
||||||
|
RLock lock = redisson.getLock("myLock");
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
RLockReactive lockReactive = redissonReactive.getLock("myLock");
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
RLockRx lockRx = redissonRx.getLock("myLock");
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
```java
|
||||||
|
// 4. Get Redis or Valkey based implementation of java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService
|
||||||
|
RExecutorService executor = redisson.getExecutorService("myExecutorService");
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
// over 50 Redis or Valkey based Java objects and services ...
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Upgrade to __[Redisson PRO](https://redisson.pro)__ with **advanced features**.
|
||||||
Binary file not shown.
|
After Width: | Height: | Size: 14 KiB |
@ -0,0 +1,30 @@
|
|||||||
|
Redisson uses high-perfomance async and lock-free Java client for Redis or Valkey. It supports both async and sync modes. The most popular use case is to execute a command not supported by Redisson yet. Please make sure that required command is not supported already with [Redis or Valkey command mapping](commands-mapping.md) list. `org.redisson.client.protocol.RedisCommands` - contains all available commands. Code example:
|
||||||
|
``` java
|
||||||
|
// Use shared EventLoopGroup only if multiple clients are used
|
||||||
|
EventLoopGroup group = new NioEventLoopGroup();
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
RedisClientConfig config = new RedisClientConfig();
|
||||||
|
config.setAddress("redis://localhost:6379") // or rediss:// for ssl connection
|
||||||
|
.setPassword("myPassword")
|
||||||
|
.setDatabase(0)
|
||||||
|
.setClientName("myClient")
|
||||||
|
.setGroup(group);
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
RedisClient client = RedisClient.create(config);
|
||||||
|
RedisConnection conn = client.connect();
|
||||||
|
//or
|
||||||
|
CompletionStage<RedisConnection> connFuture = client.connectAsync();
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
// execute SET command in sync way
|
||||||
|
conn.sync(StringCodec.INSTANCE, RedisCommands.SET, "test", 0);
|
||||||
|
// execute GET command in async way
|
||||||
|
conn.async(StringCodec.INSTANCE, RedisCommands.GET, "test");
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
conn.close()
|
||||||
|
// or
|
||||||
|
conn.closeAsync()
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
client.shutdown();
|
||||||
|
// or
|
||||||
|
client.shutdownAsync();
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
@ -0,0 +1,257 @@
|
|||||||
|
## Spring Boot
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
For Spring Boot usage please refer to [Spring Boot](integration-with-spring.md/#spring-boot-starter) article.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
## Micronaut
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Redisson integrates with [Micronaut](https://micronaut.io/) framework.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Supports Micronaut 2.0.x - 4.x.x
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
### Usage
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
**1. Add `redisson-micronaut` dependency into your project:**
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Maven
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
```xml
|
||||||
|
<dependency>
|
||||||
|
<groupId>org.redisson</groupId>
|
||||||
|
<!-- for Micronaut v2.0.x - v2.5.x -->
|
||||||
|
<artifactId>redisson-micronaut-20</artifactId>
|
||||||
|
<!-- for Micronaut v3.x.x -->
|
||||||
|
<artifactId>redisson-micronaut-30</artifactId>
|
||||||
|
<!-- for Micronaut v4.x.x -->
|
||||||
|
<artifactId>redisson-micronaut-40</artifactId>
|
||||||
|
<version>xVERSIONx</version>
|
||||||
|
</dependency>
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Gradle
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
```groovy
|
||||||
|
// for Micronaut v2.0.x - v2.5.x
|
||||||
|
compile 'org.redisson:redisson-micronaut-20:xVERSIONx'
|
||||||
|
// for Micronaut v3.x.x
|
||||||
|
compile 'org.redisson:redisson-micronaut-30:xVERSIONx'
|
||||||
|
// for Micronaut v4.x.x
|
||||||
|
compile 'org.redisson:redisson-micronaut-40:xVERSIONx'
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
**2. Add settings into `application.yml` file**
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Config structure is a Redisson YAML configuration -
|
||||||
|
[single mode](configuration.md/#single-yaml-config-format),
|
||||||
|
[replicated mode](configuration.md/#replicated-yaml-config-format),
|
||||||
|
[cluster mode](configuration.md/#cluster-yaml-config-format),
|
||||||
|
[sentinel mode](configuration.md/#sentinel-yaml-config-format),
|
||||||
|
[proxy mode](configuration.md/#proxy-mode-yaml-config-format),
|
||||||
|
[multi cluster mode](configuration.md/#multi-cluster-yaml-config-format),
|
||||||
|
[multi sentinel mode](configuration.md/#multi-sentinel-yaml-config-format)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
NOTE: Setting names in camel case should be joined with hyphens (-).
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Config example:
|
||||||
|
```yaml
|
||||||
|
redisson:
|
||||||
|
single-server-config:
|
||||||
|
address: "redis://127.0.0.1:6379"
|
||||||
|
threads: 16
|
||||||
|
netty-threads: 32
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Upgrade to __[Redisson PRO](https://redisson.pro)__ with **advanced features**.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
### Cache
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
For Micronaut Cache usage please refer to [Micronaut Cache](cache-api-implementations.md/#micronaut-cache) article.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
### Session
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Redisson provides Micronanut [Session](https://docs.micronaut.io/latest/api/io/micronaut/session/Session.html) store implementation.
|
||||||
|
Extra settings to [HttpSessionConfiguration](https://docs.micronaut.io/2.5.4/api/io/micronaut/session/http/HttpSessionConfiguration.html) object:
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|Setting name|Type|Description|
|
||||||
|
|------------|----|-----------|
|
||||||
|
|micronaut.session.http.redisson.enabled|java.lang.Boolean|Enables Session store|
|
||||||
|
|micronaut.session.http.redisson.key-prefix|java.lang.Integer|Defines string prefix applied to all objects stored in Redis.|
|
||||||
|
|micronaut.session.http.redisson.codec|java.lang.Class|Data codec applied to cache entries. Default is Kryo5Codec codec.|
|
||||||
|
|micronaut.session.http.redisson.update-mode|java.lang.String|Defines session attributes update mode.<br/>`WRITE_BEHIND` - session changes stored asynchronously.<br/>`AFTER_REQUEST` - session changes stored only on `SessionStore#save(Session)` method invocation. Default value.|
|
||||||
|
|micronaut.session.http.redisson.broadcastSessionUpdates|java.lang.Boolean|Defines broadcasting of session updates across all micronaut services.|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Config example:
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
```yaml
|
||||||
|
micronaut:
|
||||||
|
session:
|
||||||
|
http:
|
||||||
|
redisson:
|
||||||
|
enabled: true
|
||||||
|
update-mode: "WRITE_BEHIND"
|
||||||
|
broadcast-session-updates: false
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
## Quarkus
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Redisson integrates with [Quarkus](https://quarkus.io/) framework and implements [Quarkus Cache](https://quarkus.io/guides/cache).
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Supports Quarkus 1.6.x - 3.x.x
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
??? note "Native image with RemoteService. Click to expand"
|
||||||
|
To use RemoteService in native image add **dynamic-proxy.json** and **reflection-config.json** files in `quarkus.native.additional-build-args` setting.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
-H:DynamicProxyConfigurationResources=dynamic-proxy.json,-H:ReflectionConfigurationFiles=reflection-config.json
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
dynamic-proxy.json:
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
[
|
||||||
|
["<Remote Service interface name>"]
|
||||||
|
]
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
reflection-config.json:
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
[
|
||||||
|
{
|
||||||
|
"name":"<Remote Service interface name>",
|
||||||
|
"allDeclaredMethods":true
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
]
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
### Usage
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
**1. Add `redisson-quarkus` dependency into your project:**
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Maven
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
```xml
|
||||||
|
<dependency>
|
||||||
|
<groupId>org.redisson</groupId>
|
||||||
|
<!-- for Quarkus v1.6.x - v1.13.x -->
|
||||||
|
<artifactId>redisson-quarkus-16</artifactId>
|
||||||
|
<!-- for Quarkus v2.x.x -->
|
||||||
|
<artifactId>redisson-quarkus-20</artifactId>
|
||||||
|
<!-- for Quarkus v3.x.x -->
|
||||||
|
<artifactId>redisson-quarkus-30</artifactId>
|
||||||
|
<version>xVERSIONx</version>
|
||||||
|
</dependency>
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Gradle
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
```groovy
|
||||||
|
// for Quarkus v1.6.x - v1.13.x
|
||||||
|
compile 'org.redisson:redisson-quarkus-16:xVERSIONx'
|
||||||
|
// for Quarkus v2.x.x
|
||||||
|
compile 'org.redisson:redisson-quarkus-20:xVERSIONx'
|
||||||
|
// for Quarkus v3.x.x
|
||||||
|
compile 'org.redisson:redisson-quarkus-30:xVERSIONx'
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
**2. Add settings into `application.properties` file**
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Config structure is a flat Redisson YAML configuration -
|
||||||
|
[single mode](configuration.md/#single-yaml-config-format),
|
||||||
|
[replicated mode](configuration.md/#replicated-yaml-config-format),
|
||||||
|
[cluster mode](configuration.md/#cluster-yaml-config-format),
|
||||||
|
[sentinel mode](configuration.md/#sentinel-yaml-config-format),
|
||||||
|
[proxy mode](configuration.md/#proxy-mode-yaml-config-format),
|
||||||
|
[multi cluster mode](configuration.md/#multi-cluster-yaml-config-format),
|
||||||
|
[multi sentinel mode](configuration.md/#multi-sentinel-yaml-config-format)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
NOTE: Setting names in camel case should be joined with hyphens (-).
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Below is the configuration example for a single Redis or Valkey node setup.
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
quarkus.redisson.single-server-config.address=redis://localhost:6379
|
||||||
|
quarkus.redisson.single-server-config.password=null
|
||||||
|
quarkus.redisson.threads=16
|
||||||
|
quarkus.redisson.netty-threads=32
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Use `quarkus.redisson.file` setting to specify path to a config file.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
**3. Use Redisson**
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
```java
|
||||||
|
@Inject
|
||||||
|
RedissonClient redisson;
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Upgrade to __[Redisson PRO](https://redisson.pro)__ with **advanced features**.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
### Cache
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
For Quarkus Cache usage please refer to [Quarkus Cache](cache-api-implementations.md/#quarkus-cache) article.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
## Helidon
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Redisson implements [Helidon](https://helidon.io/) CDI extension for Redis.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Supports Helidon 1.4.x - 4.x.x
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
### Usage
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
**1. Add `redisson-helidon` dependency into your project:**
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Maven
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
```xml
|
||||||
|
<dependency>
|
||||||
|
<groupId>org.redisson</groupId>
|
||||||
|
<!-- for Helidon v1.4.x - v2.5.x -->
|
||||||
|
<artifactId>redisson-helidon-20</artifactId>
|
||||||
|
<!-- for Helidon v3.x.x -->
|
||||||
|
<artifactId>redisson-helidon-30</artifactId>
|
||||||
|
<!-- for Helidon v4.x.x -->
|
||||||
|
<artifactId>redisson-helidon-40</artifactId>
|
||||||
|
<version>xVERSIONx</version>
|
||||||
|
</dependency>
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Gradle
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
```groovy
|
||||||
|
// for Helidon v1.4.x - v2.5.x
|
||||||
|
compile 'org.redisson:redisson-helidon-20:xVERSIONx'
|
||||||
|
// for Helidon v3.x.x
|
||||||
|
compile 'org.redisson:redisson-helidon-30:xVERSIONx'
|
||||||
|
// for Helidon v4.x.x
|
||||||
|
compile 'org.redisson:redisson-helidon-40:xVERSIONx'
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
**2. Add settings into `META-INF/microprofile-config.properties` file**
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Config structure is a flat Redisson YAML configuration -
|
||||||
|
[single mode](configuration.md/#single-yaml-config-format),
|
||||||
|
[replicated mode](configuration.md/#replicated-yaml-config-format),
|
||||||
|
[cluster mode](configuration.md/#cluster-yaml-config-format),
|
||||||
|
[sentinel mode](configuration.md/#sentinel-yaml-config-format),
|
||||||
|
[proxy mode](configuration.md/#proxy-mode-yaml-config-format),
|
||||||
|
[multi cluster mode](configuration.md/#multi-cluster-yaml-config-format),
|
||||||
|
[multi sentinel mode](configuration.md/#multi-sentinel-yaml-config-format)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Below is the configuration example for Redisson instance named `simple`.
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
org.redisson.Redisson.simple.singleServerConfig.address=redis://127.0.0.1:6379
|
||||||
|
org.redisson.Redisson.simple.singleServerConfig.connectionPoolSize=64
|
||||||
|
org.redisson.Redisson.simple.threads=16
|
||||||
|
org.redisson.Redisson.simple.nettyThreads=32
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
**3. Use Redisson**
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
```java
|
||||||
|
@Inject
|
||||||
|
@Named("simple")
|
||||||
|
private RedissonClient redisson;
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
For injection without @Named annotation use instance name - `default`.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Upgrade to __[Redisson PRO](https://redisson.pro)__ with **advanced features**.
|
||||||
@ -0,0 +1,33 @@
|
|||||||
|
Redisson provides API to manage Redis or Valkey nodes.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Code example of operations with **Cluster** setup:
|
||||||
|
```java
|
||||||
|
RedisCluster cluster = redisson.getRedisNodes(RedisNodes.CLUSTER);
|
||||||
|
cluster.pingAll();
|
||||||
|
Collection<RedisClusterMaster> masters = cluster.getMasters();
|
||||||
|
Collection<RedisClusterMaster> slaves = cluster.getSlaves();
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Code example of operations with **Master Slave** setup:
|
||||||
|
```java
|
||||||
|
RedisMasterSlave masterSlave = redisson.getRedisNodes(RedisNodes.MASTER_SLAVE);
|
||||||
|
masterSlave.pingAll();
|
||||||
|
RedisMaster master = masterSlave.getMaster();
|
||||||
|
Collection<RedisSlave> slaves = masterSlave.getSlaves();
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Code example of operations with **Sentinel** setup:
|
||||||
|
```java
|
||||||
|
RedisSentinelMasterSlave sentinelMasterSlave = redisson.getRedisNodes(RedisNodes.SENTINEL_MASTER_SLAVE);
|
||||||
|
sentinelMasterSlave.pingAll();
|
||||||
|
RedisMaster master = sentinelMasterSlave.getMaster();
|
||||||
|
Collection<RedisSlave> slaves = sentinelMasterSlave.getSlaves();
|
||||||
|
Collection<RedisSentinel> sentinels = sentinelMasterSlave.getSentinels();
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Code example of operations with **Single** setup:
|
||||||
|
```java
|
||||||
|
RedisSingle single = redisson.getRedisNodes(RedisNodes.SINGLE);
|
||||||
|
single.pingAll();
|
||||||
|
RedisMaster instance = single.getInstance();
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
@ -0,0 +1,711 @@
|
|||||||
|
## Metrics
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
_This feature is available only in [Redisson PRO](https://redisson.pro)_
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
### Monitoring systems integration
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Redisson provides integration the most popular monitoring systems through [Micrometer](https://micrometer.io/) framework.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
**1. AppOptics**
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Required dependency:
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
* groupId: `io.micrometer`
|
||||||
|
* artifactId: `micrometer-registry-appoptics`
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Class: `org.redisson.config.metrics.AppOpticsMeterRegistryProvider`
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Parameters:
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
* `uri` - AppOptics host uri
|
||||||
|
* `hostTag` - tag mapped to host
|
||||||
|
* `apiToken` - AppOptics api token
|
||||||
|
* `numThreads` - number of threads used by scheduler (default is 2)
|
||||||
|
* `step` - update interval in ISO-8601 format (default is 1 min)
|
||||||
|
* `batchSize` - number of measurements sent per request (default is 500)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
**2. Atlas**
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Required dependency:
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
* groupId: `io.micrometer`
|
||||||
|
* artifactId: `micrometer-registry-atlas`
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Class: `org.redisson.config.metrics.AtlasMeterRegistryProvider`
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Parameters:
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
* `uri` - Atlas host uri
|
||||||
|
* `configUri` - Atlas LWC endpoint uri to retrieve current subscriptions
|
||||||
|
* `evalUri` - Atlas LWC endpoint uri to evaluate the data for a subscription
|
||||||
|
* `numThreads` - number of threads used by scheduler (default is 4)
|
||||||
|
* `step` - update interval in ISO-8601 format (default is 1 min)
|
||||||
|
* `batchSize` - number of measurements sent per request (default is 10000)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
**3. Azure**
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Required dependency:
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
* groupId: `io.micrometer`
|
||||||
|
* artifactId: `micrometer-registry-azure-monitor`
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Class: `org.redisson.config.metrics.AzureMonitorMeterRegistryProvider`
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Parameters:
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
* `instrumentationKey` - instrumentation key
|
||||||
|
* `numThreads` - number of threads used by scheduler (default is 2)
|
||||||
|
* `step` - update interval in ISO-8601 format (default is 1 min)
|
||||||
|
* `batchSize` - number of measurements sent per request (default is 500)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
**4. Amazon CloudWatch**
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Required dependency:
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
* groupId: `io.micrometer`
|
||||||
|
* artifactId: `micrometer-registry-cloudwatch`
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Class: `org.redisson.config.metrics.CloudWatchMeterRegistryProvider`
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Parameters:
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
* `accessKey` - AWS access key
|
||||||
|
* `secretKey` - AWS secret access key
|
||||||
|
* `namespace` - namespace value
|
||||||
|
* `numThreads` - number of threads used by scheduler (default is 2)
|
||||||
|
* `step` - update interval in ISO-8601 format (default is 1 min)
|
||||||
|
* `batchSize` - number of measurements sent per request (default is 500)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
**5. Datadog**
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Required dependency:
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
* groupId: `io.micrometer`
|
||||||
|
* artifactId: `micrometer-registry-datadog`
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Class: `org.redisson.config.metrics.DatadogMeterRegistryProvider`
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Parameters:
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
* `uri` - Datadog host uri
|
||||||
|
* `hostTag` - tag mapped to host
|
||||||
|
* `apiKey` - api key
|
||||||
|
* `numThreads` - number of threads used by scheduler (default is 2)
|
||||||
|
* `step` - update interval in ISO-8601 format (default is 1 min)
|
||||||
|
* `batchSize` - number of measurements sent per request (default is 500)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
**6. Dropwizard**
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Class: `org.redisson.config.metrics.DropwizardMeterRegistryProvider`
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Parameters:
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
* `sharedRegistryName` - name used to store instance in `SharedMetricRegistries`
|
||||||
|
* `nameMapper` - custom implementation of `io.micrometer.core.instrument.util.HierarchicalNameMapper`
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
**7. Dynatrace**
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Class: `org.redisson.config.metrics.DynatraceMeterRegistryProvider`
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Parameters:
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
* `uri` - Dynatrace host uri
|
||||||
|
* `apiToken` - api token
|
||||||
|
* `deviceId` - device id
|
||||||
|
* `numThreads` - number of threads used by scheduler (default is 2)
|
||||||
|
* `step` - update interval in ISO-8601 format (default is 1 min)
|
||||||
|
* `batchSize` - number of measurements sent per request (default is 500)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
**8. Elastic**
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Required dependency:
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
* groupId: `io.micrometer`
|
||||||
|
* artifactId: `micrometer-registry-elastic`
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Class: `org.redisson.config.metrics.ElasticMeterRegistryProvider`
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Parameters:
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
* `host` - Elasticsearch host uri
|
||||||
|
* `userName` - user name
|
||||||
|
* `password` - password
|
||||||
|
* `numThreads` - number of threads used by scheduler (default is 2)
|
||||||
|
* `step` - update interval in ISO-8601 format (default is 1 min)
|
||||||
|
* `batchSize` - number of measurements sent per request (default is 500)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
**9. Ganglia**
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Required dependency:
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
* groupId: `io.micrometer`
|
||||||
|
* artifactId: `micrometer-registry-ganglia`
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Class: `org.redisson.config.metrics.GangliaMeterRegistryProvider`
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Parameters:
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
* `host` - Ganglia host address
|
||||||
|
* `port` - Ganglia port
|
||||||
|
* `numThreads` - number of threads used by scheduler (default is 2)
|
||||||
|
* `step` - update interval in ISO-8601 format (default is 1 min)
|
||||||
|
* `batchSize` - number of measurements sent per request (default is 500)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
**10. Graphite**
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Required dependency:
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
* groupId: `io.micrometer`
|
||||||
|
* artifactId: `micrometer-registry-graphite`
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Class: `org.redisson.config.metrics.GraphiteMeterRegistryProvider`
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Parameters:
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
* `host` - Graphite host address
|
||||||
|
* `port` - Graphite port
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
**11. Humio**
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Required dependency:
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
* groupId: `io.micrometer`
|
||||||
|
* artifactId: `micrometer-registry-humio`
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Class: `org.redisson.config.metrics.HumioMeterRegistryProvider`
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Parameters:
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
* `uri` - Humio host uri
|
||||||
|
* `repository` - repository name
|
||||||
|
* `apiToken` - api token
|
||||||
|
* `numThreads` - number of threads used by scheduler (default is 2)
|
||||||
|
* `step` - update interval in ISO-8601 format (default is 1 min)
|
||||||
|
* `batchSize` - number of measurements sent per request (default is 500)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
**12. Influx**
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Required dependency:
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
* groupId: `io.micrometer`
|
||||||
|
* artifactId: `micrometer-registry-influx`
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Class: `org.redisson.config.metrics.InfluxMeterRegistryProvider`
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Parameters:
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
* `uri` - Influx host uri
|
||||||
|
* `db` - db name
|
||||||
|
* `userName` - user name
|
||||||
|
* `password` - password
|
||||||
|
* `numThreads` - number of threads used by scheduler (default is 2)
|
||||||
|
* `step` - update interval in ISO-8601 format (default is 1 min)
|
||||||
|
* `batchSize` - number of measurements sent per request (default is 500)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
**13. JMX**
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Required dependency:
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
* groupId: `io.micrometer`
|
||||||
|
* artifactId: `micrometer-registry-jmx`
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Class: `org.redisson.config.metrics.JmxMeterRegistryProvider`
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Parameters:
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
* `domain` - domain name
|
||||||
|
* `sharedRegistryName` - name used to store instance in `SharedMetricRegistries`
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
**14. Kairos**
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Required dependency:
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
* groupId: `io.micrometer`
|
||||||
|
* artifactId: `micrometer-registry-kairos`
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Class: `org.redisson.config.metrics.KairosMeterRegistryProvider`
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Parameters:
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
* `uri` - Kairos host uri
|
||||||
|
* `userName` - user name
|
||||||
|
* `password` - password
|
||||||
|
* `numThreads` - number of threads used by scheduler (default is 2)
|
||||||
|
* `step` - update interval in ISO-8601 format (default is 1 min)
|
||||||
|
* `batchSize` - number of measurements sent per request (default is 500)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
**15. NewRelic**
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Required dependency:
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
* groupId: `io.micrometer`
|
||||||
|
* artifactId: `micrometer-registry-new-relic`
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Class: `org.redisson.config.metrics.NewRelicMeterRegistryProvider`
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Parameters:
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
* `uri` - NewRelic host uri
|
||||||
|
* `apiKey` - api key
|
||||||
|
* `accountId` - account id
|
||||||
|
* `numThreads` - number of threads used by scheduler (default is 2)
|
||||||
|
* `step` - update interval in ISO-8601 format (default is 1 min)
|
||||||
|
* `batchSize` - number of measurements sent per request (default is 500)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
**16. Prometheus**
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Required dependency:
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
* groupId: `io.micrometer`
|
||||||
|
* artifactId: `micrometer-registry-prometheus`
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Class: `org.redisson.config.metrics.MeterRegistryWrapper`
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Parameters:
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
* `registry` - instance of `PrometheusMeterRegistry` object
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
**17. SingnalFx**
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Required dependency:
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
* groupId: `io.micrometer`
|
||||||
|
* artifactId: `micrometer-registry-signalfx`
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Class: `org.redisson.config.metrics.SingnalFxMeterRegistryProvider`
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Parameters:
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
* `apiHost` - SingnalFx host uri
|
||||||
|
* `accessToken` - access token
|
||||||
|
* `source` - application instance id
|
||||||
|
* `numThreads` - number of threads used by scheduler (default is 2)
|
||||||
|
* `step` - update interval in ISO-8601 format (default is 10 secs)
|
||||||
|
* `batchSize` - number of measurements sent per request (default is 500)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
**18. Stackdriver**
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Required dependency:
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
* groupId: `io.micrometer`
|
||||||
|
* artifactId: `micrometer-registry-stackdriver`
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Class: `org.redisson.config.metrics.StackdriverMeterRegistryProvider`
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Parameters:
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
* `projectId` - project id
|
||||||
|
* `numThreads` - number of threads used by scheduler (default is 2)
|
||||||
|
* `step` - update interval in ISO-8601 format (default is 1 min)
|
||||||
|
* `batchSize` - number of measurements sent per request (default is 500)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
**19. Statsd**
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Required dependency:
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
* groupId: `io.micrometer`
|
||||||
|
* artifactId: `micrometer-registry-statsd`
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Class: `org.redisson.config.metrics.StatsdMeterRegistryProvider`
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Parameters:
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
* `host` - Statsd host address
|
||||||
|
* `port` - Statsd port
|
||||||
|
* `flavor` - metrics format ETSY/DATADOG/TELEGRAF/SYSDIG
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
**20. Wavefront**
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Required dependency:
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
* groupId: `io.micrometer`
|
||||||
|
* artifactId: `micrometer-registry-wavefront`
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Class: `org.redisson.config.metrics.WavefrontMeterRegistryProvider`
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Parameters:
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
* `uri` - Wavefront host uri
|
||||||
|
* `source` - application instance id
|
||||||
|
* `apiToken` - api token
|
||||||
|
* `numThreads` - number of threads used by scheduler (default is 2)
|
||||||
|
* `step` - update interval in ISO-8601 format (default is 1 min)
|
||||||
|
* `batchSize` - number of measurements sent per request (default is 500)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
### Config examples
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
**JMX config**
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
```java
|
||||||
|
Config config = ... // Redisson PRO config object
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
JmxMeterRegistryProvider provider = new JmxMeterRegistryProvider();
|
||||||
|
provider.setDomain("appStats");
|
||||||
|
config.setMeterRegistryProvider(provider);
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
**Prometheus config**
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
```java
|
||||||
|
Config config = ... // Redisson PRO config object
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
PrometheusMeterRegistry registry = ...
|
||||||
|
config.setMeterRegistryProvider(new MeterRegistryWrapper(registry));
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
**Dynatrace config**
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
```java
|
||||||
|
Config config = ... // Redisson PRO config object
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
DynatraceMeterRegistryProvider p = new DynatraceMeterRegistryProvider();
|
||||||
|
p.setApiToken("Hg3M0iadsQC2Pcjk6QIW0g");
|
||||||
|
p.setUri("https://qtd9012301.live.dynatrace.com/");
|
||||||
|
p.setDeviceId("myHost");
|
||||||
|
config.setMeterRegistryProvider(p);
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
**Influx config**
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
```java
|
||||||
|
Config config = ... // Redisson PRO config object
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
InfluxMeterRegistryProvider provider = new InfluxMeterRegistryProvider();
|
||||||
|
provider.setUri("http://localhost:8086/");
|
||||||
|
provider.setDb("myinfluxdb");
|
||||||
|
provider.setUserName("admin");
|
||||||
|
provider.setPassword("admin");
|
||||||
|
config.setMeterRegistryProvider(provider);
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
### YAML config examples
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
YAML config is appended to Redisson config.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
**JMX config**
|
||||||
|
```yaml
|
||||||
|
meterRegistryProvider: !<org.redisson.config.metrics.JmxMeterRegistryProvider>
|
||||||
|
domain: "appStats"
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
**Dynatrace config**
|
||||||
|
```yaml
|
||||||
|
meterRegistryProvider: !<org.redisson.config.metrics.DynatraceMeterRegistryProvider>
|
||||||
|
apiToken: "Hg3M0iadsQC2Pcjk6QIW0g"
|
||||||
|
uri: "https://qtd9012301.live.dynatrace.com"
|
||||||
|
deviceId: "myHost"
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
**Influx config**
|
||||||
|
```yaml
|
||||||
|
meterRegistryProvider: !<org.redisson.config.metrics.InfluxMeterRegistryProvider>
|
||||||
|
uri: "http://localhost:8086/"
|
||||||
|
db: "myinfluxdb"
|
||||||
|
userName: "admin"
|
||||||
|
password: "admin"
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
### Metrics list
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
The following metrics are available:
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
**Configuration metrics**
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
* `redisson.license.expiration-year` - A Gauge of the number of the license expiration year
|
||||||
|
* `redisson.license.expiration-month` - A Gauge of the number of the license expiration month
|
||||||
|
* `redisson.license.expiration-day` - A Gauge of the number of the license expiration day
|
||||||
|
* `redisson.license.active-instances` - A Gauge of the number of active Redisson PRO clients
|
||||||
|
* `redisson.executor-pool-size` - A Gauge of the number of executor threads pool size
|
||||||
|
* `redisson.netty-pool-size` - A Gauge of the number of netty threads pool size
|
||||||
|
* `netty.eventexecutor.tasks.pending` - Number of pending tasks in Netty event executor
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
**Metrics per Redis or Valkey node**
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Base name: `redisson.redis.<host>:<port>`
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
* `status` - A Gauge of the number value of Redis or Valkey node status [1 = connected, -1 = disconnected]
|
||||||
|
* `type` - A Gauge of the number value of Redis or Valkey node type [1 = MASTER, 2 = SLAVE, 3 = SENTINEL]
|
||||||
|
<br/>
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
* `total-response-bytes` - A Meter of the total amount of bytes received from Redis or Valkey
|
||||||
|
* `response-bytes` - A Histogram of the number of bytes received from Redis or Valkey
|
||||||
|
* `total-request-bytes` - A Meter of the total amount of bytes sent to Redis or Valkey
|
||||||
|
* `request-bytes` - A Histogram of the number of bytes sent to Redis or Valkey
|
||||||
|
<br/>
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
* `connections.active` - A Counter of the number of busy connections
|
||||||
|
* `connections.free` - A Counter of the number of free connections
|
||||||
|
* `connections.max-pool-size` - A Counter of the number of maximum connection pool size
|
||||||
|
* `connections.reconnected` - A Counter of the number of reconnected connections
|
||||||
|
* `connections.total` - A Counter of the number of total connections in pool
|
||||||
|
<br/>
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
* `operations.total` - A Meter of the number of total executed operations
|
||||||
|
* `operations.total-failed` - A Meter of the number of total failed operations
|
||||||
|
* `operations.total-successful` - A Meter of the number of total successful operations
|
||||||
|
* `operations.latency` - A Histogram of the number of operations latency in milliseconds
|
||||||
|
* `operations.retry-attempt` - A Histogram of the number of operations retry attempts
|
||||||
|
<br/>
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
* `publish-subscribe-connections.active` - A Counter of the number of active publish subscribe connections
|
||||||
|
* `publish-subscribe-connections.free` - A Counter of the number of free publish subscribe connections
|
||||||
|
* `publish-subscribe-connections.max-pool-size` - A Counter of the number of maximum publish subscribe connection pool size
|
||||||
|
* `publish-subscribe-connections.total` - A Counter of the number of total publish subscribe connections in pool
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
**Metrics per RRemoteService object**
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Base name: `redisson.remote-service.<name>`
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
* `invocations.total` - A Meter of the number of total executed invocations
|
||||||
|
* `invocations.total-failed` - A Meter of the number of total failed to execute invocations
|
||||||
|
* `invocations.total-successful` - A Meter of the number of total successful to execute invocations
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
**Metrics per RExecutorService object**
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Base name: `redisson.executor-service.<name>`
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
* `tasks.submitted` - A Meter of the number of submitted tasks
|
||||||
|
* `tasks.executed` - A Meter of the number of executed tasks
|
||||||
|
<br/>
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
* `workers.active` - A Gauge of the number of busy task workers
|
||||||
|
* `workers.free` - A Gauge of the number of free task workers
|
||||||
|
* `workers.total` - A Gauge of the number of total task workers
|
||||||
|
* `workers.tasks-executed.total` - A Meter of the number of total executed tasks by workers
|
||||||
|
* `workers.tasks-executed.total-failed` - A Meter of the number of total failed to execute tasks by workers
|
||||||
|
* `workers.tasks-executed.total-successful` - A Meter of the number of total successful to execute tasks by workers
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
**Metrics per RMap object**
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Base name: `redisson.map.<name>`
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
* `hits` - A Meter of the number of get requests for data contained in cache
|
||||||
|
* `misses` - A Meter of the number of get requests for data not contained in cache
|
||||||
|
* `puts` - A Meter of the number of puts to the cache
|
||||||
|
* `removals` - A Meter of the number of removals from the cache
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
**Metrics per RMapCache object**
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Base name: `redisson.map-cache.<name>`
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
* `hits` - A Meter of the number of get requests for data contained in cache
|
||||||
|
* `misses` - A Meter of the number of get requests for data not contained in cache
|
||||||
|
* `puts` - A Meter of the number of puts to the cache
|
||||||
|
* `removals` - A Meter of the number of removals from the cache
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
**Metrics per RMapCacheV2 object**
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Base name: `redisson.map-cache-v2.<name>`
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
* `hits` - A Meter of the number of get requests for data contained in cache
|
||||||
|
* `misses` - A Meter of the number of get requests for data not contained in cache
|
||||||
|
* `puts` - A Meter of the number of puts to the cache
|
||||||
|
* `removals` - A Meter of the number of removals from the cache
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
**Metrics per RMapCacheNative object**
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Base name: `redisson.map-cache-native.<name>`
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
* `hits` - A Meter of the number of get requests for data contained in cache
|
||||||
|
* `misses` - A Meter of the number of get requests for data not contained in cache
|
||||||
|
* `puts` - A Meter of the number of puts to the cache
|
||||||
|
* `removals` - A Meter of the number of removals from the cache
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
**Metrics per RClusteredMapCache object**
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Base name: `redisson.clustered-map-cache.<name>`
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
* `hits` - A Meter of the number of get requests for data contained in cache
|
||||||
|
* `misses` - A Meter of the number of get requests for data not contained in cache
|
||||||
|
* `puts` - A Meter of the number of puts to the cache
|
||||||
|
* `removals` - A Meter of the number of removals from the cache
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
**Metrics per RClusteredMapCacheNative object**
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Base name: `redisson.clustered-map-cache-native.<name>`
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
* `hits` - A Meter of the number of get requests for data contained in cache
|
||||||
|
* `misses` - A Meter of the number of get requests for data not contained in cache
|
||||||
|
* `puts` - A Meter of the number of puts to the cache
|
||||||
|
* `removals` - A Meter of the number of removals from the cache
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
**Metrics per RLocalCachedMap object**
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Base name: `redisson.local-cached-map.<name>`
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
* `hits` - A Meter of the number of get requests for data contained in cache
|
||||||
|
* `misses` - A Meter of the number of get requests for data not contained in cache
|
||||||
|
* `puts` - A Meter of the number of puts to the cache
|
||||||
|
* `removals` - A Meter of the number of removals from the cache
|
||||||
|
<br/>
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
* `local-cache.hits` - A Meter of the number of get requests for data contained in local cache
|
||||||
|
* `local-cache.misses` - A Meter of the number of get requests for data contained in local cache
|
||||||
|
* `local-cache.evictions` - A Meter of the number of evictions for data contained in local cache
|
||||||
|
* `local-cache.size` - A Gauge of the number of local cache size
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
**Metrics per RClusteredLocalCachedMap object**
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Base name: `redisson.clustered-local-cached-map.<name>`
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
* `hits` - A Meter of the number of get requests for data contained in cache
|
||||||
|
* `misses` - A Meter of the number of get requests for data not contained in cache
|
||||||
|
* `puts` - A Meter of the number of puts to the cache
|
||||||
|
* `removals` - A Meter of the number of removals from the cache
|
||||||
|
<br/>
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
* `local-cache.hits` - A Meter of the number of get requests for data contained in local cache
|
||||||
|
* `local-cache.misses` - A Meter of the number of get requests for data contained in local cache
|
||||||
|
* `local-cache.evictions` - A Meter of the number of evictions for data contained in local cache
|
||||||
|
* `local-cache.size` - A Gauge of the number of local cache size
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
**Metrics per RLocalCachedMapCache object**
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Base name: `redisson.local-cached-map-cache.<name>`
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
* `hits` - A Meter of the number of get requests for data contained in cache
|
||||||
|
* `misses` - A Meter of the number of get requests for data not contained in cache
|
||||||
|
* `puts` - A Meter of the number of puts to the cache
|
||||||
|
* `removals` - A Meter of the number of removals from the cache
|
||||||
|
<br/>
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
* `local-cache.hits` - A Meter of the number of get requests for data contained in local cache
|
||||||
|
* `local-cache.misses` - A Meter of the number of get requests for data contained in local cache
|
||||||
|
* `local-cache.evictions` - A Meter of the number of evictions for data contained in local cache
|
||||||
|
* `local-cache.size` - A Gauge of the number of local cache size
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
**Metrics per RLocalCachedMapCacheV2 object**
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Base name: `redisson.local-cached-map-cache-v2.<name>`
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
* `hits` - A Meter of the number of get requests for data contained in cache
|
||||||
|
* `misses` - A Meter of the number of get requests for data not contained in cache
|
||||||
|
* `puts` - A Meter of the number of puts to the cache
|
||||||
|
* `removals` - A Meter of the number of removals from the cache
|
||||||
|
<br/>
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
* `local-cache.hits` - A Meter of the number of get requests for data contained in local cache
|
||||||
|
* `local-cache.misses` - A Meter of the number of get requests for data contained in local cache
|
||||||
|
* `local-cache.evictions` - A Meter of the number of evictions for data contained in local cache
|
||||||
|
* `local-cache.size` - A Gauge of the number of local cache size
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
**Metrics per RLocalCachedMapCacheNative object**
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Base name: `redisson.local-cached-map-cache-native.<name>`
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
* `hits` - A Meter of the number of get requests for data contained in cache
|
||||||
|
* `misses` - A Meter of the number of get requests for data not contained in cache
|
||||||
|
* `puts` - A Meter of the number of puts to the cache
|
||||||
|
* `removals` - A Meter of the number of removals from the cache
|
||||||
|
<br/>
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
* `local-cache.hits` - A Meter of the number of get requests for data contained in local cache
|
||||||
|
* `local-cache.misses` - A Meter of the number of get requests for data contained in local cache
|
||||||
|
* `local-cache.evictions` - A Meter of the number of evictions for data contained in local cache
|
||||||
|
* `local-cache.size` - A Gauge of the number of local cache size
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
**Metrics per RClusteredLocalCachedMapCache object**
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Base name: `redisson.clustered-local-cached-map-cache.<name>`
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
* `hits` - A Meter of the number of get requests for data contained in cache
|
||||||
|
* `misses` - A Meter of the number of get requests for data not contained in cache
|
||||||
|
* `puts` - A Meter of the number of puts to the cache
|
||||||
|
* `removals` - A Meter of the number of removals from the cache
|
||||||
|
<br/>
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
* `local-cache.hits` - A Meter of the number of get requests for data contained in local cache
|
||||||
|
* `local-cache.misses` - A Meter of the number of get requests for data contained in local cache
|
||||||
|
* `local-cache.evictions` - A Meter of the number of evictions for data contained in local cache
|
||||||
|
* `local-cache.size` - A Gauge of the number of local cache size
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
**Metrics per RTopic object**
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Base name: `redisson.topic.<name>`
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
* `messages-sent` - A Meter of the number of messages sent for topic
|
||||||
|
* `messages-received` - A Meter of the number of messages received for topic
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
**Metrics per RBucket object**
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Base name: `redisson.bucket.<name>`
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
* `gets` - A Meter of the number of get operations executed for bucket object
|
||||||
|
* `sets` - A Meter of the number of set operations executed for bucket object
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
**Metrics per JCache object**
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Base name: `redisson.JCache.<name>`
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
* `cache.evictions` - A Meter of the number of evictions for data contained in JCache
|
||||||
|
* `cache.puts` - A Meter of the number of puts to the JCache
|
||||||
|
* `hit.cache.gets` - A Meter of the number of get requests for data contained in JCache
|
||||||
|
* `miss.cache.gets` - A Meter of the number of get requests for data contained in JCache
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
## Tracing
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
_This feature is available only in [Redisson PRO](https://redisson.pro)_
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Redisson provides integration with the most popular tracer libraries through [Micrometer Observation API](https://docs.micrometer.io/micrometer/reference/observation.html) and [Micrometer Tracing](https://docs.micrometer.io/tracing/reference/) framework. This feature allows to gather extra statistics about invoked Redisson methods: name, arguments, invocation path, duration and frequency.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Configuration metrics per Tracing event.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
* `invocation` - Redisson method with arguments. Arguments are included only if `includeArgs` set `true`
|
||||||
|
* `object_name` - Redisson object name
|
||||||
|
* `address` - Redis or Valkey server address
|
||||||
|
* `username` - username used to connect to Redis or Valkey server
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
### OpenZipkin Brave
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Configuration example:
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
```java
|
||||||
|
OkHttpSender sender = OkHttpSender.create("http://localhost:9411/api/v2/spans");
|
||||||
|
AsyncZipkinSpanHandler zipkinSpanHandler = AsyncZipkinSpanHandler.create(sender);
|
||||||
|
StrictCurrentTraceContext braveCurrentTraceContext = StrictCurrentTraceContext.create();
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Tracing tracing = Tracing.newBuilder()
|
||||||
|
.localServiceName("myservice")
|
||||||
|
.currentTraceContext(braveCurrentTraceContext)
|
||||||
|
.sampler(Sampler.ALWAYS_SAMPLE)
|
||||||
|
.addSpanHandler(zipkinSpanHandler)
|
||||||
|
.build();
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
config.setTracingProvider(new BraveTracingProvider(tracing));
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Required dependencies:
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
1. groupId: `io.zipkin.reporter2`, artifactId: `zipkin-sender-okhttp3`
|
||||||
|
2. groupId: `io.zipkin.reporter2`, artifactId: `zipkin-reporter-brave`
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
### OpenTelemetry
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Configuration example:
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
```java
|
||||||
|
SpanExporter spanExporter = new ZipkinSpanExporterBuilder()
|
||||||
|
.setSender(URLConnectionSender.create("http://localhost:9411/api/v2/spans"))
|
||||||
|
.build();
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
SdkTracerProvider sdkTracerProvider = SdkTracerProvider.builder()
|
||||||
|
.addSpanProcessor(BatchSpanProcessor.builder(spanExporter).build())
|
||||||
|
.build();
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
OpenTelemetrySdk openTelemetrySdk = OpenTelemetrySdk.builder()
|
||||||
|
.setPropagators(ContextPropagators.create(B3Propagator.injectingSingleHeader()))
|
||||||
|
.setTracerProvider(sdkTracerProvider)
|
||||||
|
.build();
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
io.opentelemetry.api.trace.Tracer otelTracer = openTelemetrySdk.getTracerProvider().get("io.micrometer.micrometer-tracing");
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
config.setTracingProvider(new OtelTracingProvider(otelTracer, openTelemetrySdk.getPropagators()));
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Required dependencies:
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
1. groupId: `io.opentelemetry`, artifactId: `opentelemetry-exporter-zipkin`
|
||||||
|
2. groupId: `io.zipkin.reporter2`, artifactId: `zipkin-sender-urlconnection`
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
@ -0,0 +1,18 @@
|
|||||||
|
Redisson is the Java Client and Real-Time Data Platform for [Redis](https://redis.io) or [Valkey](https://valkey.io). Providing the most convenient and easiest way to work with Redis or Valkey. Redisson objects provide an abstraction layer between Redis or Valkey and your Java code, which allowing maintain focus on data modeling and application logic.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Redisson is compatible with the following Redis and Valkey cloud providers:
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
* [AWS ElastiCache](https://docs.aws.amazon.com/AmazonElastiCache/latest/UserGuide/Replication.html)
|
||||||
|
* [AWS ElastiCache Cluster](https://docs.aws.amazon.com/AmazonElastiCache/latest/UserGuide/Clusters.html)
|
||||||
|
* [Azure Redis Cache](https://azure.microsoft.com/en-us/services/cache/)
|
||||||
|
* [Google Cloud Memorystore for Redis](https://cloud.google.com/memorystore/docs/redis/)
|
||||||
|
* [HUAWEI Distributed Cache Service for Redis](https://www.huaweicloud.com/en-us/product/dcs.html)
|
||||||
|
* [Aiven Redis hosting](https://aiven.io/redis)
|
||||||
|
* [RLEC Multiple Active Proxy](https://docs.redislabs.com/latest/rs/administering/designing-production/networking/multiple-active-proxy/)
|
||||||
|
* and many others.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Use the [Redis or Valkey commands mapping](commands-mapping.md) table to find the Redisson method for a particular Redis or Valkey command.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Redisson is Based on the [Netty](http://netty.io/) framework and is [Redis](http://redis.io) 3.0+ and JDK 1.8+ compatible.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Try __[Redisson PRO](https://redisson.pro)__ with **advanced features** and **support by SLA**.
|
||||||
@ -0,0 +1,115 @@
|
|||||||
|
Multiple commands can be sent in a batch using `RBatch` object in a single network call. Command batches allows to reduce the overall execution time of a group of commands. In Redis or Valkey this approach called [Pipelining](https://redis.io/topics/pipelining).
|
||||||
|
Follow options could be supplied during object creation:
|
||||||
|
```java
|
||||||
|
BatchOptions options = BatchOptions.defaults()
|
||||||
|
// Sets execution mode
|
||||||
|
//
|
||||||
|
// ExecutionMode.REDIS_READ_ATOMIC - Store batched invocations in Redis and execute them atomically as a single command
|
||||||
|
//
|
||||||
|
// ExecutionMode.REDIS_WRITE_ATOMIC - Store batched invocations in Redis and execute them atomically as a single command
|
||||||
|
//
|
||||||
|
// ExecutionMode.IN_MEMORY - Store batched invocations in memory on Redisson side and execute them on Redis. Default mode
|
||||||
|
//
|
||||||
|
// ExecutionMode.IN_MEMORY_ATOMIC - Store batched invocations on Redisson side and executes them atomically on Redis or Valkey as a single command
|
||||||
|
.executionMode(ExecutionMode.IN_MEMORY)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
// Inform Redis or Valkey not to send reply back to client. This allows to save network traffic for commands with batch with big
|
||||||
|
.skipResult()
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
// Synchronize write operations execution across defined amount of Redis or Valkey slave nodes
|
||||||
|
//
|
||||||
|
// sync with 2 slaves with 1 second for timeout
|
||||||
|
.syncSlaves(2, 1, TimeUnit.SECONDS)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
// Response timeout
|
||||||
|
.responseTimeout(2, TimeUnit.SECONDS)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
// Retry interval for each attempt to send Redis or Valkey commands batch
|
||||||
|
.retryInterval(2, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
// Attempts amount to re-send Redis or Valkey commands batch if it wasn't sent due to network delays or other issues
|
||||||
|
.retryAttempts(4);
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Result Batch object contains follow data:
|
||||||
|
```java
|
||||||
|
// list of result objects per command in batch
|
||||||
|
List<?> responses = res.getResponses();
|
||||||
|
// amount of successfully synchronized slaves during batch execution
|
||||||
|
int slaves = res.getSyncedSlaves();
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
Code example for **Sync / Async** mode:
|
||||||
|
```java
|
||||||
|
RBatch batch = redisson.createBatch(BatchOptions.defaults());
|
||||||
|
batch.getMap("test1").fastPutAsync("1", "2");
|
||||||
|
batch.getMap("test2").fastPutAsync("2", "3");
|
||||||
|
batch.getMap("test3").putAsync("2", "5");
|
||||||
|
RFuture<Long> future = batch.getAtomicLong("counter").incrementAndGetAsync();
|
||||||
|
batch.getAtomicLong("counter").incrementAndGetAsync();
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
// result could be acquired through RFuture object returned by batched method
|
||||||
|
// or
|
||||||
|
// through result list by corresponding index
|
||||||
|
future.whenComplete((res, exception) -> {
|
||||||
|
// ...
|
||||||
|
});
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
BatchResult res = batch.execute();
|
||||||
|
// or
|
||||||
|
Future<BatchResult> resFuture = batch.executeAsync();
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
List<?> list = res.getResponses();
|
||||||
|
Long result = list.get(4);
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Code example of **[Reactive](https://www.javadoc.io/doc/org.redisson/redisson/latest/org/redisson/api/RTransactionReactive.html) interface** usage:
|
||||||
|
```java
|
||||||
|
RBatchReactive batch = redisson.createBatch(BatchOptions.defaults());
|
||||||
|
batch.getMap("test1").fastPut("1", "2");
|
||||||
|
batch.getMap("test2").fastPut("2", "3");
|
||||||
|
batch.getMap("test3").put("2", "5");
|
||||||
|
Mono<Long> commandMono = batch.getAtomicLongAsync("counter").incrementAndGet();
|
||||||
|
batch.getAtomicLongAsync("counter").incrementAndGet();
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
// result could be acquired through Reactive object returned by batched method
|
||||||
|
// or
|
||||||
|
// through result list by corresponding index
|
||||||
|
commandMono.doOnNext(res -> {
|
||||||
|
// ...
|
||||||
|
}).subscribe();
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Mono<BatchResult> resMono = batch.execute();
|
||||||
|
resMono.doOnNext(res -> {
|
||||||
|
List<?> list = res.getResponses();
|
||||||
|
Long result = list.get(4);
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
// ...
|
||||||
|
}).subscribe();
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Code example of **[RxJava3](https://www.javadoc.io/doc/org.redisson/redisson/latest/org/redisson/api/RTransactionRx.html) interface** usage:
|
||||||
|
```java
|
||||||
|
RBatchRx batch = redisson.createBatch(BatchOptions.defaults());
|
||||||
|
batch.getMap("test1").fastPut("1", "2");
|
||||||
|
batch.getMap("test2").fastPut("2", "3");
|
||||||
|
batch.getMap("test3").put("2", "5");
|
||||||
|
Single<Long> commandSingle = batch.getAtomicLongAsync("counter").incrementAndGet();
|
||||||
|
batch.getAtomicLongAsync("counter").incrementAndGet();
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
// result could be acquired through RxJava3 object returned by batched method
|
||||||
|
// or
|
||||||
|
// through result list by corresponding index
|
||||||
|
commandSingle.doOnSuccess(res -> {
|
||||||
|
// ...
|
||||||
|
}).subscribe();
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Mono<BatchResult> resSingle = batch.execute();
|
||||||
|
resSingle.doOnSuccess(res -> {
|
||||||
|
List<?> list = res.getResponses();
|
||||||
|
Long result = list.get(4);
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
// ...
|
||||||
|
}).subscribe();
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
In cluster environment batch executed in map\reduce way. It aggregates commands for each node and sends them simultaneously, then result got from each node added to common result list.
|
||||||
@ -0,0 +1,107 @@
|
|||||||
|
## LUA Scripting
|
||||||
|
Redisson provides `RScript` object to execute Lua script. It has atomicity property and used to process data on Redis or Valkey side. Script could be executed in two modes:
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
* `Mode.READ_ONLY` scripts are executed as read operation
|
||||||
|
* `Mode.READ_WRITE` scripts are executed as write operation
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
One of the follow types returned as a script result object:
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
* `ReturnType.BOOLEAN` - Boolean type.
|
||||||
|
* `ReturnType.INTEGER` - Integer type.
|
||||||
|
* `ReturnType.MULTI` - List type of user defined type.
|
||||||
|
* `ReturnType.STATUS` - Lua String type.
|
||||||
|
* `ReturnType.VALUE` - User defined type.
|
||||||
|
* `ReturnType.MAPVALUE` - Map value type.
|
||||||
|
* `ReturnType.MAPVALUELIST` - List of Map value type.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Code example:
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
```java
|
||||||
|
RBucket<String> bucket = redisson.getBucket("foo");
|
||||||
|
bucket.set("bar");
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
RScript script = redisson.getScript(StringCodec.INSTANCE);
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
String r = script.eval(Mode.READ_ONLY,
|
||||||
|
"return redis.call('get', 'foo')",
|
||||||
|
RScript.ReturnType.VALUE);
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
// execute the same script stored in Redis or Valkey lua script cache
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
// load lua script into Redis or Valkey cache to all master instances
|
||||||
|
String res = script.scriptLoad("return redis.call('get', 'foo')");
|
||||||
|
// res == 282297a0228f48cd3fc6a55de6316f31422f5d17
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
// call lua script by sha digest
|
||||||
|
Future<Object> r1 = redisson.getScript().evalShaAsync(Mode.READ_ONLY,
|
||||||
|
"282297a0228f48cd3fc6a55de6316f31422f5d17",
|
||||||
|
RScript.ReturnType.VALUE, Collections.emptyList());
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
## Functions
|
||||||
|
Redisson provides `RFunction` object to execute [Functions](https://redis.io/topics/functions-intro). It has atomicity property and used to process data on Redis or Valkey side. Function can be executed in two modes:
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
* `Mode.READ` executes function as read operation
|
||||||
|
* `Mode.WRITE` executes function as write operation
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
One of the follow types returned as a script result object:
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
* `ReturnType.BOOLEAN` - Boolean type
|
||||||
|
* `ReturnType.LONG` - Long type
|
||||||
|
* `ReturnType.LIST` - List type of user defined type.
|
||||||
|
* `ReturnType.STRING` - plain String type
|
||||||
|
* `ReturnType.VALUE` - user defined type
|
||||||
|
* `ReturnType.MAPVALUE` - Map Value type. Codec.getMapValueDecoder() and Codec.getMapValueEncoder() methods are used for data deserialization or serialization
|
||||||
|
* `ReturnType.MAPVALUELIST` - List type, which consists of objects of Map Value type. Codec.getMapValueDecoder() and Codec.getMapValueEncoder() methods are used for data deserialization or serialization
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Code example:
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
```java
|
||||||
|
RFunction f = redisson.getFunction();
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
// load function
|
||||||
|
f.load("lib", "redis.register_function('myfun', function(keys, args) return args[1] end)");
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
// execute function
|
||||||
|
String value = f.call(RFunction.Mode.READ, "myfun", RFunction.ReturnType.STRING, Collections.emptyList(), "test");
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Code example of <b>Async interface</b> usage:
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
```java
|
||||||
|
RFunction f = redisson.getFunction();
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
// load function
|
||||||
|
RFuture<Void> loadFuture = f.loadAsync("lib", "redis.register_function('myfun', function(keys, args) return args[1] end)");
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
// execute function
|
||||||
|
RFuture<String> valueFuture = f.callAsync(RFunction.Mode.READ, "myfun", RFunction.ReturnType.STRING, Collections.emptyList(), "test");
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Code example of <b>Reactive interface</b> usage:
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
```java
|
||||||
|
RedissonReactiveClient redisson = redissonClient.reactive();
|
||||||
|
RFunctionReactive f = redisson.getFunction();
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
// load function
|
||||||
|
Mono<Void> loadMono = f.load("lib", "redis.register_function('myfun', function(keys, args) return args[1] end)");
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
// execute function
|
||||||
|
Mono<String> valueMono = f.callAsync(RFunction.Mode.READ, "myfun", RFunction.ReturnType.STRING, Collections.emptyList(), "test");
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Code example of <b>RxJava3 interface</b> usage:
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
```java
|
||||||
|
RedissonRxClient redisson = redissonClient.rxJava();
|
||||||
|
RFunctionRx f = redisson.getFunction();
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
// load function
|
||||||
|
Completable loadMono = f.load("lib", "redis.register_function('myfun', function(keys, args) return args[1] end)");
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
// execute function
|
||||||
|
Maybe<String> valueMono = f.callAsync(RFunction.Mode.READ, "myfun", RFunction.ReturnType.STRING, Collections.emptyList(), "test");
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
@ -0,0 +1,125 @@
|
|||||||
|
## Overview
|
||||||
|
Redisson offers ability to run as standalone node and participate in distributed computing. Such Nodes are used to run [MapReduce](data-and-services/services.md#mapreduce-service), [ExecutorService](data-and-services/services.md#executor-service), [ScheduledExecutorService](data-and-services/services.md#scheduled-executor-service) tasks or [RemoteService](data-and-services/services.md#remote-service) services. All tasks are kept in Redis until their execution moment.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Packaged as a single jar and could be downloaded [here](https://repo1.maven.org/maven2/org/redisson/redisson-all/).
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
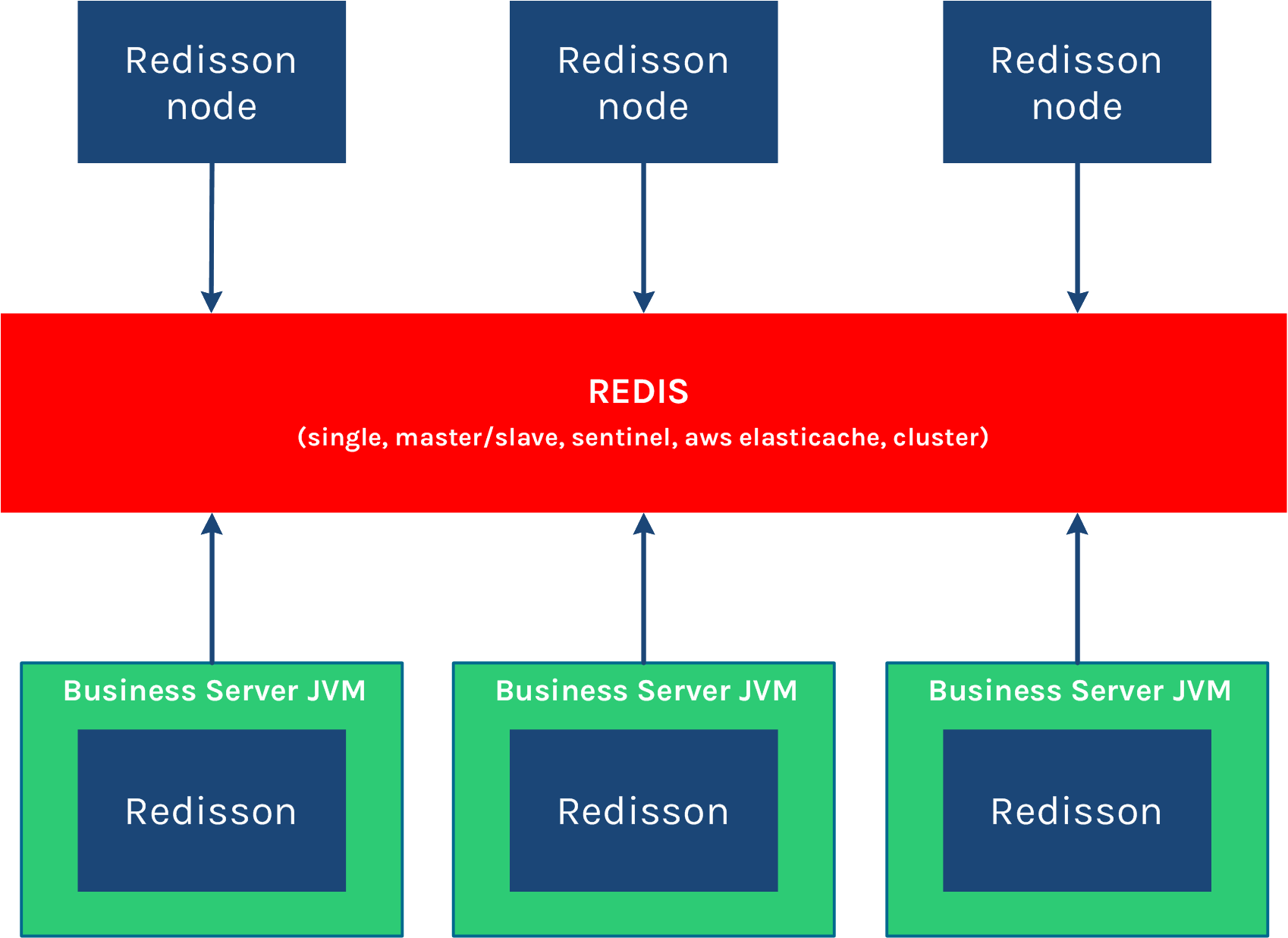
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
## Configuration
|
||||||
|
### Settings
|
||||||
|
Redisson node uses same [configuration](configuration.md) as Redisson framework with additional settings. Threads amount available for ExecutorService set through `threads` setting.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
**mapReduceWorkers**
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Default value: `0`
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
MapReduce workers amount.
|
||||||
|
`0 = current_processors_amount`
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
**executorServiceWorkers**
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Default value: `null`
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Map with <b>key</b> as service name and <b>value</b> as workers amount.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
**redissonNodeInitializer**
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Default value: `null`
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Listener runs during Redisson node startup.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
**beanFactory**
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Default value: `null`
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Defines Spring Bean Factory instance to execute tasks with Spring's '@Autowired', '@Value' or JSR-330's '@Inject' annotation.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
### YAML config format
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Below is the configuration example for cluster mode with appended Redisson node settings in YAML format.
|
||||||
|
```yaml
|
||||||
|
---
|
||||||
|
clusterServersConfig:
|
||||||
|
nodeAddresses:
|
||||||
|
- "//127.0.0.1:7004"
|
||||||
|
- "//127.0.0.1:7001"
|
||||||
|
- "//127.0.0.1:7000"
|
||||||
|
scanInterval: 1000
|
||||||
|
threads: 0
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
executorServiceWorkers:
|
||||||
|
myService1: 123
|
||||||
|
myService2: 421
|
||||||
|
redissonNodeInitializer: !<org.mycompany.MyRedissonNodeInitializer> {}
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
## Initialization listener
|
||||||
|
Redisson node allows to execute initialization logic during startup via `RedissonNodeInitializer` listener. It allows, for example, register your remote service implementations which should be available in Redisson node's classpath, or execute other useful logic. For example, notify all subscribers about new Redisson node is available.
|
||||||
|
```java
|
||||||
|
public class MyRedissonNodeInitializer implements RedissonNodeInitializer {
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
@Override
|
||||||
|
public void onStartup(RedissonNode redissonNode) {
|
||||||
|
RMap<String, Integer> map = redissonNode.getRedisson().getMap("myMap");
|
||||||
|
// ...
|
||||||
|
// or
|
||||||
|
redisson.getRemoteService("myRemoteService").register(MyRemoteService.class, new MyRemoteServiceImpl(...));
|
||||||
|
// or
|
||||||
|
reidsson.getTopic("myNotificationTopic").publish("New node has joined. id:" + redissonNode.getId() + " remote-server:" + redissonNode.getRemoteAddress());
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
## How to run
|
||||||
|
### As Embedded node
|
||||||
|
Redisson node can be embedded into your application:
|
||||||
|
```java
|
||||||
|
// Redisson config
|
||||||
|
Config config = ...
|
||||||
|
// Redisson Node config
|
||||||
|
RedissonNodeConfig nodeConfig = new RedissonNodeConfig(config);
|
||||||
|
Map<String, Integer> workers = new HashMap<String, Integer>();
|
||||||
|
workers.put("test", 1);
|
||||||
|
nodeConfig.setExecutorServiceWorkers(workers);
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
// create Redisson node
|
||||||
|
RedissonNode node = RedissonNode.create(nodeConfig);
|
||||||
|
// or create Redisson node with existing Redisson instance
|
||||||
|
RedissonNode node = RedissonNode.create(nodeConfig, redisson);
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
node.start();
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
//...
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
node.shutdown();
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
### From command-line
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
1. Download Redisson node jar [here](https://repo1.maven.org/maven2/org/redisson/redisson-all/)
|
||||||
|
2. Create yaml configuration file
|
||||||
|
3. Run node using follow command line:
|
||||||
|
`java -jar redisson-all.jar config.yaml`
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
don't forget to add `-Xmx` and `-Xms` params
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
### Using Docker
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
**with Redis or Valkey instance**
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
1. Run Redis
|
||||||
|
`docker run -d --name redis-node redis`
|
||||||
|
2. Redisson Node
|
||||||
|
`docker run -d --network container:redis-node -e JAVA_OPTS="<java-opts>" -v <path-to-config>:/opt/redisson-node/redisson.conf redisson/redisson-node`
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
`<path-to-config>` - path to YAML configuration of Redisson Node
|
||||||
|
`<java-opts>` - JVM params
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
**without Redis or Valkey instance**
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
1. Redisson Node
|
||||||
|
`docker run -d -e JAVA_OPTS="<java-opts>" -v <path-to-config>:/opt/redisson-node/redisson.conf redisson/redisson-node`
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
`<path-to-config>` - path to YAML configuration of Redisson Node
|
||||||
|
`<java-opts>` - JVM params
|
||||||
@ -0,0 +1,140 @@
|
|||||||
|
## Transactions management
|
||||||
|
`RMap`, `RMapCache`, `RLocalCachedMap`, `RSet`, `RSetCache` and `RBucket` Redisson objects may participant in Transaction with ACID properties. It uses locks for write operations and maintains data modification operations list until `commit()` method is executed. Acquired locks are released after `rollback()` method execution. Implementation throws `org.redisson.transaction.TransactionException` in case of any error during commit/rollback execution.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Transaction isolation level is: `READ_COMMITTED`.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Follow Transaction options are available:
|
||||||
|
```java
|
||||||
|
TransactionOptions options = TransactionOptions.defaults()
|
||||||
|
// Synchronization data timeout between Redis or Valkey master participating in transaction and its slaves.
|
||||||
|
// Default is 5000 milliseconds.
|
||||||
|
.syncSlavesTimeout(5, TimeUnit.SECONDS)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
// Response timeout
|
||||||
|
// Default is 3000 milliseconds.
|
||||||
|
.responseTimeout(3, TimeUnit.SECONDS)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
// Defines time interval for each attempt to send transaction if it hasn't been sent already.
|
||||||
|
// Default is 1500 milliseconds.
|
||||||
|
.retryInterval(2, TimeUnit.SECONDS)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
// Defines attempts amount to send transaction if it hasn't been sent already.
|
||||||
|
// Default is 3 attempts.
|
||||||
|
.retryAttempts(3)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
// If transaction hasn't committed within <code>timeout</code> it will rollback automatically.
|
||||||
|
// Default is 5000 milliseconds.
|
||||||
|
.timeout(5, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
For execution in Redis or Valkey cluster use {} brackets for collocation data on the same slot otherwise CROSSSLOT error is thrown by Redis.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Code example for Redis or Valkey cluster:
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
```java
|
||||||
|
RMap<String, String> map = transaction.getMap("myMap{user:1}");
|
||||||
|
map.put("1", "2");
|
||||||
|
String value = map.get("3");
|
||||||
|
RSet<String> set = transaction.getSet("mySet{user:1}")
|
||||||
|
set.add(value);
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Code example of **Sync / Async** exection:
|
||||||
|
```java
|
||||||
|
RedissonClient redisson = Redisson.create(config);
|
||||||
|
RTransaction transaction = redisson.createTransaction(TransactionOptions.defaults());
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
RMap<String, String> map = transaction.getMap("myMap");
|
||||||
|
map.put("1", "2");
|
||||||
|
String value = map.get("3");
|
||||||
|
RSet<String> set = transaction.getSet("mySet")
|
||||||
|
set.add(value);
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
try {
|
||||||
|
transaction.commit();
|
||||||
|
} catch(TransactionException e) {
|
||||||
|
transaction.rollback();
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
// or
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
RFuture<Void> future = transaction.commitAsync();
|
||||||
|
future.exceptionally(exception -> {
|
||||||
|
transaction.rollbackAsync();
|
||||||
|
});
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Code example of **Reactive** exection:
|
||||||
|
```java
|
||||||
|
RedissonReactiveClient redisson = Redisson.create(config).reactive();
|
||||||
|
RTransactionReactive transaction = redisson.createTransaction(TransactionOptions.defaults());
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
RMapReactive<String, String> map = transaction.getMap("myMap");
|
||||||
|
map.put("1", "2");
|
||||||
|
Mono<String> mapGet = map.get("3");
|
||||||
|
RSetReactive<String> set = transaction.getSet("mySet")
|
||||||
|
set.add(value);
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Mono<Void> mono = transaction.commit();
|
||||||
|
mono.onErrorResume(exception -> {
|
||||||
|
return transaction.rollback();
|
||||||
|
});
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Code example of **RxJava3** exection:
|
||||||
|
```java
|
||||||
|
RedissonRxClient redisson = Redisson.create(config).rxJava();
|
||||||
|
RTransactionRx transaction = redisson.createTransaction(TransactionOptions.defaults());
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
RMapRx<String, String> map = transaction.getMap("myMap");
|
||||||
|
map.put("1", "2");
|
||||||
|
Maybe<String> mapGet = map.get("3");
|
||||||
|
RSetRx<String> set = transaction.getSet("mySet")
|
||||||
|
set.add(value);
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Completable res = transaction.commit();
|
||||||
|
res.onErrorResumeNext(exception -> {
|
||||||
|
return transaction.rollback();
|
||||||
|
});
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
## XA Transactions
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
_This feature is available only in [Redisson PRO](https://redisson.pro) edition._
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Redisson provides [XAResource](https://docs.oracle.com/javaee/7/api/javax/transaction/xa/XAResource.html) implementation to participate in JTA transactions. `RMap`, `RMapCache`, `RLocalCachedMap`, `RSet`, `RSetCache` and `RBucket` Redisson objects may participant in Transaction.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Transaction isolation level is: `READ_COMMITTED`.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
For execution in Redis or Valkey cluster use {} brackets for collocation data on the same slot otherwise CROSSSLOT error is thrown by Redis.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Code example for Redis or Valkey cluster:
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
```java
|
||||||
|
RMap<String, String> map = transaction.getMap("myMap{user:1}");
|
||||||
|
map.put("1", "2");
|
||||||
|
String value = map.get("3");
|
||||||
|
RSet<String> set = transaction.getSet("mySet{user:1}")
|
||||||
|
set.add(value);
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Code example:
|
||||||
|
```java
|
||||||
|
// transaction obtained from JTA compatible transaction manager
|
||||||
|
Transaction globalTransaction = transactionManager.getTransaction();
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
RXAResource xaResource = redisson.getXAResource();
|
||||||
|
globalTransaction.enlistResource(xaResource);
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
RTransaction transaction = xaResource.getTransaction();
|
||||||
|
RBucket<String> bucket = transaction.getBucket("myBucket");
|
||||||
|
bucket.set("simple");
|
||||||
|
RMap<String, String> map = transaction.getMap("myMap");
|
||||||
|
map.put("myKey", "myValue");
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
transactionManager.commit();
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
## Spring Transaction Manager
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
For Spring Transaction Manager usage please refer to [Spring Transaction Manager](integration-with-spring.md/#spring-transaction-manager) article.
|
||||||
@ -0,0 +1,89 @@
|
|||||||
|
## Tomcat Session
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Redisson implements Redis or Valkey based Tomcat Session Manager. It stores session of [Apache Tomcat](http://tomcat.apache.org) in Redis or Valkey and allows to distribute requests across a cluster of Tomcat servers. Implements non-sticky session management backed by Redis.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Supports Apache Tomcat 7.x, 8.x, 9.x, 10.x
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Usage:
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
**1. Add session manager**
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Add `RedissonSessionManager` in global context - `tomcat/conf/context.xml` or per application context - `tomcat/conf/server.xml`
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
```xml
|
||||||
|
<Manager className="org.redisson.tomcat.RedissonSessionManager"
|
||||||
|
configPath="${catalina.base}/redisson.conf"
|
||||||
|
readMode="REDIS" updateMode="DEFAULT" broadcastSessionEvents="false"
|
||||||
|
keyPrefix=""/>
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
`keyPrefix` - string prefix applied to all keys. Allows to connect different Tomcat environments to the same Redis or Valkey instance.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
`readMode` - read Session attributes mode. Two modes are available:
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
* `MEMORY` - stores attributes into local Tomcat Session and Redis. Further Session updates propagated to local Tomcat Session using Redis-based events.
|
||||||
|
* `REDIS` - stores attributes into Redis or Valkey only. Default mode.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
`broadcastSessionEvents` - if `true` then `sessionCreated` and `sessionDestroyed` events are broadcasted across all Tomcat instances and cause all registered HttpSessionListeners to be triggered. Default is `false`.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
`broadcastSessionUpdates` - if `true` and `readMode=MEMORY` then session updates are broadcasted across all Tomcat instances. Default is `true`.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
`updateMode` - Session attributes update mode. Two modes are available:
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
* `DEFAULT` - session attributes are stored into Redis or Valkey only through the `Session.setAttribute` method. Default mode.
|
||||||
|
* `AFTER_REQUEST`
|
||||||
|
* In `readMode=REDIS` all changes of session attributes made through the `Session.setAttribute` method are accumulated in memory and stored into Redis or Valkey only after the end of the request.
|
||||||
|
* In `readMode=MEMORY` all session attributes are always stored into Redis or Valkey after the end of the request regardless of the `Session.setAttribute` method invocation. It is useful in case when some objects stored in session change their own state without `Session.setAttribute` method execution. Updated attributes are removed from all other Session instances if `broadcastSessionUpdates=true` and reloaded from Redis or Valkey when these attributes are requested.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
`configPath` - path to Redisson YAML config. See [configuration](configuration.md) page for more details. In case session manager is configured programatically, a config object can be passed using the `setConfig()` method
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Shared Redisson instance
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Amount of Redisson instances created by Tomcat for multiple contexts could be reduced through JNDI registry:
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
1. Add shared redisson instance produced by `JndiRedissonFactory` into `tomcat/conf/server.xml` in `GlobalNamingResources` tag area:
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
```xml
|
||||||
|
<GlobalNamingResources>
|
||||||
|
<Resource name="bean/redisson"
|
||||||
|
auth="Container"
|
||||||
|
factory="org.redisson.JndiRedissonFactory"
|
||||||
|
configPath="${catalina.base}/conf/redisson.yaml"
|
||||||
|
closeMethod="shutdown"/>
|
||||||
|
</GlobalNamingResources>
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
2. Add `JndiRedissonSessionManager` with resource link to redisson instance into `tomcat/conf/context.xml`
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
```xml
|
||||||
|
<ResourceLink name="bean/redisson"
|
||||||
|
global="bean/redisson"
|
||||||
|
type="org.redisson.api.RedissonClient" />
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
<Manager className="org.redisson.tomcat.JndiRedissonSessionManager"
|
||||||
|
readMode="REDIS"
|
||||||
|
jndiName="bean/redisson" />
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
**2. Copy two jars into `TOMCAT_BASE/lib` directory:**
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
[redisson-all-3.36.0.jar](https://repo1.maven.org/maven2/org/redisson/redisson-all/3.36.0/redisson-all-3.36.0.jar)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Tomcat 7.x - [redisson-tomcat-7-3.36.0.jar](https://repo1.maven.org/maven2/org/redisson/redisson-tomcat-7/3.36.0/redisson-tomcat-7-3.36.0.jar)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Tomcat 8.x - [redisson-tomcat-8-3.36.0.jar](https://repo1.maven.org/maven2/org/redisson/redisson-tomcat-8/3.36.0/redisson-tomcat-8-3.36.0.jar)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Tomcat 9.x - [redisson-tomcat-9-3.36.0.jar](https://repo1.maven.org/maven2/org/redisson/redisson-tomcat-9/3.36.0/redisson-tomcat-9-3.36.0.jar)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Tomcat 10.x - [redisson-tomcat-10-3.36.0.jar](https://repo1.maven.org/maven2/org/redisson/redisson-tomcat-10/3.36.0/redisson-tomcat-10-3.36.0.jar)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Upgrade to __[Redisson PRO](https://redisson.pro)__ with **advanced features**.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
## Spring Session
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
For Spring Session usage please refer to [Spring Session](integration-with-spring.md/#spring-session) article.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
## Micronaut Session
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
For Micronaut Session usage please refer to [Micronaut Session](microservices-integration.md/#session) article.
|
||||||
Loading…
Reference in New Issue